尼群地平对肺缺血再灌注损伤形态学变化的影响
作者:向明章 蒋耀光 王如文 范士志 牛会军
单位:向明章 第三军医大学附属新桥医院胸外科 重庆,400037;蒋耀光 王如文 范士志 牛会军 第三军医大学附属大坪医院胸外科) 重庆,400042
关键词:肺缺血再灌注损伤;显微镜检查;钙超载;尼群地平
第三军医大学学报990413 提 要 目的:为尼群地平防治肺缺血再灌注损伤提供实验依据。方法:采用大鼠肺在体缺血再灌注模型,将36只大鼠随机分成损伤对照组和尼群地平处理组,各组在缺血后、再灌注2 h、4 h后处死动物,通过大体、光镜和透射电镜观察及肺干/湿重比值测定,观察肺缺血再灌注损伤早期形态学变化。结果:肺缺血再灌注损伤早期出现以肺泡毛细血管膜通透性增加为特征的组织细胞损害,肺实质细胞胞浆和细胞器肿胀、空化变性、核淡染,Ⅱ型上皮细胞板层体排空、数目减少。尼群地平处理后,损伤肺组织形态变化减轻。结论:尼群地平对肺缺血再灌注损伤具有保护作用。
, 百拇医药
中图法分类号 R563;R619.9
Effects of nitrendipine on pulmonary morphological changes after ischemio-reperfusion injury in rats
Xiang Mingzhang, Jiang Yaoguang, Wang Ruwen, Fan Shizhi, Niu Huijun
Department of Thoracic Surgery, Xinqiao Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing,400037
Abstract Objective: To establish a theoretical basis for the employment of nitrendipine to prevent and treat pulmonary ischemio-reperfusion injury. Methods: After an ischemia model by occluding the hilus of the left lung was established in 36 rats, they were divided into 2 groups: the control group of ischemio-reperfusion injury (IR, n=18) and the nitrendipine-treated group (NT, n=18) of which the rats received an intravenous injection of nitrendipine 30 minutes before and 45 minutes after normothermic ischemia respectively. After 45 minutes of lung ischemia, the rats were killed in the 0 h, 2 h and 4 h after reperfusion. Then macroscopic inspection and optical and transmission electron microscopies were performed to assess the morphological changes of the injured lung tissues and their dry/wet weight ratio was measured as well. Results: The early morphological changes of the lungs after ischemio-reperfusion injury were characterized by an increase of the permeability of the alveolo-capillary membrane and infiltration of inflammatory cells. Under electron microscopy, there were moderate to severe degree of swelling, bleb formation in the cytoplasm and organelles, and understaining of the nuclei in the alveolar cells and the endothelium. Laminar bodies of the alveolar type Ⅱ cells were empitied. The pulmonary morphological changes became exacerbated as the time of reperfusion was prolonged. The specimens of the NT group revealed slight to moderate degrees of damages in the injured lung tissues. Conclusion: Nitrendipine provides protection for the lungs during ischemio-reperfusion injury by blocking the calcium channel and inhibitting Ca2+ influx to decrease cellular damages observed on optical and transmission electron microacopies.
