尼群地平对大鼠肺缺血再灌注损伤后TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8变化的影响
作者:向明章 蒋耀光 王如文 范士志
单位:向明章 第三军医大学附属新桥医院胸外科 重庆,400037;蒋耀光 王如文 范士志 第三军医大学附属大坪医院胸外科 重庆,400042
关键词:肺损伤;缺血再灌注损伤;细胞因子;钙超载;肺静态顺应性;尼群地平
第三军医大学学报ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE MILITARIS TERTIAE1999年 第21卷 第1期 VOL
提 要:目的观察尼群地平(Nitrendipine)对大鼠早期肺缺血再灌注损伤的防治作用和可能的机制。方法:将72只大鼠随机分为手术对照组(OC)、肺缺血再灌注损伤组(IR)和尼群地平处理组(NT),采用肺在体缺血再灌注模型,动态测定肺组织和血浆肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、白介素-6(IL-6)、白介素-8(IL-8)、肺组织总钙、肺组织干/湿重比值(D/W)和肺静态顺应性(Cst)变化。结果:肺缺血再灌注损伤早期肺组织总钙水平升高,肺组织TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8相继释放增加并与肺D/W、肺Cst下降呈显著相关性。尼群地平处理后,肺组织总钙和TNF-α、IL-6、IL-8水平显著降低(P<0.05和P<0.01),肺D/W升高,肺Cst改善。结论:尼群地平可通过阻滞钙通道,减少细胞钙内流,抑制炎性细胞因子释放,减轻肺缺血再灌注损伤。
, http://www.100md.com
中图法分类号:R563
Therapeutic effects of nitrendipine on early pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats
Xiang Mingzhang, Jiang Yaoguang, Wang Ruwen, Fan Shizhi
(Department of Thoracic Surgery, Xinqiao Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, 400037)
Abstract Objective: To determine the therapeutic effects of nitrendipine on early pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury and to explore its possible mechanism. Methods: Seventy-two rats were randomized into the opetation control group (OC), pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury group (IR) and nitrendipine-treated group (NT). The animals in IR were inflicted on pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury through occlusion of left lung hilus for 45 min while those in NT were inflicted on the same injury and treated with nitrendipine. The dynamic changes of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin -6 (IL-6) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) in both the pulmonary tissue and plasma were observed. The total calcium level of the pulmonary tissue, dry-wet weight ratios of the lung tissue (D/W) and static lung compliance (Cst) were also measured during pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion. Results: As compared with OC, the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8 and total calcium in the pulmonary tissue in IR were significantly increased (P<0.05 and 0.01). These four parameters and D/W and Cst were correlated to one another. In NT, the four parameters were markedly decreased (P<0.05 and 0.01). Conclusion: Nitrendipine can reduce Ca2+ influx of the cells by blocking dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel to inhibit the release of inflammatory cytokines. Therefore, it can alleviate the pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury.
