关键词:视网膜母细胞瘤/免疫学;内皮,血管;内皮生长因子;免疫组织化学
【摘要 】 目的 研究视网膜母细胞瘤(retinoblastoma,RB)中血管内皮生长因子(vascularendothelial growth factor,VEGF)表达与RB组织学分裂和浸润能力的关系。 方法 应用链霉亲和素蛋白-生物素酶标免疫组织化学方法(labellstreptavidin biotin method,LSAB法),对40例RB组织中VEGF的表达进行分析。 结果 分化型RB(13例)组织VEGF表达低于未分化型(27例)(P<0.05);视神经浸润组(14例)VEGF表达明显高于视神经未浸润组(26例)(P<0.05)。 结论 VEGF表达与RB组织学分型及浸润能力相关。
中国图书资料分类法分类号 R739.7 R446.6
Immunohistochemical studies on vascular endothelial growth factor in retinoblastoma
FU Tao,SONG Xiuwen,LI Li,et al.
Department of Ophthalmology,the First Affiloated Hospital,Henan MedicalUniversity,Zhengzhou 450052,China
【Abstract 】 Objective Toinvestigate the relationship between the expression of vascular endothelial growthfactor(VEGF)and the retinoblastome(RB)differentiation degree and the infitrationcapability. Method The VEGF expression in RB tissues of 40 cases was analysed byusing LSAB immunohistochemical method. Results The VEGF expression in differentiatedRB tissues of 13 cases was markedly lower than that in non-differentiaed RB tissues of 27cases(P<0.05);The VEGF expression in RB tissues of the optic nerve infiltratedgroup(14 cases) was significantly higher than of the optic nerve non-infiltrated group(26cases)(P<0.05). Conclusion The results indicate that the VEGF expression issignficantly related with the differentiation degree and infiltration capability of RB.
【Key words 】 Retinoblastoma/immunology Endothelium,vascular Endothelial growth factorsImmunohistochemistry
血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)是新近确定的一种促血管生成因子,是具有高度潜能的血管内皮细胞分裂素[1] ,并可增加血管通透性[2] 。研究表明,VEGF在多种肿瘤血管基质形成中起重要作用。视网膜母细胞瘤(RB)是婴幼儿较常见的眼内肿瘤,生长因子在调节RB生长过程中的作用了解甚少。我们采用LSAB免疫组织化学法探讨VEGF在RB组织中的表达情况。
1 材料和方法
1 .1 材料 40例RB组织来自洛阳医专附属医院、邢台市眼科医院、安阳市眼科医院1987年1月~1997年6月间存档蜡块,RB患儿术前均未行化学治疗和放射治疗。10例正常视网膜组织取自无眼球疾病的供角膜移植后的供体眼球,作为正常对照。
1.2 主要试剂 抗VEGF抗体(工作浓度1∶100)、LSAB试剂盒分别为SantaCrus、Zymed公司产品,购于中山生物技术有限公司。
1.3 实验方法 ①参照文献[3] 作组织病理学分型;②VEGF免疫组织化学染色,采用LSAB免疫组织化学方法,作微波抗原修复;③实验对照采用结肠癌VEGF阳性表达组织作阳性对照;磷酸缓冲液及正常羊血清代替I抗分别作空白对照和替代对照。
1.4 结果判定[4] 以细胞浆着淡黄色至棕褐色颗粒为阳性细胞,计数5~10个视野,分别按 



1.5 统计学处理 采用频数表资料两样本比较的秩和检验,取P<0.05为显著性检验标准。
2 结果
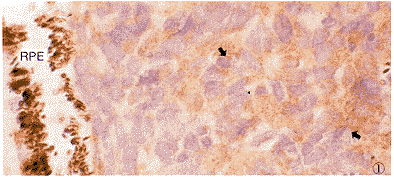
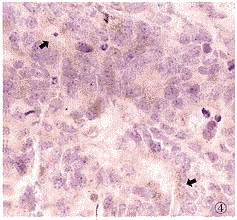
2.1 VEGF免疫组织化学染色 40例RB组织中,37例VEGF阳性表达(92.5%),为细胞浆着色,呈黄至棕黄色均匀细颗粒状。阳性细胞主要为肿瘤实质细胞(图1),坏死区周围细胞强表达。假菊形团结构中,阳性细胞多分布于其外围,近中央的肿瘤细胞不表达(图2)。另外,血管内皮细胞亦可见阳性染色(图3)。10例正常视网膜组织中,仅1例有弱的VEGF阳性表达,定位于视锥视杆层(图4)。