, 百拇医药
Key words ischemio-reperfusion injury/pulmonary; microscopy; calcium overloading; nitrendipine
一些急性肺损伤和肺移植实验模型表明了细胞钙内流是肺缺血再灌注损伤的重要发病环节[1]。本实验采用大鼠肺在体缺血再灌注损伤模型,观察了肺缺血再灌注损伤早期组织形态学变化以及二氢吡啶类钙通道阻滞剂尼群地平(Nitrendipine,NT)的影响,以期为尼群地平用于防治肺缺血再灌注损伤提供依据。
1 材料与方法
按先前报道的方法[2]建立肺缺血再灌注损伤模型后,将健康Wistar大鼠36只,随机分为二组:①损伤对照组(IR,n=18):开胸阻断肺门45 min后放开行再灌注;②尼群地平处理组(NT,n=18):于肺门阻断前30 min和再灌注前分别经颈静脉注入0.01%NT1/2总量。IR组同法注入等量林格氏液。两组于缺血后、再灌注2 h、4 h分别活杀6只动物,立即开胸观察左肺大体病理变化,冠状面剖开左肺成前后两部分,前半部分入10%中性福尔马林固定,经梯度乙醇脱水、低温石蜡包埋、切片、HE染色后,光镜观察并摄片。从后半部分取1 mm3小块肺组织入3%戊二醛固定,1%锇酸后固定,梯度丙酮脱水,Epon 812包埋,超薄切片,醋酸钠、柠檬酸铅复染后,JEM-100SX型透射电镜观察摄片。另取100 g肺组织采用干湿重法测定干/湿重比值(D/W),数据用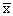 ±s表示,用t检验行统计学分析。
±s表示,用t检验行统计学分析。
, http://www.100md.com
2 结果
2.1 肺缺血45 min后形态学变化
IR组缺血后肉眼见肺呈暗红色;光镜下见部分肺泡萎陷、毛细血管充血;电镜下见间质水肿,毛细血管内中性粒细胞、血小板聚集。NT组缺血后肺颜色较淡,光镜下见肺充血减轻;电镜下主要见间质轻度水肿。
2.2 肺缺血再灌注2 h后形态学变化
再灌注2h后,IR组肉眼见肺充血、水肿明显,气管内有泡沫样分泌物。光镜下见肺泡间隔以中性粒细胞为主的炎细胞浸润,肺泡腔内可见水肿液和红细胞及渗出的炎细胞,毛细血管腔内有中性粒细胞扣押。电镜下见间质纤维结构模糊、排列紊乱,毛细血管腔内白细胞聚集,内皮细胞吞饮小泡增多,空化变性,表面微绒毛形成指状突起,内皮连续性中断,基底膜水肿、增厚,肺泡Ⅰ型上皮细胞肿胀变性,见图1,Ⅱ型上皮细胞胞浆疏松,线粒体电子密度降低、局灶性空化变性,偶见板层体排空。NT组肉眼、光镜及电镜下的变化均较IR组减轻。
, 百拇医药
图1 IR组再灌注2 h后Ⅰ型上皮细胞肿胀、胞浆变性(△),基底膜局灶性肿胀、增厚(*),内皮细胞胞浆肿胀、吞饮小泡增多(↑) (TEM×8 000)
Fig 1 After 2 hours of reperfusion, alveolar type Ⅰ cells with swelling and degeneration of cytoplasm (△), basal membranes with focal swelling and thickening (*),endothelial cells with swelling of cytoplasm and increased numbers of phagosome (↑) could been seen in the specimens from IR group (TEM×8 000)
2.3 肺缺血再灌注4 h后形态学变化
, 百拇医药
再灌注4 h后,IR组肉眼见肺表面斑点状出血,切面见气管腔内有泡沫样和血性液体溢出。光镜下见肺泡腔大量炎细胞渗出和水肿液积聚,见图2。电镜下见基底膜水肿明显;Ⅰ型上皮细胞坏死脱落;Ⅱ型上皮细胞线粒体嵴消失、空化变性,板层体数目减少,排空增多,见图3,核轻度肿胀、染色质减少;肺泡腔可见脱落的Ⅱ型细胞。NT组肉眼见肺表面出血点明显减少,切面见气管腔内有少许泡沫样和血性液体溢出。光镜下见肺泡腔内出血渗出及炎细胞浸润明显减轻,见图4。电镜下见内皮细胞、基底膜及肺泡上皮细胞的病变均较IR减轻。
图2 IR组再灌注4 h后肺泡腔内明显出血、渗出、浸润及水肿液积聚 (HE×200)
Fig 2 After 4 hours of reperfusion,in the specimens from IR group, evident hemorrhages,exudation,infiltration and accumulation of effusion fluid could been seen in the alvolar spaces (HE×200)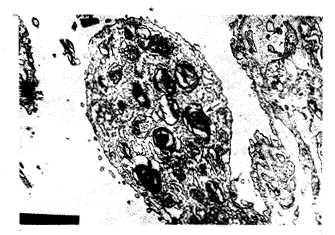
, http://www.100md.com
图3 IR组再灌注4 h后Ⅱ型上皮细胞胞浆疏松,板层体排空(↑),线粒体空化变性(*),内质网扩张(#) (TEM×8 000)