, 百拇医药
Key words pulmonary injury; ischemia-reperfusion injury; cytokine; calcium overload; static lung compliance; nitrendipine
细胞内钙超载和炎性细胞因子的参与是引起缺血再灌注损伤的重要环节。钙通道阻滞剂(Calcium channel blockers,CCBs)可改善保存肺功能,减轻肺缺血再灌注损伤[1]。CCBs能否减少肺缺血再灌注损伤早期炎性细胞因子的释放,尚未见报道。本研究观察了尼群地平(Nitrendipine,NT)对大鼠肺在体缺血再灌注早期肺和血浆TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8的影响,探讨其防治作用和可能的机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 动物模型与分组
按文献[2]建立肺缺血再灌注损伤模型后,将72只成年健康Wistar大鼠随机分成3组:①手术对照组(OC,n=24):开胸后不阻断肺门;②肺缺血再灌注损伤组(IR,n=24):开胸阻断肺门45 min后放开行再灌注;③尼群地平处理组(NT,n=24):按0.5 mg/kg体重于肺门阻断前30 min和再灌注前分别经静脉注射0.01%NT1/2量。OC组和IR组同法注射等量Ringer氏液。各组分4个时相点各处死6只动物,留取标本,进行检测。
, 百拇医药
1.2 检测指标及方法
1.2.1左肺组织和血浆肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、白介素-6(IL-6)、白介素-8(IL-8)含量采用放免法检测TNF-α(药盒由301医院东亚免疫技术研究所提供),酶联免疫吸附法测定IL-6和IL-8(药盒由第四军医大学免疫学教研室提供)。Lowry法测定肺匀浆蛋白质浓度。
1.2.2 左肺组织总钙水平采用原子吸收光谱法测定。
1.2.3 左肺组织干/湿重比值(D/W)采用干湿重法测定。
1.2.4 左肺静态顺应性(Cst)参照文献[3]测定和计算单位体重的总肺顺应性(C2.94)、低容量肺顺应性(C0.49)和肺扩张指数(EI)。
1.3 统计学处理
, 百拇医药
数据以 ±s表示,组间比较用t检验,有关数据作相关性分析。
±s表示,组间比较用t检验,有关数据作相关性分析。
2 结果
2.1 TNF-α含量变化
结果见表1,缺血再灌注后,IR组肺组织TNF-α含量呈进行性升高,NT组各时相肺组织TNF-α含量较IR组递减,除再灌注4h仍显著高于OC组外,其余各时相已接近于OC组水平。
表 1 肺组织和血浆TNF-α含量变化(n=6, ±s)
±s)
Tab 1 Changes in TNF-α content of lung tissue and plasma(n=6, ±s)
±s)
, 百拇医药
Lung tissue(WB/ng*mg-1)
Plasma(ρB/ng*ml-1)
Time
OC
IR
NT
OC
IR
NT
Post-ischemia
6.40±1.01
, 百拇医药
7.79±1.02
6.60±1.21
1.23±0.17
1.58±0.13
1.53±0.12
Post-reperfusion
1 h
6.75±0.84
9.07±0.87*
7.88±0.78△
1.47±0.19
, http://www.100md.com
1.70±0.16
1.58±0.13
2 h
6.93±0.93
9.77±0.85* *
8.00±0.68△
1.62±0.13
1.93±0.15
1.72±0.12* *
4 h
7.01±1.25
, http://www.100md.com
9.94±1.19* *
8.34±1.03* △
1.77±0.16
1.97±0.16
1.82±0.15
*:P<0.05,* *:P<0.01 vs OC;△:P<0.05 vs IR
2.2 IL-6含量变化
结果见表2,IR组肺组织IL-6含量于再灌注4 h后非常显著高于OC组,NT组肺组织IL-6含量于再灌注4 h后下降近OC组水平(P>0.05)。
表 2 肺组织和血浆IL-6含量变化(n=6, ±s)
±s)
, 百拇医药
Tab 2 Changes in IL-6 content of lung tissue and plasma (n=6, ±s)
±s)
Lung tissue(WB/ng*mg-1)
Plasma(ρB/ng*ml-1)
Time
OC
IR
NT
OC
IR
, http://www.100md.com
NT
Post-ischemia
2.16±0.32
2.21±0.40
2.18±0.30
0.42±0.06
0.44±0.04
0.44±0.06
Post-reperfusion
1 h
2.20±0.36
2.22±0.31
, 百拇医药
2.22±0.33
0.43±0.06
0.45±0.04
0.44±0.05
2 h
2.23±0.33
2.42±0.30
2.27±0.34
0.43±0.04
0.45±0.07
0.44±0.06
4 h
, 百拇医药
2.23±0.37
3.19±0.29* *
2.68±0.36
0.44±0.06
0.45±0.05
0.45±0.04
* *:P<0.01 vs OC