2.2 VEGF表达与RB组织学分型的关系 40例RB组织中分化型13例,未分化型27例。分化型RB细胞VEGF表达较弱,而未分化型RB细胞VEGF表达较强,经统计学检验,两型间VEGF表达有差异(P<0.05)(表1)(图1,5)。
2.3 VEGF表达与RB细胞浸润视神经的关系 视神经浸润组14例,其VEGF表达明显强于26例视神经未浸润组,分化型与未分化型RB视神经浸润有显著差异(P<0.05)(表2)。
3 讨论
VEGF是高效的内皮细胞有丝分裂素,直接促进内皮细胞增生;并作用于内皮细胞,增加内皮细胞的通透性,对肿瘤血管基质的形成及肿瘤细胞生物学行为均有重要影响。VEGF在多种人类恶性肿瘤中有高表达,但RB中的表达情况报道甚少。
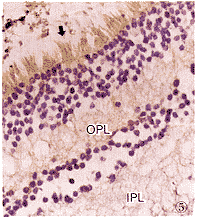
图1 RB组织VEGF免疫组织化学染色(未分化型)。VEGF阳性表达,RB细胞浆呈阳性染色(箭)。RPE:视网膜色素上皮层 LSAB法 ×1000 图2 RB组织假菊形团VEGF免疫组织化学染色。假菊形团中VEGF阳性表达,VEGF阳性细胞分布于外围的RB细胞浆(箭)LSAB法 ×250 图3 RB组织血管内皮细胞VEGF免疫组织化学染色。RB组织血管内皮细胞浆呈阳性染色(箭) LSAB法 ×1000 图4 正常视网膜VEGF免疫组织化学染色。正常视网膜视锥视杆层VEGF阳性表达(箭)LSAB法 ×200 图5 分化型RB组织VEGF免疫组织化学染色。分化型RB组织RB细胞浆呈VEGF弱阳性表达(箭)。OPL:外丛状层;IPL:内丛状层 LSAB法 ×250
Fig.1 VEGF immunohistochemical reaction of RB tissue(non-differentiated)、VEGFpositive expressed,cytoplasm of RB cells showed positive reaction(arrow) LSAB method ×1000 Fig.2 VEGFimmunohistochemical reaction in paeudorosete VEGF potitive expressed cells located atouter part of paudorosette(arrow) LSAB method ×250 Fig.3 VEGFimmunohistochemical reaction in vascular endothelial cells of RB tessiue.Cytoplasm ofvascular endothelial cells in RB showed VEGF positive reaction(arrow) LSAB method ×1000 Fig.4 VEGFimmunohistochemical recction in normal retina.Rods and cones of normal retina.showedpositive VEGF reaction(arrow) LSAB method ×200 Fig.5 VEGF immunohistochemicalreaction in differentiated RB tissue.Cytoplasm of differentiated RB cells showed weakpositive VEGF expression(arrow) LSAB method ×250
表1 VEGF表达与RB组织学分型的关系
Tab.1 Correlation between VEGF expression and
RB cell differentiation
| Defferentiation | No. | Intensity of VEGF expression | P value | |||
| - | + | ++ | +++ | |||
| Differentiated | 13 | 2 | 8 | 3 | 0 | <0.05 |
| Non-differentiated | 27 | 1 | 7 | 11 | 8 | |
表2 VEGF表达与RB浸润视神经的关系
Tab.2 Correlation between VEGF expression and
infltration of optic nerve
| Defferentiation | No. | Intensity of VEGF expression | P value | |||
| - | + | ++ | +++ | |||
| Infiltrated | 14 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 7 | <0.05 |
| Non-infiltrated | 26 | 2 | 13 | 10 | 1 | |