Fig 3 After 4 hours of reperfusion,alveolar type Ⅱ cells with inattentive cytoplasm containing emptied laminar bodies(↑), dilated endoplasmic reticulum(#) and degenerated mitochondria (*) are visible in some samples from IR group (TEM×8 000)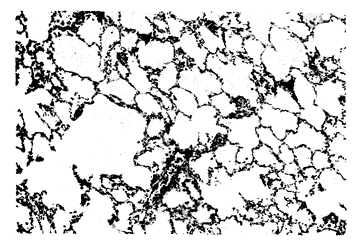
图4 NT组再灌注4 h后肺泡间隔增厚,肺泡腔内出血、渗出及炎性细胞浸润明显减轻 (HE×200)
, http://www.100md.com
Fig 4 After 4 hours of reperfusion, lighter tissue damage including a small degree of alveolar septae thickening and alleviated hemorrhages, exudation and infiltration of inflammatory cells in the alveolar spaces could been observed in the specimens from NT group (HE×200)
2.4 肺组织D/W比值变化,见表1
IR组再灌注后左肺D/W比值呈进行性下降,4h降至最低,NT组D/W比值虽仍呈下降趋势,但比值明显高于IR组。
表1 肺组织D/W比值变化(n=6,x±s)
, http://www.100md.com
Tab 1 Changes of dry-wet weight ratiosof lung tissue (n=6,x±s) Group
Post-ischemia
Post-reperfusion
2 h
4 h
IR
0.18±0.01
0.15±0.01☆ ☆
0.14±0.01☆ ☆
NT
, http://www.100md.com
0.18±0.02
0.17±0.02△
0.16±0.02☆ △
☆:P<0.05,☆ ☆:P<0.01 vs Post-ischemia;△:P<0.05 vs IR
3 讨论
肺由于其具有独特易损害的组织结构和对缺血损害的高度敏感性,肺移植后常常发生缺血再灌注损伤和难以预料的移植肺早期功能障碍,已有许多实验研究了其发生的可能原因和防治方法[3~5],但少有研究评价钙通道阻滞剂尼群地平对肺缺血再灌注损伤早期形态变化的影响。
Ca2+是机体内重要的第二信使物质,不仅可直接激活具有多种重要生理意义的细胞内机械活动,而且作为Ca2+信号系统转导细胞信号的重要成分,与其他细胞内信号系统相联系,调节着细胞的多种生理功能。缺血、缺氧和再灌注刺激可诱发细胞钙内流,造成细胞内钙超载,即胞内钙稳态的破坏。细胞内钙超载一方面影响细胞能量代谢,另一方面激活溶酶体酶、磷脂酶A2以及蛋白激酶C等钙敏感性酶类,引起细胞膜和细胞器损害,使炎症介质和炎性细胞因子释放增加,加重或促进缺血再灌注损伤的形态学变化[6~8]。
, 百拇医药
本实验采用大鼠左肺门阻断缺血45 min后再灌注4 h,明显造成了缺血再灌注肺组织结构损害,肺缺血45 min后即出现充血、水肿,随着再灌注时间延长,肺损伤进一步加重,肺水肿更为明显,至4 h时,肺泡腔内有血性渗出和水肿液积聚,电镜下可见肺实质细胞胞浆和细胞器肿胀、空化变性,Ⅱ型上皮细胞板层体排空、数目减少以及基底膜肿胀。这种以血管高通透性肺水肿为特征的病理变化与文献报道的肺缺血再灌注损伤早期形态改变相一致[9]。NT处理后,缺血再灌注肺组织细胞形态改变、炎性细胞浸润减轻和肺水含量减少,表明NT对肺缺血再灌注损伤具有保护作用。NT是新型二氢吡啶类钙通道阻滞剂,可阻滞过多Ca2+经电压依赖性钙通道进入细胞,降低细胞内游离Ca2+水平,从而减轻或延缓细胞内钙超载而引发的一系列有害作用所造成的组织形态改变。
综上所述,本实验模型较好地模拟了移植肺缺血再灌注损伤早期形态学改变,适当应用钙通道阻滞剂尼群地平可减缓肺缺血再灌注损伤和肺水肿的形成。
, 百拇医药
作者简介:向明章,男,36岁,副主任医师,硕士
参考文献
1 Bryan C L, Cohn D I, Gibbons W J, et al. Lung transplantation. The reimplantation response. Crit Care Rep,1991,2(3):217
2 向明章,蒋耀光,王如文,等.尼群地平对缺血再灌注肺脂质过氧化反应的影响.中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,1998,5(2):76
3 Yamashita M, Schmid R A, Ando K, et al. Nitroprusside ameliorates lung allograft reperfusion injury. Ann Thorac Surg,1996,62(3):791
, 百拇医药
4 Lindberg L, Kimblad P O, Sjoberg T, et al. Inhaled nitric oxide reveals and attenuates endothelial dysfunction after lung transplantation. Ann Thorac Surg,1996,62(6):1639