2.3 IL-8含量变化
结果见表3,IR组肺组织IL-8含量于再灌注4 h后显著高于OC组,NT组肺组织IL-8再灌注4 h降低至OC组水平(P>0.05)。
表 3 肺组织和血浆IL-8含量变化(n=6, ±s)
±s)
, 百拇医药
Tab 3 Changes in IL-8 content of lung tissue and plasma(n=6, ±s)
±s)
Lung tissue(WB/ng*mg-1)
Plasma (ρB/ng*ml-1)
Time
OC
IR
NT
OC
IR
, 百拇医药
NT
Post-ischemia
2.49±0.38
2.52±0.32
2.47±0.36
0.29±0.06
0.29±0.06
0.28±0.04
Post-reperfusion
1 h
2.49±0.33
2.55±0.38
, 百拇医药
2.49±0.46
0.29±0.06
0.29±0.06
0.29±0.05
2 h
2.50±0.40
2.56±0.34
2.52±0.39
0.29±0.07
0.29±0.06
0.29±0.04
4 h
, 百拇医药
2.51±0.35
3.20±0.34*
2.72±0.41
0.29±0.06
0.29±0.08
0.29±0.04
*:P<0.05 vs OC
2.4 肺组织总钙水平变化
再灌注后各时相IR组和NT组肺组织总钙水平均分别较OC组有非常显著升高(P<0.01),NT组升幅非常明显低于IR组(P<0.01),见图1。
2.5 肺组织D/W变化
, 百拇医药
IR组再灌注1h,肺组织D/W已较OC组显著下降(P<0.05),4 h降至最低(P<0.01)。NT组再灌注后肺组织D/W虽较OC组仍呈下降趋势,但比值明显高于IR组(P<0.05)。
2.6 肺Cst变化
见表4,IR组缺血再灌注后Cst各项指标均较OC组呈进行性下降,NT组较IR组明显改善,EI与OC组比较已无明显差别。
2.7 相关性分析
见表5,肺组织总钙与肺组织TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8均呈显著正相关。肺组织TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8与C2.94均呈显著负相关。肺组织TNF-α与D/W、EI也均呈显著负相关。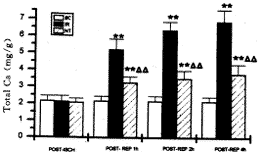
, 百拇医药 图 1 左肺组织总钙水平变化 (mg/g干肺,n=6, ±s)
±s)
Fig 1 Changes in total calcium level of left lung tissue (mg/g dry lung,n=6, ±s)* *:P<0.01 vs OC;△ △:P<0.05 vs IR
±s)* *:P<0.01 vs OC;△ △:P<0.05 vs IR
表 4 肺静态顺应性变化(n=6, ±s)
±s)
Tab 4 Changes in static lung compliance (n=6, ±s) Groups
±s) Groups
, http://www.100md.com
C2.94(ml*kpa-1*kg-1)
C0.49(ml*kpa-1*kg-1)
EI
OC post-ischemia
11.08±0.98
33.80±0.86
0.48±0.02
post-reperfusion 1 h
11.06±1.02
, 百拇医药
33.21±0.90
0.47±0.03
2 h
11.03±1.03
33.28±0.90
0.48±0.02
4 h
11.02±1.12
34.25±0.87
0.48±0.01
IR post-ischemia
10.13±1.18
, 百拇医药
31.27±1.43* *
0.46±0.06
post-reperfnsion 1 h
9.73±0.65*
29.91±1.21* *
0.46±0.04
2 h
8.44±0.73* *
27.07±1.12* *
0.41±0.03* *
, 百拇医药
4 h
8.06±0.84* *
26.47±1.41* *
0.39±0.04* *
NT post-ischemia
10.77±0.78
32.16±1.09
0.47±0.04
post-reperfusion 1 h
10.11±0.75
, 百拇医药
31.06±1.48*
0.46±0.04
2 h
9.29±0.83*
29.21±0.60* * △ △
0.45±0.03
4 h
8.99±0.74* *
27.84±1.10* * △
0.44±0.03△
, http://www.100md.com
*:P<0.05,* *:P<0.01 vs OC △:P<0.05,△ △:P<0.01 vs IR
表 5 肺组织TNF-α、IL-6、IL-8与血浆TNF-α及其与肺组织总钙、D/W、Cst间相关性
Tab 5 Correlations of TNF-α,IL-6,IL-8 in lung tissue and TNF-α in plasma with total calcicm, D/W, Cst of lung tissue
D/W
C2.94
EI
Total calcium
, 百拇医药 Plasma TNF-α
Lung TNF-α
-0.89*
-0.92* *
-0.85*
+0.88*
+0.88*
Plasma TNF-α
-0.40
-0.81*
-0.02
, 百拇医药
+0.59
Lung IL-6
-0.63
-0.81*
-0.86*
+0.85*
+0.45
Lung IL-8
-0.35
-0.81*
-0.71
, 百拇医药
+0.89*
+0.30
