 |
 |
关键词:膀胱肿瘤;癌;微卫星不稳定
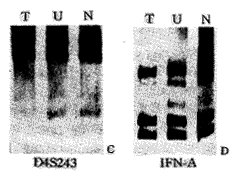
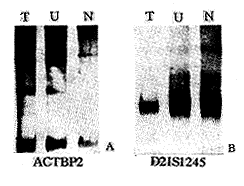
摘要 目的 探讨染色体微卫星不稳定性(MSI)及杂合性丢失(LOH)在膀胱癌早期诊断中的意义。 方法 运用位于4、5、9、21号染色体上的四对微卫星标志,结合PCR银染技术,分别检测22例膀胱癌患者肿瘤组织及尿脱落细胞染色体MSI及LOH。 结果 肿瘤及尿液标本MSI的发生率分别为23%、19%,LOH发生率分别为41%、18%,至少有一个位点出现MSI或LOH分别为59%及32%。不同年龄、性别、临床分期、肿瘤组织分级的患者MSI与LOH的发生率差异均无显著性(P>0.05)。 结论 检查尿液中肿瘤脱落细胞的MSI及LOH可能成为膀胱癌筛选及监测复发的辅助方法。
Loss of heterozygosity andmicrosatellite instability in bladder cancer
HUANG Yi,CHEN Zhongxin,XIE Shusheng,et al.
Department of Urology, Third Hospital of Beijing Medical University,Beijing 100083
Abstract Objective To evaluate theloss of heterozygosity (LOH) and microsatellite instability (MSI) in the early diagnosisof bladder cancer. Methods LOH and MSI were studied in the tumor tissue and urinesediment of 22 cases of bladder cancer by means of PCR amplification of 4 polymorphicmicrosatellites DNA loci on chromosome 4,5,9 and 21. Results 5 tumors (23%) and 4urine sediments (19%) showed MSI;10 tumors (41%) and 4 urine sediments (18%) showed LOH atone or more loci.Molecular genomic change (MSI or LOH) at one or more loci was observed in59% of the tumors (13/22) and in 32% of urine sediments (7/22).The frequency of either MSIor LOH was not significantly related to the tumor grade,tumor stage,patients's age or sex(P>0.05). Conclusions DNA microsatellite analysis of droped tumor cells in urinemight be a useful additional method for early diagnosis of bladder cancer.
......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 9295 字符。