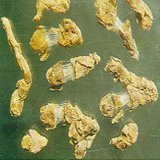
Coltsfoot Flower
http://www.100md.com
《e Natural Health Center》
 |
 |
 |
Herbs for Relieving Cough and Asthma
Coltsfoot Flower
Latin:
Flos Farfarae
Origin:
The flower bud of Tussilago farfara L., a perennial plant of the family Compositae. Native to Europe or Eurasia, the plant is grown in damp soils and disturbed areas in North America, China, Britain, France, Spain, Turkey, Chile, and other countries.
, 百拇医药
The name 'Tussilago' comes from the Latin 'tussis' which means cough. This reflects a common use of the plant. The Coltsfoot name refers to the shape of the leaves.
The plant has been used since pre history to relieve coughs and other respiratory problems. It is made into herbal teas (un-opened flowers and leaves) and is found in commercial cough preparations. It is an ingredient in concoctions used to treat diarrhea. The leaves are sometimes smoked for relief of congestion. The crushed leaves or a leaf decoction is used externally where it may be applied to sores, injuries, rashes and painful joints.
, http://www.100md.com
The perennial plant grows to about 0.2 m by 1 m at a fast rate. It is in flower from February to April, and the seeds ripen from March to May. The flowers are hermaphrodite (have both male and female organs) and are pollinated by bees and flies. The plant can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It requires moist soil. The plant can tolerate maritime exposure.
In China, coltsfoot is mainly produced in the provinces Henan, Gansu, Shanxi, Shaanxi, etc. Harvested in December or before the flower comes out of the ground before the ground is frozen. Procedure: Remove stalk and dry the bud in the air for use when raw or after being fried with honey.
, http://www.100md.com
Properties:
Pungent and slightly bitter in flavor, warm in nature, it is related to the lung channel.
Functions:
Moisturizes the lungs to resolve phlegm and arrest coughing.
An effective soothing and expectorant herb, coltsfoot is one of the most popular European remedies for the treatment of a wide range of chest complaints. It is widely available in health food shops. The leaves are commonly used in Europe, though the flowering stems (which contain higher levels of pyrrolizidine alkaloids) are preferred in China.
, 百拇医药
Applications:
Treats a variety of coughs.
This is a common herb for the treatment of coughs. Its properties and functions are similar to those of the tatarian aster root (Radix Asteris). The tatarian aster root is good at resolving phlegm, while this herb is good at arresting coughing and the two herbs are often used in mutual reinforcement with each other.
Being pungent in taste, warm in nature and moistening in property, this herb is especially applicable to coughs due to cold.
, http://www.100md.com
a) Coughs due to cold:
This herb is often used in combination with ephedra, etc.
b) Coughs due to the lung-heat:
This herb is used in combination with white mulberry root-bark and Mongolian snakegourd (Fructus Trichosanthis).
c) Coughs due to deficiency of the lung-qi:
This herb can be used in combination with ginseng and milk vetch root (Radix Astragali seu Hedysari).
, 百拇医药
d) Irritating dry coughs due to yin deficiency:
This herb is used in combination with straight ladybell root (Radix Adenophorae Strictae) and ophiopogon root.
e) Prolonged dyspnea (difficult breathing) and coughs with bloody sputum:
This herb is often used in combination with lily bulb, e.g., Baihua Gao.
f) Coughing out of purulent sputum due to pulmonary abscess:
, 百拇医药
This herb is used in combination with balloon flower root (Radix Platycodi), Job's tears (Semen Coicis), etc., e.g., Kuandong Tang.
Dosage and Administration:
5-10 g.
Decoct this herb for oral administration.
It should be used when raw to treat violent coughs due to affection caused by exopathogens and used after being fried to treat prolonged coughs due to internal injuries.
, 百拇医药
Cautions on Use:
Some caution should be employed in the use of this herb--the flowers should not be used except under professional supervision, the leaves should not be used for more than 4-6 weeks at a time, the herb should not be taken whilst pregnant or breast-feeding and it should not be given to children under the age of six.
The plant, particularly the flowering stem, contains traces of liver-affecting pyrrolizidine alkaloids and is potentially toxic in large doses. These alkaloids have not proved toxic at low dosages in tests and there is no suggestion that this plant should not be used medicinally. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are largely destroyed when the plant is boiled to make a decoction, anyway.
, http://www.100md.com
Reference Materials:
'Shen Nong's Herbal Classic' :
"Coughs and dyspnea with abnormal rising of qi, proneness to tachypnea and inflammation of the throat."
Herbs Traced to Shen Nong's 'Herbal Classic' :
"Moisturizing the lungs and removing phlegm as well as arresting coughs and relieving dyspnea."
'Annotation on Shen Nong's Herbal Classic' :
, http://www.100md.com
"In the two books 'The Essential Recipes Worth a Thousand Pieces of Gold' and 'The Medical Secrets of an Official', both the tatarian aster root (Radix Asteris) and the common coltsfoot flower (Flos Farfarae) are always used together in nine recipes out of ten for the treatment of coughs with dyspnea or prolonged coughs.
However, their differences can also be seen indistinctly in the two books 'The Essential Recipes Worth a Thousand Pieces of Gold' and 'The Medical Secrets of an Official'. For the treatment of coughs, coughing out of bloody and purulent sputum, and aphonia or coughs due to excessive wind-cold or retained fluids, the common coltsfoot flower is not used so much in more cases but the tatarian aster root is used instead. In most cases, the common coltsfoot flower is always used together with warming herbs and tonifying herbs."
, 百拇医药
Toxic or Side Effects:
Modern Researches:
This herb contains faradiol and its heterogeneous structure arnidiol, inulin, hyperin, triterpenoid saponins, salts, volatile oil, sterols, tannins, etc.
The large mucilage content in the flowering stem accounts for most of the medical benefit derived from the plant.
The alcohol extract and decoction of this herb can raise blood pressures and its ether extract can inhibit the gastrointestinal smooth muscles together with a spasmolytic effect.
, 百拇医药
Studies from the 1950s recent research shows plant sterols lower cholesterol.
Inulin increases dietary fiber, increase the body's absorption of calcium and may have beneficial effects on bacteria in the digestive track including providing some protection from bacterial decease. It is also suspected to cause food allergies in some people. It is an ingredient in many foods where it may be used as a fat or sugar substitute. It is filling and tastes sweet but is not absorbed into the blood.
, 百拇医药
Modern research has shown that extracts of the whole plant can increase immune resistance.
Reported in 'The Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants,' (Dorling Kindersley. London 1996), in a Chinese trial 75% of patients suffering from bronchial asthma showed some improvement after treatment with this plant, though the anti-asthmatic effect was short-lived.
A poultice of the flowers has a soothing effect on a range of skin disorders including eczema, ulcers, sores, bites and inflammations., 百拇医药