*:P<0.05, * *:P<0.01
3 讨论
Ca2+的跨膜流动和细胞内Ca2+浓度变化对炎性细胞因子的合成和释放是必不可少的[4]。本研究发现,大鼠肺缺血后再灌注,肺组织总钙水平明显升高,间接反映了组织细胞内游离Ca2+水平的增高,即胞内Ca2+稳态的破坏。与肺组织总钙水平升高同步,肺缺血后再灌注,肺组织TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8含量相继升高,其中TNF-α首先升高,升幅最大,其次为IL-6,而IL-8升高偏晚,升幅也最小。相关分析表明,肺组织总钙水平与肺组织TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8含量均呈显著正相关。间接提示肺组织细胞因子的释放增加与细胞内Ca2+浓度变化有一定关系。此外,肺内炎性细胞因子含量升高与肺组织损害指标D/W、Cst变化时间上一致,均呈明显相关关系,从而表明炎性细胞因子在肺缺血再灌注损伤中发挥了重要作用。
, 百拇医药
本研究还发现,整个实验过程中,血浆TNF-α水平有一定程度升高,并与C2.94呈显著负相关,但升幅明显低于肺内TNF-α水平,而血浆IL-6、IL-8变化不明显。这一方面提示肺缺血再灌注损伤时血浆炎性细胞因子水平的变化滞后于肺内炎性细胞因子水平的变化,另一方面也表明肺缺血再灌注损伤时炎性细胞因子可能主要由肺内产生并留存于肺组织,通过自分泌/旁分泌形式发挥生物学效应。
有研究证实,二氢吡啶CCBs可抑制淋巴细胞、单核/巨噬细胞的激活,减少TNF-α、IL-1和IL-6的合成[5,6],肾移植病人给予CCBs后,血浆TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-2和IL-6水平降低[7]。本研究发现,NT处理后,肺D/W升高,Cst改善,再灌注肺组织总钙水平降低,各时相肺组织TNF-α含量均不同程度地较IR组减少,IL-6和IL-8含量于再灌注4 h后下降近OC组水平,说明NT通过阻滞Ca2+通道,减少细胞Ca2+内流,对上述细胞因子产生有一定抑制作用。但其确切机制尚需进一步探讨。有学者[8]认为Ca2+激活的磷酸化耦联可能与转录因子激活和细胞因子基因表达有关。还有研究报道[5],二氢吡啶CCBs可阻断TNF-α转录。
, http://www.100md.com
综上所述,本研究初步显示了NT可以抑制大鼠肺缺血再灌注损伤早期肺组织TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8含量的升高,适当应用CCBs可避免或减轻肺缺血再灌注损伤。
作者简介:向明章,男,36,硕士,副主任医师
参考文献
[1] Hachida M, Morton D L. The protection of ischemic lung with verapamil and hydralazine. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,1988,95(2):178
[2] 向明章,蒋耀光,王如文,等.尼群地平对缺血再灌注肺脂质过氧化反应的影响.中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,1998,5(2):76
[3] Ennema J J, Kobayashi T, Robertson B, et al. Inactivation of exogenous surfactant in experimental respiratory failure induced by hyperoxia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand,1988,32(8):665
, 百拇医药
[4] Hotchkiss R S, Karl I E. Calcium: a regulation of the inflammatory response in endotoxemia and sepsis. New Horiz,1996,4(1):58
[5] Lichtman S N, Wang J, Zhang C, et al. Endocytosis and Ca2+ are required for endotoxin-stimulated TNF-alpha release by rat Kupffer cells. Am J Physiol,1996,271(5 Ptl):G920
[6] Weir M R, Gomolka D, Pepplar R, et al. Mechanisms responsible for inhibition of lymphocyte activation by agents which block membrane calcium or potassium channels. Transplant Proc,1993,25(1):605
, 百拇医药
[7] Carozzi S, Nasini M G, Pietrucci A, et al. Immunosuppressive effects of different calcium channel blockers in human kidney allografts. Transplant Proc,1995,27(1):1054
[8] Shapira L, Takashiba S, Champagne C, et al. Involvement of PKC and protein tyrosine kinase in LPS-induced TNF-α and IL-Ⅰβ production by human monocytes. J Immunol,1994,153(4):1818
