一种水溶黑粉菌多糖的结构和抗肿瘤活性研究
作者:白日霞 薛 业
单位:大连民族学院化工系,大连116600
关键词:黑粉菌;多糖;抗肿瘤活性
摘 要 从药用黑粉菌中用2
摘 要 从药用黑粉菌中用2%氢氧化钠分离提取出一种具有(1→6)分支的(1→3)-β-D葡聚糖(BR-1).多糖 BR-1的纯度用凝胶过滤和超离心进行了鉴定.分子量为15万. BR-1的一级结构分别用13C核磁共振法、甲基化法、高碘酸氧化法和Smith降解等方法进行了确定.BR-1对小白鼠肉瘤S-180的抑瘤率为94.0%.
Structural and Antitumor Activity Investigation of a Water
, 百拇医药
Soluble Ustilago maydis (DC. ) Polysaccharides
Bai Rixia1,Xue Ye
(Dalian Nationality College, Dalian 116600, China)
Abstract A water soluble, (1→6)-branched, (1→3)- β-D-glucan(BR-1) was isolated from 2% sodium hydroxide extract of the Ustilago maydis (DC.).BR-1 was homogeneous by gel filtration on Sepharose 4B and Ultracentrifugal analysis. The molecular weight of BR-1 was estimated to be 1.5×105. From the results of 13C-NMR spectra, methylation analysis, periodate oxidation, Smith degradation, it was concluded that BR-1 has a main chain composed of β -(1→3)-linked D-glucopyranosyl residues. The side chain was a β-(1→6)-linked D-glucopyranosyl group. The antitumor activity of BR-1 was 94.0% against Saroma 180.
, 百拇医药
Key words Ustilago maydis (DC.) ;polysaccharide;antitumor activity
Results and Discussion
The polysaccharide(BR-1) was composed of D-glucosyl residues, as shown by paper chromatography and gas chromatography of the hydrolyzate. BR-1 showed characteristic absorbance at 890 cm-1 in the infrared spectrum, indicating the presence of the β -D configuration. The total sugar content was found to be 99.2% by the phenol-sulfuric acid method. The calibration cure was made by gel filtration of standard dextrans on Sepharose 4B with water.The molecular weight of BR-1 was estimated to be 1.5×105.
, http://www.100md.com
BR-1 was oxidized with 15 mmol.L-1 sodium metaperiodate for 72 hrs at 4~10℃. The periodate comsumption and formic acid production per hexosyl residue were 0.8 and 0.4 mol. The oxidized polysaccharide was treated with sodium borohydride, and the resulting polyalcohol was hydrolyzed with acid.The Smith degradation product was analyzed by gas chromatography and glycerol and glucose were detected in the molar ratio of 2∶3. The glycerol must have arisen from the terminal residues, and the occurrence of glucose must be due to the presence of oxidation resistant D-glucose, such as (1→3)-linked residues.
, http://www.100md.com
The 13C-NMR shifts for the BR-1 are given in Table 1. The 13C-NMR spectrum showed three signals for anomeric carbons, three linkages carbons and others unsubst carbons. And the anomeric carbons are β type because the chemical shift of C-1 for α-Glc were about δ 98~99.
BR-1 was methylated by the new method of Ciucanu〔1〕. After every time the product showed no infrared spectrum absorption for free hydroxyl groups.Hydrolysis of the methylated glycan yielded a mixture of methylated ethers listed in Table 2.
, http://www.100md.com
Tab.1 The 13C-NMR spectral of BR-1 and their assignments
Sugar unit
Carbon atom
Chemical shifts of
BR-1
Chemical shifts of
Smith degraded
Peak high ratio
of C-1 of BR-1
Peak high ratio
, 百拇医药
of C-1 of Smith
degraded
——1Glc3——
C-1
102.4
102.4
1.00
1.00
C-3
84.6
84.5
——Glc1——
, 百拇医药
C-1
100.5
2.14
C-3
75.4
——1Glc36——
C-1
103.4
103.3
2.08
2.0
C-3
, http://www.100md.com
84.2
84.2
C-6
68.9
63.8
Tab.2 Methylation analysis of BR-1
Methylated sugar
Main mass fragments
m/e
Molar ratio
Mode of linkage
, 百拇医药
2,3,4,6-Me4-Glc
43,45,87,101,117,129,145,161,205
2
1→
2,4,6-Me3-Glc
43,45,87,101,117,161
1
1→3
2,4-Me2-Glc
43,87,117,129,189
, 百拇医药
2
1→3,6
The methylated sugar was identified by comparing their retention time in gas chromatography and their mass spectra, and the methylation analysis indicated the presence 2,3,4,6-tetra-,2,4,6-tri, and 2,4-di-O-methyl-D-glucose in the molar ratio of 2∶1∶2. The results suggested that this glucan had many nonreducing end-groups(40%) and a backbone of (1→3)-linked D-glucopyranosyl residues, and contained many branching points of (1→6)-linked D-glucopyranosyl residues (40%) at O-6 of the (1→3)-linked D-glucosyl residues.