5 Aoe N, Trachiotis G D, Okabayashi K, et al. Administration of prostaglandin E1 after lung transplantation improves early graft function. Ann Thorac Surg,1994,58(3):655
6 Paull D E, Keagy B A, Kron E J, et al. Reperfusion injury in the lung preserved for 24 hours. Ann Thorac Surg,1989,47(2):187
, 百拇医药
7 Xu D, Lu Q, Deitch E A. Calcium and phospholipase A2 appear to be involved in the pathogenesis of hemorrhagic shock induced mucosal injury and bacterial translocation. Crit Care Med,1995,23(1):125
8 Serrick C, Adoumie R, Giaid A, et al. The early release of interleukin-2, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma after ischemia-reperfusion injury in the lung allograft. Transplantation,1994,58(11):1158
9 Higgins R S D, Letsou G V, Sanchez J A, et al. Improved ultrastructural lung preservation with prostaglandin E1 as donor pretreatment in a primate model of heart-lung transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,1993,105(6):965
收稿:1998-09-10
修回:1999-01-11, 百拇医药
单位:向明章 第三军医大学附属新桥医院胸外科 重庆,400037;蒋耀光 王如文 范士志 牛会军 第三军医大学附属大坪医院胸外科) 重庆,400042
关键词:肺缺血再灌注损伤;显微镜检查;钙超载;尼群地平
第三军医大学学报990413 提 要 目的:为尼群地平防治肺缺血再灌注损伤提供实验依据。方法:采用大鼠肺在体缺血再灌注模型,将36只大鼠随机分成损伤对照组和尼群地平处理组,各组在缺血后、再灌注2 h、4 h后处死动物,通过大体、光镜和透射电镜观察及肺干/湿重比值测定,观察肺缺血再灌注损伤早期形态学变化。结果:肺缺血再灌注损伤早期出现以肺泡毛细血管膜通透性增加为特征的组织细胞损害,肺实质细胞胞浆和细胞器肿胀、空化变性、核淡染,Ⅱ型上皮细胞板层体排空、数目减少。尼群地平处理后,损伤肺组织形态变化减轻。结论:尼群地平对肺缺血再灌注损伤具有保护作用。
, 百拇医药
中图法分类号 R563;R619.9
Effects of nitrendipine on pulmonary morphological changes after ischemio-reperfusion injury in rats
Xiang Mingzhang, Jiang Yaoguang, Wang Ruwen, Fan Shizhi, Niu Huijun
Department of Thoracic Surgery, Xinqiao Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing,400037
Abstract Objective: To establish a theoretical basis for the employment of nitrendipine to prevent and treat pulmonary ischemio-reperfusion injury. Methods: After an ischemia model by occluding the hilus of the left lung was established in 36 rats, they were divided into 2 groups: the control group of ischemio-reperfusion injury (IR, n=18) and the nitrendipine-treated group (NT, n=18) of which the rats received an intravenous injection of nitrendipine 30 minutes before and 45 minutes after normothermic