收稿:1998-04-01;修回:1998-09-28, http://www.100md.com
单位:向明章 第三军医大学附属新桥医院胸外科 重庆,400037;蒋耀光 王如文 范士志 第三军医大学附属大坪医院胸外科 重庆,400042
关键词:肺损伤;缺血再灌注损伤;细胞因子;钙超载;肺静态顺应性;尼群地平
第三军医大学学报ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE MILITARIS TERTIAE1999年 第21卷 第1期 VOL
提 要:目的观察尼群地平(Nitrendipine)对大鼠早期肺缺血再灌注损伤的防治作用和可能的机制。方法:将72只大鼠随机分为手术对照组(OC)、肺缺血再灌注损伤组(IR)和尼群地平处理组(NT),采用肺在体缺血再灌注模型,动态测定肺组织和血浆肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、白介素-6(IL-6)、白介素-8(IL-8)、肺组织总钙、肺组织干/湿重比值(D/W)和肺静态顺应性(Cst)变化。结果:肺缺血再灌注损伤早期肺组织总钙水平升高,肺组织TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8相继释放增加并与肺D/W、肺Cst下降呈显著相关性。尼群地平处理后,肺组织总钙和TNF-α、IL-6、IL-8水平显著降低(P<0.05和P<0.01),肺D/W升高,肺Cst改善。结论:尼群地平可通过阻滞钙通道,减少细胞钙内流,抑制炎性细胞因子释放,减轻肺缺血再灌注损伤。
, http://www.100md.com
中图法分类号:R563
Therapeutic effects of nitrendipine on early pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats
Xiang Mingzhang, Jiang Yaoguang, Wang Ruwen, Fan Shizhi
(Department of Thoracic Surgery, Xinqiao Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, 400037)
Abstract Objective: To determine the therapeutic effects of nitrendipine on early pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury and to explore its possible mechanism. Methods: Seventy-two rats were randomized into the opetation control group (OC), pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury group (IR) and nitrendipine-treated group (NT). The animals in IR were inflicted on pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury through occlusion of left lung hilus for 45 min while those in NT were inflicted on the same injury and treated with nitrendipine. The dynamic changes of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin -6 (IL-6) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) in both the pulmonary tissue and plasma were observed. The total calcium level of the pulmonary tissue, dry-wet weight ratios of the lung tissue (D/W) and static lung compliance (Cst) were also measured during pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion. Results: As compared with OC, the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8 and total calcium in the pulmonary tissue in IR were significantly increased (P<0.05 and 0.01). These four parameters and D/W and Cst were correlated to one another. In NT, the four parameters were markedly decreased (P<0.05 and 0.01). Conclusion: Nitrendipine can reduce Ca2+ influx of the cells by blocking dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel to inhibit the release of inflammatory cytokines. Therefore, it can alleviate the pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury.