, 百拇医药
So its basic structure is probably expressed in the following formula: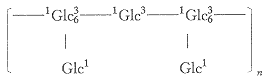
Tab.3 Antitumor activity of the polysaccharides of BR-1 and its Smith degraded
Sample
Dose/mg.kg-1×days
Average weight/g
Inhibition ratio/%
, http://www.100md.com
BR-1
10×10
0.053
94.0
Smith degraded
10×10
0.38
57.2
Experiments
Materials The Ustilago maydis(DC.) was obtained from Daqing city.Sepharose 4B and standard dextrans were purchased from Sigma chemical company.
, 百拇医药
General methods All the evaporations were performed under diminished pressure at 40~45℃. Infrared spectra were recorded on Shimadzu IR-408 infrared spectrometer. Paper chromatography was performed on the Xinhua filter paper with the following solvent system (v∶v) 4∶1∶5 1-butanol-ethanol -2% aqueous ammonia. Gas chromatography was performed in a SP-501 apparatus equipped with aflamer ionization detertor.A glass column (3 mm×2 m)was used. The columns used were 3% of silicone OV-225 on Chromosorb W (80~100 mesh) at 170℃. Ultracentrifugal analysis was conducted in 0.9% sodium chloride with HITACHI 282 analytical ultracentrifuge at 55 000 r/min at 15.7℃. GC-MS was conducted with JEOL JMS-D 300 apparatus equipped with a glass column (0.3 mm×60 m) packed with 3% OV-225.
, http://www.100md.com
Isolation of the BR-l The dried Ustilago maydis (DC.) (200 g) was extracted twice with hot water (90℃). The residual material was suspended in 0.1 mol .L-1sodium hydroxide for 24 hrs at room temperature under nitrogen. The alkali suspension was centrifuged, and the resulting brownish extract was neutralized with acetic acid. The precipitated polysaccaride was collected by centrifugation. The precipitate was redissolved in 0.1 mol.L-1 sodium hydroxide a small amount of insoluble material was removed by centrifugation,and the supernatant was neutralized with acetic acid. The same treatment was repeated three times. The resulting precipitate was dissolved in water, and the solution treated with methanol to get the purified polysaccharide BR-1 (0.5 g).
, 百拇医药
Gel-filtration A solution (0.5%) of BR-1 in water was applied to a column (1 cm×80 cm) of Sepharose 4B. The column was eluted with water. The effluent was collected in 2 mL fractions. The carbohydrate content of each fraction was determined by the phenol-sulfuric acid method.
Periodate Oxidation and Smith degradation BR-1 (30 mg) was suspended in 15 mmol. L-1 sodium metaperiodate and kept at 4~10℃ in the dark.The periodate consumption was determined by the spectrophotometric method〔3〕.The formic acid was titrated with 0.01 mol.L-1 sodium hydroxide after the reduction of the excess periodate with ethylene glycol. The oxidation was complete for 72 hrs. The oxidation mixture was treated with ethylene glycol,dialyzed, and the contents were reduced with sodium borohydride for 24 hrs.The mixture was treated with acetic acid, dialyzed, and then lyophilized. The residual material was divided into three parts: The first part was treated with 1 mol.L-1 sulfuric acid for 40 hrs at 25 ℃ and the product was analyzed by gas chromatography. The second part was treated with 13C-NMR spectra .The third part was tested with bioassy as follows.