ischemia respectively. After 45 minutes of lung ischemia, the rats were killed in the 0 h, 2 h and 4 h after reperfusion. Then macroscopic inspection and optical and transmission electron microscopies were performed to assess the morphological changes of the injured lung tissues and their dry/wet weight ratio was measured as well. Results: The early morphological changes of the lungs after ischemio-reperfusion injury were characterized by an increase of the permeability of the alveolo-capillary membrane and infiltration of inflammatory cells. Under electron microscopy, there were moderate to severe degree of swelling, bleb formation in the cytoplasm and organelles, and understaining of the nuclei in the alveolar cells and the endothelium. Laminar bodies of the alveolar type Ⅱ cells were empitied. The pulmonary morphological changes became exacerbated as the time of reperfusion was prolonged. The specimens of the NT group revealed slight to moderate degrees of damages in the injured lung tissues. Conclusion: Nitrendipine provides protection for the lungs during ischemio-reperfusion injury by blocking the calcium channel and inhibitting Ca2+ influx to decrease cellular damages observed on optical and transmission electron microacopies.
, 百拇医药
Key words ischemio-reperfusion injury/pulmonary; microscopy; calcium overloading; nitrendipine
一些急性肺损伤和肺移植实验模型表明了细胞钙内流是肺缺血再灌注损伤的重要发病环节[1]。本实验采用大鼠肺在体缺血再灌注损伤模型,观察了肺缺血再灌注损伤早期组织形态学变化以及二氢吡啶类钙通道阻滞剂尼群地平(Nitrendipine,NT)的影响,以期为尼群地平用于防治肺缺血再灌注损伤提供依据。
1 材料与方法
按先前报道的方法[2]建立肺缺血再灌注损伤模型后,将健康Wistar大鼠36只,随机分为二组:①损伤对照组(IR,n=18):开胸阻断肺门45 min后放开行再灌注;②尼群地平处理组(NT,n=18):于肺门阻断前30 min和再灌注前分别经颈静脉注入0.01%NT1/2总量。IR组同法注入等量林格氏液。两组于缺血后、再灌注2 h、4 h分别活杀6只动物,立即开胸观察左肺大体病理变化,冠状面剖开左肺成前后两部分,前半部分入10%中性福尔马林固定,经梯度乙醇脱水、低温石蜡包埋、切片、HE染色后,光镜观察并摄片。从后半部分取1 mm3小块肺组织入3%戊二醛固定,1%锇酸后固定,梯度丙酮脱水,Epon 812包埋,超薄切片,醋酸钠、柠檬酸铅复染后,JEM-100SX型透射电镜观察摄片。另取100 g肺组织采用干湿重法测定干/湿重比值(D/W),数据用
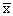 ±s表示,用t检验行统计学分析。
±s表示,用t检验行统计学分析。, http://www.100md.com
2 结果
2.1 肺缺血45 min后形态学变化
IR组缺血后肉眼见肺呈暗红色;光镜下见部分肺泡萎陷、毛细血管充血;电镜下见间质水肿,毛细血管内中性粒细胞、血小板聚集。NT组缺血后肺颜色较淡,光镜下见肺充血减轻;电镜下主要见间质轻度水肿。
2.2 肺缺血再灌注2 h后形态学变化