, 百拇医药
Key words pulmonary injury; ischemia-reperfusion injury; cytokine; calcium overload; static lung compliance; nitrendipine
细胞内钙超载和炎性细胞因子的参与是引起缺血再灌注损伤的重要环节。钙通道阻滞剂(Calcium channel blockers,CCBs)可改善保存肺功能,减轻肺缺血再灌注损伤[1]。CCBs能否减少肺缺血再灌注损伤早期炎性细胞因子的释放,尚未见报道。本研究观察了尼群地平(Nitrendipine,NT)对大鼠肺在体缺血再灌注早期肺和血浆TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8的影响,探讨其防治作用和可能的机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 动物模型与分组
按文献[2]建立肺缺血再灌注损伤模型后,将72只成年健康Wistar大鼠随机分成3组:①手术对照组(OC,n=24):开胸后不阻断肺门;②肺缺血再灌注损伤组(IR,n=24):开胸阻断肺门45 min后放开行再灌注;③尼群地平处理组(NT,n=24):按0.5 mg/kg体重于肺门阻断前30 min和再灌注前分别经静脉注射0.01%NT1/2量。OC组和IR组同法注射等量Ringer氏液。各组分4个时相点各处死6只动物,留取标本,进行检测。
, 百拇医药
1.2 检测指标及方法
1.2.1左肺组织和血浆肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、白介素-6(IL-6)、白介素-8(IL-8)含量采用放免法检测TNF-α(药盒由301医院东亚免疫技术研究所提供),酶联免疫吸附法测定IL-6和IL-8(药盒由第四军医大学免疫学教研室提供)。Lowry法测定肺匀浆蛋白质浓度。
1.2.2 左肺组织总钙水平采用原子吸收光谱法测定。
1.2.3 左肺组织干/湿重比值(D/W)采用干湿重法测定。
1.2.4 左肺静态顺应性(Cst)参照文献[3]测定和计算单位体重的总肺顺应性(C2.94)、低容量肺顺应性(C0.49)和肺扩张指数(EI)。
1.3 统计学处理
, 百拇医药
数据以
 ±s表示,组间比较用t检验,有关数据作相关性分析。
±s表示,组间比较用t检验,有关数据作相关性分析。2 结果
2.1 TNF-α含量变化
结果见表1,缺血再灌注后,IR组肺组织TNF-α含量呈进行性升高,NT组各时相肺组织TNF-α含量较IR组递减,除再灌注4h仍显著高于OC组外,其余各时相已接近于OC组水平。
表 1 肺组织和血浆TNF-α含量变化(n=6,
 ±s)
±s)Tab 1 Changes in TNF-α content of lung tissue and plasma(n=6,
 ±s)
±s), 百拇医药
Lung tissue(WB/ng*mg-1)
Plasma(ρB/ng*ml-1)
Time
OC
IR
NT
OC
IR
NT
Post-ischemia
6.40±1.01
, 百拇医药
7.79±1.02
6.60±1.21
1.23±0.17
1.58±0.13
1.53±0.12
Post-reperfusion
1 h
6.75±0.84
9.07±0.87*
7.88±0.78△
1.47±0.19
, http://www.100md.com
1.70±0.16
1.58±0.13
2 h
6.93±0.93
9.77±0.85* *
8.00±0.68△
1.62±0.13
1.93±0.15
1.72±0.12* *
4 h
7.01±1.25
, http://www.100md.com
9.94±1.19* *
8.34±1.03* △
1.77±0.16
1.97±0.16
1.82±0.15
*:P<0.05,* *:P<0.01 vs OC;△:P<0.05 vs IR
2.2 IL-6含量变化
结果见表2,IR组肺组织IL-6含量于再灌注4 h后非常显著高于OC组,NT组肺组织IL-6含量于再灌注4 h后下降近OC组水平(P>0.05)。
表 2 肺组织和血浆IL-6含量变化(n=6,
 ±s)
±s), 百拇医药
Tab 2 Changes in IL-6 content of lung tissue and plasma (n=6,
 ±s)
±s)Lung tissue(WB/ng*mg-1)
Plasma(ρB/ng*ml-1)
Time
OC
IR
NT
OC
IR
, http://www.100md.com
NT
Post-ischemia
2.16±0.32
2.21±0.40
2.18±0.30
0.42±0.06
0.44±0.04
0.44±0.06
Post-reperfusion
1 h
2.20±0.36
2.22±0.31
, 百拇医药
2.22±0.33
0.43±0.06
0.45±0.04
0.44±0.05
2 h
2.23±0.33
2.42±0.30
2.27±0.34
0.43±0.04
0.45±0.07
0.44±0.06
4 h
, 百拇医药
2.23±0.37
3.19±0.29* *
2.68±0.36
0.44±0.06
0.45±0.05
0.45±0.04
* *:P<0.01 vs OC