, http://www.100md.com
Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer 13C-NMR spectra were obtained at 100.00 MHz with a Bruker DRX-400 spectrometer. BR-1 (10 mg) was suspended in CDCl3 (1. 5 mL) . The sample was dispersed by placing the 5 mm sample tubes in a bath-type sonicator to achieve well resolved 13C spectra.All the spectra were obtained at 85 ℃.All the spectra were broad-band proton-decoupled.
Methylation analysis BR-1 (10 mg) was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (10 mL) for five minutes. Then the sodium hydroxide-dimethyl sulfoxide (10 mL)-methy iodide (5 mL) was added. The mixture was stirred for seven min, then diluted with water (20 mL) and added chloroform (30 mL), stirred and centrifuged for 5 min at 3000 r/min to afford the chloroform layer, then methylation was finished after evaporating chloroform. The methylated sugar was hydrolyzed with sulfuric acid. The neutralized hydrolyzate was deionized〔4〕.The resulting substance was analyzed by GC-MS.
, http://www.100md.com
Assay of antitumor activity A piece of Saroma 180 tumor fragment was transplanted subcutaneously into the mice of the ICR/JCL strain. The samples dissolved in saline solution were intraperitoneally injected daily for 10 d. Starting 24 hrs after tumor implantation,the tumor was weighed at the end of 5 weeks. The inhibition ratio was calculated by comparing the average weight of the tumors of the treated mice with that of untreated controls.
REFERENCES
, 百拇医药
1 Ciucanu I , Kerek F. Reexamined the mechanism of basecatalyzed methylation in dipolar solvents.Carbohydrate Res, 1984, 13(1) :209~210
2 Bai Rixia,Li Jufeng.Studies on antitumor activity of polyporus Umbellatus Fr. polysaccharide. Journal of Qiqihar Teachers College,1995, 15(2) :24~25
3 Bai Rixia, Zhang Yishen. Study on water soluble polysaccharide from Marasmius androsaceus(L:Fr)Fr.Zhenjun Xuebao, 1990,9(2) :161~167
4 Bai Rixia. Characterization of water soluble polysaccharide of alkaline extraction from Marasmius androsaceus(L:Fr)Fr. Shengwu Huaxue Zazhi , 1994, 10(3) :305~307
Received : 1999-07-26, 百拇医药
单位:大连民族学院化工系,大连116600
关键词:黑粉菌;多糖;抗肿瘤活性
摘 要 从药用黑粉菌中用2
摘 要 从药用黑粉菌中用2%氢氧化钠分离提取出一种具有(1→6)分支的(1→3)-β-D葡聚糖(BR-1).多糖 BR-1的纯度用凝胶过滤和超离心进行了鉴定.分子量为15万. BR-1的一级结构分别用13C核磁共振法、甲基化法、高碘酸氧化法和Smith降解等方法进行了确定.BR-1对小白鼠肉瘤S-180的抑瘤率为94.0%.
Structural and Antitumor Activity Investigation of a Water
, 百拇医药
Soluble Ustilago maydis (DC. ) Polysaccharides
Bai Rixia1,Xue Ye
(Dalian Nationality College, Dalian 116600, China)
Abstract A water soluble, (1→6)-branched, (1→3)- β-D-glucan(BR-1) was isolated from 2% sodium hydroxide extract of the Ustilago maydis (DC.).BR-1 was homogeneous by gel filtration on Sepharose 4B and Ultracentrifugal analysis. The molecular weight of BR-1 was estimated to be 1.5×105. From the results of 13C-NMR spectra, methylation analysis, periodate oxidation, Smith degradation, it was concluded that BR-1 has a main chain composed of β -(1→3)-linked D-glucopyranosyl residues. The side chain was a β-(1→6)-linked D-glucopyranosyl group. The antitumor activity of BR-1 was 94.0% against Saroma 180.
, 百拇医药
Key words Ustilago maydis (DC.) ;polysaccharide;antitumor activity
Results and Discussion
The polysaccharide(BR-1) was composed of D-glucosyl residues, as shown by paper chromatography and gas chromatography of the hydrolyzate. BR-1 showed characteristic absorbance at 890 cm-1 in the infrared spectrum, indicating the presence of the β -D configuration. The total sugar content was found to be 99.2% by the phenol-sulfuric acid method. The calibration cure was made by gel filtration of standard dextrans on Sepharose 4B with water.The molecular weight of BR-1 was estimated to be 1.5×105.
