 |
关键词:氟烷 肝线粒体 高压液相 肝炎
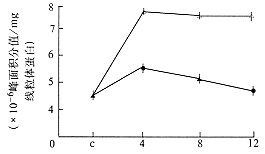
【摘要】 目的 探讨氟烷性肝炎的发病机理。 方法 将传统吸入麻醉药氟烷与新吸入麻醉药七氟醚对比,用高压液相技术分析肝线粒体膜磷脂在麻醉药作用后的脂质成分改变。 结果 氟烷在低浓度即可使肝线粒体主磷脂降解,溶血卵磷脂增加,在高浓度时有不可逆转的肝细胞损伤作用;而七氟醚只有主磷脂降解。溶血卵磷脂增加的倾向。 结论 氟烷致肝线粒体脂质改变可能为氟烷性肝炎的根本原因。
EXPERIMENTAL RESCARCH ONPHOSPHOLIPIDS VARIATION OF HALOTHANE ON LIVER MITOCHONDRIA
Sui Bo, Yu Weifeng, Zhang Guangming, et al. Department of Anesthesia, Jinan Military General Hospital, Jinan 250031.
【Abstract】 Objective To studythe pathogenesis of halothane hepatotoxicity. Methods By using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) technologythe effects of different concen-trtions of halothane and sevoflurane on mitochondrialmembrane phospholipids composition of rat liver were analyzed. Results Halothanein low concentrtion have the functions to mitochondria membrane major phospholipidsdegradation and increases lysophosphatidylcholive, that in high concentration halot hanedamages mitochondria membrane irreversibly and sevoflurane only has a tropism of major phospho-lipids degradation and increases lysophosphotidylcholive. Conclusion Thepathogenesis of halthane hepatotoxicity was the phospholipids variation on livermitochondria.
......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 12228 字符。