再灌注2h后,IR组肉眼见肺充血、水肿明显,气管内有泡沫样分泌物。光镜下见肺泡间隔以中性粒细胞为主的炎细胞浸润,肺泡腔内可见水肿液和红细胞及渗出的炎细胞,毛细血管腔内有中性粒细胞扣押。电镜下见间质纤维结构模糊、排列紊乱,毛细血管腔内白细胞聚集,内皮细胞吞饮小泡增多,空化变性,表面微绒毛形成指状突起,内皮连续性中断,基底膜水肿、增厚,肺泡Ⅰ型上皮细胞肿胀变性,见图1,Ⅱ型上皮细胞胞浆疏松,线粒体电子密度降低、局灶性空化变性,偶见板层体排空。NT组肉眼、光镜及电镜下的变化均较IR组减轻。

, 百拇医药
图1 IR组再灌注2 h后Ⅰ型上皮细胞肿胀、胞浆变性(△),基底膜局灶性肿胀、增厚(*),内皮细胞胞浆肿胀、吞饮小泡增多(↑) (TEM×8 000)
Fig 1 After 2 hours of reperfusion, alveolar type Ⅰ cells with swelling and degeneration of cytoplasm (△), basal membranes with focal swelling and thickening (*),endothelial cells with swelling of cytoplasm and increased numbers of phagosome (↑) could been seen in the specimens from IR group (TEM×8 000)
2.3 肺缺血再灌注4 h后形态学变化
, 百拇医药
再灌注4 h后,IR组肉眼见肺表面斑点状出血,切面见气管腔内有泡沫样和血性液体溢出。光镜下见肺泡腔大量炎细胞渗出和水肿液积聚,见图2。电镜下见基底膜水肿明显;Ⅰ型上皮细胞坏死脱落;Ⅱ型上皮细胞线粒体嵴消失、空化变性,板层体数目减少,排空增多,见图3,核轻度肿胀、染色质减少;肺泡腔可见脱落的Ⅱ型细胞。NT组肉眼见肺表面出血点明显减少,切面见气管腔内有少许泡沫样和血性液体溢出。光镜下见肺泡腔内出血渗出及炎细胞浸润明显减轻,见图4。电镜下见内皮细胞、基底膜及肺泡上皮细胞的病变均较IR减轻。

图2 IR组再灌注4 h后肺泡腔内明显出血、渗出、浸润及水肿液积聚 (HE×200)
Fig 2 After 4 hours of reperfusion,in the specimens from IR group, evident hemorrhages,exudation,infiltration and accumulation of effusion fluid could been seen in the alvolar spaces (HE×200)

, http://www.100md.com
图3 IR组再灌注4 h后Ⅱ型上皮细胞胞浆疏松,板层体排空(↑),线粒体空化变性(*),内质网扩张(#) (TEM×8 000)
Fig 3 After 4 hours of reperfusion,alveolar type Ⅱ cells with inattentive cytoplasm containing emptied laminar bodies(↑), dilated endoplasmic reticulum(#) and degenerated mitochondria (*) are visible in some samples from IR group (TEM×8 000)

图4 NT组再灌注4 h后肺泡间隔增厚,肺泡腔内出血、渗出及炎性细胞浸润明显减轻 (HE×200)
, http://www.100md.com
Fig 4 After 4 hours of reperfusion, lighter tissue damage including a small degree of alveolar septae thickening and alleviated hemorrhages, exudation and infiltration of inflammatory cells in the alveolar spaces could been observed in the specimens from NT group (HE×200)
2.4 肺组织D/W比值变化,见表1
IR组再灌注后左肺D/W比值呈进行性下降,4h降至最低,NT组D/W比值虽仍呈下降趋势,但比值明显高于IR组。
表1 肺组织D/W比值变化(n=6,x±s)
, http://www.100md.com
Tab 1 Changes of dry-wet weight ratiosof lung tissue (n=6,x±s) Group
Post-ischemia
Post-reperfusion
2 h
4 h
IR
0.18±0.01
0.15±0.01☆ ☆
0.14±0.01☆ ☆
NT
, http://www.100md.com
0.18±0.02
0.17±0.02△
0.16±0.02☆ △
☆:P<0.05,☆ ☆:P<0.01 vs Post-ischemia;△:P<0.05 vs IR
3 讨论
肺由于其具有独特易损害的组织结构和对缺血损害的高度敏感性,肺移植后常常发生缺血再灌注损伤和难以预料的移植肺早期功能障碍,已有许多实验研究了其发生的可能原因和防治方法[3~5],但少有研究评价钙通道阻滞剂尼群地平对肺缺血再灌注损伤早期形态变化的影响。