2.3 IL-8含量变化
结果见表3,IR组肺组织IL-8含量于再灌注4 h后显著高于OC组,NT组肺组织IL-8再灌注4 h降低至OC组水平(P>0.05)。
表 3 肺组织和血浆IL-8含量变化(n=6,
 ±s)
±s), 百拇医药
Tab 3 Changes in IL-8 content of lung tissue and plasma(n=6,
 ±s)
±s)Lung tissue(WB/ng*mg-1)
Plasma (ρB/ng*ml-1)
Time
OC
IR
NT
OC
IR
, 百拇医药
NT
Post-ischemia
2.49±0.38
2.52±0.32
2.47±0.36
0.29±0.06
0.29±0.06
0.28±0.04
Post-reperfusion
1 h
2.49±0.33
2.55±0.38
, 百拇医药
2.49±0.46
0.29±0.06
0.29±0.06
0.29±0.05
2 h
2.50±0.40
2.56±0.34
2.52±0.39
0.29±0.07
0.29±0.06
0.29±0.04
4 h
, 百拇医药
2.51±0.35
3.20±0.34*
2.72±0.41
0.29±0.06
0.29±0.08
0.29±0.04
*:P<0.05 vs OC
2.4 肺组织总钙水平变化
再灌注后各时相IR组和NT组肺组织总钙水平均分别较OC组有非常显著升高(P<0.01),NT组升幅非常明显低于IR组(P<0.01),见图1。
2.5 肺组织D/W变化
, 百拇医药
IR组再灌注1h,肺组织D/W已较OC组显著下降(P<0.05),4 h降至最低(P<0.01)。NT组再灌注后肺组织D/W虽较OC组仍呈下降趋势,但比值明显高于IR组(P<0.05)。
2.6 肺Cst变化
见表4,IR组缺血再灌注后Cst各项指标均较OC组呈进行性下降,NT组较IR组明显改善,EI与OC组比较已无明显差别。
2.7 相关性分析
见表5,肺组织总钙与肺组织TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8均呈显著正相关。肺组织TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8与C2.94均呈显著负相关。肺组织TNF-α与D/W、EI也均呈显著负相关。

, 百拇医药 图 1 左肺组织总钙水平变化 (mg/g干肺,n=6,
 ±s)
±s)Fig 1 Changes in total calcium level of left lung tissue (mg/g dry lung,n=6,
 ±s)* *:P<0.01 vs OC;△ △:P<0.05 vs IR
±s)* *:P<0.01 vs OC;△ △:P<0.05 vs IR表 4 肺静态顺应性变化(n=6,
 ±s)
±s)Tab 4 Changes in static lung compliance (n=6,
 ±s) Groups
±s) Groups, http://www.100md.com
C2.94(ml*kpa-1*kg-1)
C0.49(ml*kpa-1*kg-1)
EI
OC post-ischemia
11.08±0.98
33.80±0.86
0.48±0.02
post-reperfusion 1 h
11.06±1.02
, 百拇医药
33.21±0.90
0.47±0.03
2 h
11.03±1.03
33.28±0.90
0.48±0.02
4 h
11.02±1.12
34.25±0.87
0.48±0.01
IR post-ischemia
10.13±1.18
, 百拇医药
31.27±1.43* *
0.46±0.06
post-reperfnsion 1 h
9.73±0.65*
29.91±1.21* *
0.46±0.04
2 h
8.44±0.73* *
27.07±1.12* *
0.41±0.03* *
, 百拇医药
4 h
8.06±0.84* *
26.47±1.41* *
0.39±0.04* *
NT post-ischemia
10.77±0.78
32.16±1.09
0.47±0.04
post-reperfusion 1 h
10.11±0.75
, 百拇医药
31.06±1.48*
0.46±0.04
2 h
9.29±0.83*
29.21±0.60* * △ △
0.45±0.03
4 h
8.99±0.74* *
27.84±1.10* * △
0.44±0.03△
, http://www.100md.com
*:P<0.05,* *:P<0.01 vs OC △:P<0.05,△ △:P<0.01 vs IR
表 5 肺组织TNF-α、IL-6、IL-8与血浆TNF-α及其与肺组织总钙、D/W、Cst间相关性
Tab 5 Correlations of TNF-α,IL-6,IL-8 in lung tissue and TNF-α in plasma with total calcicm, D/W, Cst of lung tissue
D/W
C2.94
EI
Total calcium
, 百拇医药 Plasma TNF-α
Lung TNF-α
-0.89*
-0.92* *
-0.85*
+0.88*
+0.88*
Plasma TNF-α
-0.40
-0.81*
-0.02
, 百拇医药
+0.59
Lung IL-6
-0.63
-0.81*
-0.86*
+0.85*
+0.45
Lung IL-8
-0.35
-0.81*
-0.71
, 百拇医药
+0.89*
+0.30
*:P<0.05, * *:P<0.01
3 讨论