, http://www.100md.com
BR-1 was oxidized with 15 mmol.L-1 sodium metaperiodate for 72 hrs at 4~10℃. The periodate comsumption and formic acid production per hexosyl residue were 0.8 and 0.4 mol. The oxidized polysaccharide was treated with sodium borohydride, and the resulting polyalcohol was hydrolyzed with acid.The Smith degradation product was analyzed by gas chromatography and glycerol and glucose were detected in the molar ratio of 2∶3. The glycerol must have arisen from the terminal residues, and the occurrence of glucose must be due to the presence of oxidation resistant D-glucose, such as (1→3)-linked residues.
, http://www.100md.com
The 13C-NMR shifts for the BR-1 are given in Table 1. The 13C-NMR spectrum showed three signals for anomeric carbons, three linkages carbons and others unsubst carbons. And the anomeric carbons are β type because the chemical shift of C-1 for α-Glc were about δ 98~99.
BR-1 was methylated by the new method of Ciucanu〔1〕. After every time the product showed no infrared spectrum absorption for free hydroxyl groups.Hydrolysis of the methylated glycan yielded a mixture of methylated ethers listed in Table 2.
, http://www.100md.com
Tab.1 The 13C-NMR spectral of BR-1 and their assignments
Sugar unit
Carbon atom
Chemical shifts of
BR-1
Chemical shifts of
Smith degraded
Peak high ratio
of C-1 of BR-1
Peak high ratio
, 百拇医药
of C-1 of Smith
degraded
——1Glc3——
C-1
102.4
102.4
1.00
1.00
C-3
84.6
84.5
——Glc1——
, 百拇医药
C-1
100.5
2.14
C-3
75.4
——1Glc36——
C-1
103.4
103.3
2.08
2.0
C-3
, http://www.100md.com
84.2
84.2
C-6
68.9
63.8
Tab.2 Methylation analysis of BR-1
Methylated sugar
Main mass fragments
m/e
Molar ratio
Mode of linkage
, 百拇医药
2,3,4,6-Me4-Glc
43,45,87,101,117,129,145,161,205
2
1→
2,4,6-Me3-Glc
43,45,87,101,117,161
1
1→3
2,4-Me2-Glc
43,87,117,129,189
, 百拇医药
2
1→3,6
The methylated sugar was identified by comparing their retention time in gas chromatography and their mass spectra, and the methylation analysis indicated the presence 2,3,4,6-tetra-,2,4,6-tri, and 2,4-di-O-methyl-D-glucose in the molar ratio of 2∶1∶2. The results suggested that this glucan had many nonreducing end-groups(40%) and a backbone of (1→3)-linked D-glucopyranosyl residues, and contained many branching points of (1→6)-linked D-glucopyranosyl residues (40%) at O-6 of the (1→3)-linked D-glucosyl residues.
, 百拇医药
So its basic structure is probably expressed in the following formula:
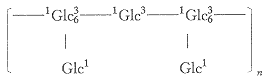
Tab.3 Antitumor activity of the polysaccharides of BR-1 and its Smith degraded
Sample
Dose/mg.kg-1×days
Average weight/g
Inhibition ratio/%
, http://www.100md.com
BR-1
10×10
0.053
94.0
Smith degraded
10×10
0.38
57.2
Experiments
Materials The Ustilago maydis(DC.) was obtained from Daqing city.Sepharose 4B and standard dextrans were purchased from Sigma chemical company.
, 百拇医药
General methods All the evaporations were performed under diminished pressure at 40~45℃. Infrared spectra were recorded on Shimadzu IR-408 infrared spectrometer. Paper chromatography was performed on the Xinhua filter paper with the following solvent system (v∶v) 4∶1∶5 1-butanol-ethanol -2% aqueous ammonia. Gas chromatography was performed in a SP-501 apparatus equipped with aflamer ionization detertor.A glass column (3 mm×2 m)was used. The columns used were 3% of silicone OV-225 on Chromosorb W (80~100 mesh) at 170℃. Ultracentrifugal analysis was conducted in 0.9% sodium chloride with HITACHI 282 analytical ultracentrifuge at 55 000 r/min at 15.7℃. GC-MS was conducted with JEOL JMS-D 300 apparatus equipped with a glass column (0.3 mm×60 m) packed with 3% OV-225.