本实验结果表明,VEGF表达与RB的组织学分型相关,未分化型RB细胞VEGF表达明显高于分化型。Tanigawa等[5] 对胃癌的研究中发现胃癌中VEGF表达与组织学分型相关,但高分化癌组织VEGF表达强于低分化癌组织,其报道胃癌中VEGF表达阳性率为71%。本研究中,RB组织VEGF阳性表达率为92.5%。Ellis等[6] 报道VEGF在几乎所有的良、恶性结肠上皮中均表达。这种VEGF在不同组织类型中表达的差异可能与不同肿瘤细胞的生物学特性及不同肿瘤组织的肿瘤微环境有关。
本研究显示肿瘤细胞浸润视神经组的RB组织,其VEGF表达明显高于视神经未浸润组(P<0.05)。这一结果表明,RB细胞表达VEGF与RB肿瘤进展浸润能力有关。其机制可能通过自分泌方式刺激肿瘤细胞自身增生或通过增加肿瘤微血管密度,改善肿瘤组织微环境来实现。
本研究发现VEGF阳性染色细胞除RB细胞外,还可见于肿瘤血管内皮细胞,与Kvanta等[7] 研究结果相一致。Kvanta认为血管内皮细胞的阳性染色是肿瘤细胞分泌的VEGF积聚于邻近血管所致。但Qu-Hong等[8] 对肿瘤血管内皮细胞的超微免疫组织化学研究发现在肿瘤血管内皮的囊状空泡样细胞器中有VEGF的过表达,故RB组织中血管内皮细胞VEGF阳性染色是自身分泌抑或局部面积聚尚须进一步研究。
在实验性肿瘤模型中,抗VEGF单克隆抗体可以减少肿瘤内微血管密度并抑制肿瘤生长[9] 。玻璃体内注射VEGF抗体可以抑制与视网膜缺血性疾病有关的虹膜新生血管的产生[10] 。对其深入研究,不仅有助于RB预后的判断,也将为RB的治疗开辟新的前景。
参考文献
1 Ferrara N.The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in patholo-gicalangiogenesis.Breast Cancer Res Treat,1995,36:127-137.
2 Berkman RA,Merrill MJ,Reinhold WC,et al.Expression of the vascular permeabilityfactor/vascular endothelial growth factor gene in central nervous system neoplasms.JClin Invest,1993,91:153-159.
3 王延华,许云海.视网膜母细胞瘤的病理分型方法.眼科新进展,1984,4:161.
4 Sinicrop FA,Ruan SB,Cleary KR,et al.Bcl-2 and p53 oncoprotein expression duringcolorectal tumorigenesis.Cancer Res,1995,55:237-241.
5 Tanigawa N,Amaya H,Matsumura M,et al.Correlation between expression of vascularendothelial growth fadctor and tumor vascu-larity,and patient outcome in human gastriccarcinoma.J Clin Oncol,1997,15:826-832.
6 Ellis LM,Atha T,Cai S.Angiogenic factor expression in primary and metastatic humancolorectal cancers.Proc Assoc Cancer Res,1994,35:67-69.
7 Kvanta A,Steen B,Seregard S.Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF) inretinoblastoma but not in posterior uveal melanoma.Exp Eye Res,1996,63:511-518.
8 Qu-Hong,Nagy JA,Senger DR,et al.Ultrastructural localization of vascularpermeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor(VPF/VEGF)to the abluminal plasmamembrane and vesiculovacu-olar organelle of tumor microvascular endothelium.JHistochem Cytochem,1995,43:381-389.
9 Kim KJ,Li B,Winer J,et al.Inhibition of vascular endothelial
growth factor-induced angiogenesis supresses tumor growth in vivo.Science,1993,362:841-844.
10 Adamis AP,Shima DT,Tolentino MJ,et al.Inhibition of vascular
endothelial growth factor prevents retinal ischemia-associated iris-
neoveacuarization in a nonhuman primate.Arch Ophthalmol,1996,114:66-71.
(收稿:1999-02-01 修回:1999-07-05) , 百拇医药