磁共振显像对缺血性脑水肿的动态实验研究
磁共振显像|脑缺血|脑水肿|高血压,关键词:
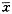 |
关键词:磁共振显像;脑缺血;脑水肿;高血压
【摘要】 目的 探讨缺血性脑水肿的演变规律及慢性高血压对其的影响,评价磁共振显像(MRI)在脑缺血研究中的价值。方法 采用肾血管性高血压鼠(RHR)与正常鼠对比,制成局部脑梗死模型,应用MRI对缺血性脑水肿急性期进行动态研究,选择病灶所在最大层面测量病灶中心区和对侧对应区的T2 值和ρ值。结果 在缺血后1h T2 与ρ值就已开始明显延长,在缺血7天内,MRI均有明显信号改变。高血压鼠组T2 值在缺血早期均较对照组延长,该组病灶对侧半球也可出现信号改变。结论 MRI是早期检测脑水肿的直接方法,高血压鼠脑水肿形成较正常鼠早且程度重,其病灶对全脑血流动力学亦产生影响。以上结果对临床治疗有指导价值。
Adynamic study of MRI in experimental focal cerebral ischemic edema
Huang Haiwei Huang Ruxun Su Zhenpei
( Department ofNeurology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yet-sun University of Medical Science.Guangzhou. 510080. Tel:87606221 )
【
Abstract 】 Objective To study (1) the pattern ofdevelopment of ischemic cerebral edema; (2) the influence of chronic hypertention oncerebral ischemia; (3) the values of MRI on experimental cerebral ischemia. Methods Focal cerebral infarctmodel was prepared on renal vescular hypertensive rats and normal rats. By using MRIdynamic changes of T2 and ρ value during acute phase of focal cerebral infarction wereobserved. Results T2 and ρ value significantly prolonged from 1 h after ischemia,especially in test group. Obvious signal changes were pressent in MRI up to 7 days after ischemia. The signal changes in corresponding contralateral regions were present in thetest group. Conclusions MRI was sensitive to acute change of ischemia. The formingof cerebral edema was earlier in hypertensive rats than that in normal rats, anddeveloping pattern of cerebral edema was also different between them. The results mighthave implication for developing clinical therapy for stroke.【 Key words 】 MRICerebral ischemia Cerebral edema Hypertension ▲
缺血性脑水肿是脑梗死后的重要继发性病理改变 ......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 27727 字符。