Ca2+是机体内重要的第二信使物质,不仅可直接激活具有多种重要生理意义的细胞内机械活动,而且作为Ca2+信号系统转导细胞信号的重要成分,与其他细胞内信号系统相联系,调节着细胞的多种生理功能。缺血、缺氧和再灌注刺激可诱发细胞钙内流,造成细胞内钙超载,即胞内钙稳态的破坏。细胞内钙超载一方面影响细胞能量代谢,另一方面激活溶酶体酶、磷脂酶A2以及蛋白激酶C等钙敏感性酶类,引起细胞膜和细胞器损害,使炎症介质和炎性细胞因子释放增加,加重或促进缺血再灌注损伤的形态学变化[6~8]。
, 百拇医药
本实验采用大鼠左肺门阻断缺血45 min后再灌注4 h,明显造成了缺血再灌注肺组织结构损害,肺缺血45 min后即出现充血、水肿,随着再灌注时间延长,肺损伤进一步加重,肺水肿更为明显,至4 h时,肺泡腔内有血性渗出和水肿液积聚,电镜下可见肺实质细胞胞浆和细胞器肿胀、空化变性,Ⅱ型上皮细胞板层体排空、数目减少以及基底膜肿胀。这种以血管高通透性肺水肿为特征的病理变化与文献报道的肺缺血再灌注损伤早期形态改变相一致[9]。NT处理后,缺血再灌注肺组织细胞形态改变、炎性细胞浸润减轻和肺水含量减少,表明NT对肺缺血再灌注损伤具有保护作用。NT是新型二氢吡啶类钙通道阻滞剂,可阻滞过多Ca2+经电压依赖性钙通道进入细胞,降低细胞内游离Ca2+水平,从而减轻或延缓细胞内钙超载而引发的一系列有害作用所造成的组织形态改变。
综上所述,本实验模型较好地模拟了移植肺缺血再灌注损伤早期形态学改变,适当应用钙通道阻滞剂尼群地平可减缓肺缺血再灌注损伤和肺水肿的形成。
, 百拇医药
作者简介:向明章,男,36岁,副主任医师,硕士
参考文献
1 Bryan C L, Cohn D I, Gibbons W J, et al. Lung transplantation. The reimplantation response. Crit Care Rep,1991,2(3):217
2 向明章,蒋耀光,王如文,等.尼群地平对缺血再灌注肺脂质过氧化反应的影响.中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,1998,5(2):76
3 Yamashita M, Schmid R A, Ando K, et al. Nitroprusside ameliorates lung allograft reperfusion injury. Ann Thorac Surg,1996,62(3):791
, 百拇医药
4 Lindberg L, Kimblad P O, Sjoberg T, et al. Inhaled nitric oxide reveals and attenuates endothelial dysfunction after lung transplantation. Ann Thorac Surg,1996,62(6):1639
5 Aoe N, Trachiotis G D, Okabayashi K, et al. Administration of prostaglandin E1 after lung transplantation improves early graft function. Ann Thorac Surg,1994,58(3):655
6 Paull D E, Keagy B A, Kron E J, et al. Reperfusion injury in the lung preserved for 24 hours. Ann Thorac Surg,1989,47(2):187
, 百拇医药
7 Xu D, Lu Q, Deitch E A. Calcium and phospholipase A2 appear to be involved in the pathogenesis of hemorrhagic shock induced mucosal injury and bacterial translocation. Crit Care Med,1995,23(1):125
8 Serrick C, Adoumie R, Giaid A, et al. The early release of interleukin-2, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma after ischemia-reperfusion injury in the lung allograft. Transplantation,1994,58(11):1158
9 Higgins R S D, Letsou G V, Sanchez J A, et al. Improved ultrastructural lung preservation with prostaglandin E1 as donor pretreatment in a primate model of heart-lung transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,1993,105(6):965
收稿:1998-09-10
修回:1999-01-11, 百拇医药