Ca2+的跨膜流动和细胞内Ca2+浓度变化对炎性细胞因子的合成和释放是必不可少的[4]。本研究发现,大鼠肺缺血后再灌注,肺组织总钙水平明显升高,间接反映了组织细胞内游离Ca2+水平的增高,即胞内Ca2+稳态的破坏。与肺组织总钙水平升高同步,肺缺血后再灌注,肺组织TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8含量相继升高,其中TNF-α首先升高,升幅最大,其次为IL-6,而IL-8升高偏晚,升幅也最小。相关分析表明,肺组织总钙水平与肺组织TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8含量均呈显著正相关。间接提示肺组织细胞因子的释放增加与细胞内Ca2+浓度变化有一定关系。此外,肺内炎性细胞因子含量升高与肺组织损害指标D/W、Cst变化时间上一致,均呈明显相关关系,从而表明炎性细胞因子在肺缺血再灌注损伤中发挥了重要作用。
, 百拇医药
本研究还发现,整个实验过程中,血浆TNF-α水平有一定程度升高,并与C2.94呈显著负相关,但升幅明显低于肺内TNF-α水平,而血浆IL-6、IL-8变化不明显。这一方面提示肺缺血再灌注损伤时血浆炎性细胞因子水平的变化滞后于肺内炎性细胞因子水平的变化,另一方面也表明肺缺血再灌注损伤时炎性细胞因子可能主要由肺内产生并留存于肺组织,通过自分泌/旁分泌形式发挥生物学效应。
有研究证实,二氢吡啶CCBs可抑制淋巴细胞、单核/巨噬细胞的激活,减少TNF-α、IL-1和IL-6的合成[5,6],肾移植病人给予CCBs后,血浆TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-2和IL-6水平降低[7]。本研究发现,NT处理后,肺D/W升高,Cst改善,再灌注肺组织总钙水平降低,各时相肺组织TNF-α含量均不同程度地较IR组减少,IL-6和IL-8含量于再灌注4 h后下降近OC组水平,说明NT通过阻滞Ca2+通道,减少细胞Ca2+内流,对上述细胞因子产生有一定抑制作用。但其确切机制尚需进一步探讨。有学者[8]认为Ca2+激活的磷酸化耦联可能与转录因子激活和细胞因子基因表达有关。还有研究报道[5],二氢吡啶CCBs可阻断TNF-α转录。
, http://www.100md.com
综上所述,本研究初步显示了NT可以抑制大鼠肺缺血再灌注损伤早期肺组织TNF-α、IL-6和IL-8含量的升高,适当应用CCBs可避免或减轻肺缺血再灌注损伤。
作者简介:向明章,男,36,硕士,副主任医师
参考文献
[1] Hachida M, Morton D L. The protection of ischemic lung with verapamil and hydralazine. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,1988,95(2):178
[2] 向明章,蒋耀光,王如文,等.尼群地平对缺血再灌注肺脂质过氧化反应的影响.中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,1998,5(2):76
[3] Ennema J J, Kobayashi T, Robertson B, et al. Inactivation of exogenous surfactant in experimental respiratory failure induced by hyperoxia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand,1988,32(8):665
, 百拇医药
[4] Hotchkiss R S, Karl I E. Calcium: a regulation of the inflammatory response in endotoxemia and sepsis. New Horiz,1996,4(1):58
[5] Lichtman S N, Wang J, Zhang C, et al. Endocytosis and Ca2+ are required for endotoxin-stimulated TNF-alpha release by rat Kupffer cells. Am J Physiol,1996,271(5 Ptl):G920
[6] Weir M R, Gomolka D, Pepplar R, et al. Mechanisms responsible for inhibition of lymphocyte activation by agents which block membrane calcium or potassium channels. Transplant Proc,1993,25(1):605
, 百拇医药
[7] Carozzi S, Nasini M G, Pietrucci A, et al. Immunosuppressive effects of different calcium channel blockers in human kidney allografts. Transplant Proc,1995,27(1):1054
[8] Shapira L, Takashiba S, Champagne C, et al. Involvement of PKC and protein tyrosine kinase in LPS-induced TNF-α and IL-Ⅰβ production by human monocytes. J Immunol,1994,153(4):1818
收稿:1998-04-01;修回:1998-09-28, http://www.100md.com