, http://www.100md.com
Isolation of the BR-l The dried Ustilago maydis (DC.) (200 g) was extracted twice with hot water (90℃). The residual material was suspended in 0.1 mol .L-1sodium hydroxide for 24 hrs at room temperature under nitrogen. The alkali suspension was centrifuged, and the resulting brownish extract was neutralized with acetic acid. The precipitated polysaccaride was collected by centrifugation. The precipitate was redissolved in 0.1 mol.L-1 sodium hydroxide a small amount of insoluble material was removed by centrifugation,and the supernatant was neutralized with acetic acid. The same treatment was repeated three times. The resulting precipitate was dissolved in water, and the solution treated with methanol to get the purified polysaccharide BR-1 (0.5 g).
, 百拇医药
Gel-filtration A solution (0.5%) of BR-1 in water was applied to a column (1 cm×80 cm) of Sepharose 4B. The column was eluted with water. The effluent was collected in 2 mL fractions. The carbohydrate content of each fraction was determined by the phenol-sulfuric acid method.
Periodate Oxidation and Smith degradation BR-1 (30 mg) was suspended in 15 mmol. L-1 sodium metaperiodate and kept at 4~10℃ in the dark.The periodate consumption was determined by the spectrophotometric method〔3〕.The formic acid was titrated with 0.01 mol.L-1 sodium hydroxide after the reduction of the excess periodate with ethylene glycol. The oxidation was complete for 72 hrs. The oxidation mixture was treated with ethylene glycol,dialyzed, and the contents were reduced with sodium borohydride for 24 hrs.The mixture was treated with acetic acid, dialyzed, and then lyophilized. The residual material was divided into three parts: The first part was treated with 1 mol.L-1 sulfuric acid for 40 hrs at 25 ℃ and the product was analyzed by gas chromatography. The second part was treated with 13C-NMR spectra .The third part was tested with bioassy as follows.
, http://www.100md.com
Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer 13C-NMR spectra were obtained at 100.00 MHz with a Bruker DRX-400 spectrometer. BR-1 (10 mg) was suspended in CDCl3 (1. 5 mL) . The sample was dispersed by placing the 5 mm sample tubes in a bath-type sonicator to achieve well resolved 13C spectra.All the spectra were obtained at 85 ℃.All the spectra were broad-band proton-decoupled.
Methylation analysis BR-1 (10 mg) was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (10 mL) for five minutes. Then the sodium hydroxide-dimethyl sulfoxide (10 mL)-methy iodide (5 mL) was added. The mixture was stirred for seven min, then diluted with water (20 mL) and added chloroform (30 mL), stirred and centrifuged for 5 min at 3000 r/min to afford the chloroform layer, then methylation was finished after evaporating chloroform. The methylated sugar was hydrolyzed with sulfuric acid. The neutralized hydrolyzate was deionized〔4〕.The resulting substance was analyzed by GC-MS.
, http://www.100md.com
Assay of antitumor activity A piece of Saroma 180 tumor fragment was transplanted subcutaneously into the mice of the ICR/JCL strain. The samples dissolved in saline solution were intraperitoneally injected daily for 10 d. Starting 24 hrs after tumor implantation,the tumor was weighed at the end of 5 weeks. The inhibition ratio was calculated by comparing the average weight of the tumors of the treated mice with that of untreated controls.
REFERENCES
, 百拇医药
1 Ciucanu I , Kerek F. Reexamined the mechanism of basecatalyzed methylation in dipolar solvents.Carbohydrate Res, 1984, 13(1) :209~210
2 Bai Rixia,Li Jufeng.Studies on antitumor activity of polyporus Umbellatus Fr. polysaccharide. Journal of Qiqihar Teachers College,1995, 15(2) :24~25
3 Bai Rixia, Zhang Yishen. Study on water soluble polysaccharide from Marasmius androsaceus(L:Fr)Fr.Zhenjun Xuebao, 1990,9(2) :161~167
4 Bai Rixia. Characterization of water soluble polysaccharide of alkaline extraction from Marasmius androsaceus(L:Fr)Fr. Shengwu Huaxue Zazhi , 1994, 10(3) :305~307
Received : 1999-07-26, 百拇医药