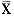 |
关键词:心肌病,充血性;心力衰竭,充血性;心律失常
【摘要】 目的 探讨老年人扩张型心肌病(DCM)的临床特征。 方法 通过临床观察对42例老年和86例非老年DCM患者的临床资料进行对比分析。 结果 (1)老年组醛固酮值〔(294±78) pmol/L〕较非老年组〔(208±69) pmol/L〕明显增高(P<0.05);(2)老年组室性心律失常发生率(61.9%)较非老年组(90.7%)低(P<0.05);(3)老年组低血钾、低血镁发生率高(分别为54.8%和28.6%),对洋地黄敏感性增加,易发生洋地黄中毒(31.0%);(4)老年组的病程〔(11.0±4.5)年〕和平均生存期〔(6.7±4.3)年〕均较非老年人〔分别为(5.1±2.6)和(3.2±2.6)年〕长(均为P<0.05);(5)老年组的主要死因是充血性心力衰竭(81.4%)。 结论 老年人DCM的预后比非老年人相对要好,发病年龄越早,预后越差。心力衰竭、电解质失衡及交感神经兴奋是老年人DCM室性心律失常的主要原因。
The clinical characteristics of dilatedcardiomyopathy in the elderly
GUO Hangyuan, LU Duan, WANG Jianan, et al.Affiliated Sir Run Shaw Hospital of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310016
【Abstract】 Objective To study theclinical characteristics of dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) in the elderly. Methods Theclinical data of dilated cardiomyopathy in 42 elderly and 86 non-elderly cases werecomparatively analyzed through clinical observations. Results Aldosteronein the elderly with DCM was higher than that in the non-elderly 〔(294±78) pmol/L vs(208±69) pmol/L,(P<0.05)〕.The incidence of ventricular arrhythmia in the elderly waslower than in the non-elderly (61.9% vs 90.7%, P<0.05). Incidences of hypokalemia andhypomagnesiemia were higher in the elderly (54.8% and 28.6%). The old patients were apt todigitalis in toxication due to sensitivity to digitalis increased (31.0%).Course ofdisease and mean survival period in the elderly with DCM was longer than in thenon-elderly 〔(11.0±4.5)yrs and (6.7±4.3)yrs vs (5.1±2.6)yrs and (3.2±2.6) yrs (all P<0.05)〕. The main cause of death was congestive heart failure in the elderly with DCM(81.4%) and ventricular arrhythmia in the non-elderly. Conclusions Theprognosis in the elderly with DCM was better than in the non-elderly, the earlier the ageof onset, the worse the prognosis. The main reasons of ventricular arrhythmia in theelderly were heart failure, electrolyte imbalance and sympathetic excitation.
......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 10652 字符。