3D-SCTA对颅内动脉瘤的临床应用价值
作者:关丽明 高思佳 曲海源 王强 李松柏 徐克 王晓峰
单位:关丽明 高思佳 曲海源 王强 李松柏 徐克(中国医科大学附属第一临床学院放射科,辽宁沈阳110001);王晓峰(沈阳市第四人民医院放射科,辽宁沈阳110031)
关键词:脑动脉瘤;体层摄影术;X线计算机;血管造影术;数字减影
中国临床医学影像杂志000102
[摘要]目的:评价3D-SCTA对颅内动脉瘤的临床应用价值。方法:DSA检查诊为颅内动脉瘤,但瘤颈、载瘤动脉或瘤体立体形态显示不满意的患者11例,行3D-SCTA检查,重建方法采用最大强度投影(MIP)和表面遮盖成像(SSD)。全部病例均经手术证实。结果:11例术中共发现15个动脉瘤,螺旋CT血管造影及三维重建与DSA均检出14个动脉瘤,漏诊1个脉络膜前动脉瘤,检出率为933%。在DSA检出的14个动脉瘤中,12个动脉瘤的瘤颈显示不满意,3D-SCTASSD图像全部得以明确;10个动脉瘤的载瘤动脉显示不理想,在3D-SCTASSD上可清晰显示8个,1个脉络膜前动脉起始部动脉瘤和1个后交通动脉起始部动脉瘤未能明确显示。SSD图像可使血管和颅骨同时显示,但对小血管的显示不及DSA,DSA正常显示的后交通动脉约30%在3D-SCTA上未显示。SSD图像可清晰显示动脉瘤颈部的解剖关系、载瘤动脉、邻近血管及周围骨结构。结论:螺旋CT血管造影及三维重建对Willis环周围瘤体大于4mm的颅内动脉瘤可达到与DSA同样的检出率,可以明确DSA显示不理想的动脉瘤的瘤颈、载瘤动脉情况,但对瘤周小血管的显示不及DSA。
, 百拇医药
[中图分类号]R739.41 [文献标识码]A [文章编号]1008-1062(2000)01-0004-03
Assessment of intracranial aneurysms by three- dimensional spiral CT angiography
GUAN Li-ming,GAO Si-jia,QV Hai-yuan,WANG Qiang,LI Song-bai,XU Ke,WANG Xiao-feng
Department of Radiology,the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University,Shenyang 110001,China
Abstract:Objective:To evaluate the diagnostic value of Three- dimensional Spiral CT Angiography(3D- SCTA)for intracranial aneurysms.Methods:For dissatisfied with the display of the aneurysm s neck and loading artery examined by Digital Subtraction Angiography(DSA),3D- SCTA study was performed in 11 patients with intracranial aneurysm.After all data transferred to computer workstation,Maximum Intensity projection(MIP)、 Surface Shaded Display(SSD)and pseudo color encoding techniques were used to reconstruct 3D images.Aneurysms were analyzed for size of the neck and relationship of the aneurysm with surrounding arteries,and neighboring bone structure.Results:In eleven patients,15 cerebral aneurysms ranging from 2 to 20mm in maximum diameter were found on operation,1 aneurysm in anterior choroidal artery was located outside the imaging volume of 3D- SCTA and DSA.The detection rate of the two techniques for the remaining 14 aneurysms was 93 3% .12(86% )of the 14 aneurysms and 8 of the 10 aneurysms,which neck and/or the loading artery was shown poorly on DSA,were identified on 3D- SCTA.The remaining 2 aneurysms were not also displayed clearly on 3D- SCTA.However,3D- SCTA is not as good at displaying the small arteries such as posterior communicating artery as DSA.Conclusions:3D- SCTA is comparable to DSA in detecting cerebral aneurysms larger than 4mm in diameter located around the circle of Willis and is more accurate and direct for the neck of aneurysm,loading artery,surrounding artery and neighboring bone structure which are identified poorly on DSA the same as the image of small vessels on 3D- SCTA is not so distinguished as on DSA. - dimensional Spiral CT Angiography(3D- SCTA)for intracranial aneurysms.Methods:For dissatisfied with the display of the aneurysm s neck and loading artery examined by Digital Subtraction Angiography(DSA),3D- SCTA study was performed in 11 patients with intracranial aneurysm.After all data transferred to computer workstation,Maximum Intensity projection(MIP)、 Surface Shaded Display(SSD)and pseudo color encoding techniques were used to reconstruct 3D images.Aneurysms were analyzed for size of the neck and relationship of the aneurysm with surrounding arteries,and neighboring bone structure.Results:In eleven patients,15 cerebral aneurysms ranging from 2 to 20mm in maximum diameter were found on operation,1 aneurysm in anterior choroidal artery was located outside the imaging volume of 3D- SCTA and DSA.The detection rate of the two techniques for the remaining 14 aneurysms was 93 3% .12(86% )of the 14 aneurysms and 8 of the 10 aneurysms,which neck and/or the loading artery was shown poorly on DSA,were identified on 3D- SCTA.The remaining 2 aneurysms were not also displayed clearly on 3D- SCTA.However,3D- SCTA is not as good at displaying the small arteries such as posterior communicating artery as DSA.Conclusions:3D- SCTA is comparable to DSA in detecting cerebral aneurysms larger than 4mm in diameter located around the circle of Willis and is more accurate and direct for the neck of aneurysm,loading artery,surrounding artery and neighboring bone structure which are identified poorly on DSA the same as the image of small vessels on 3D- SCTA is not so distinguished as on DSA.
, 百拇医药
Key words:cerebral aneurysm;tomography,X-ray computed;angiography,digital subtraction
螺旋CT血管造影及三维重建是近年来新发展起来的扫描技术,有关其在颅内动脉瘤诊断方面的应用,国内已有报道,但这些文章大都侧重介绍3D-SCTA的成像原理、方法及临床应用,对3D-SCTA与DSA的比较方面则不够深入,本文收集了我院1998年12月~1999年8月DSA检查诊为颅内动脉瘤,但瘤颈、载瘤动脉或瘤体立体形态显示不满意的11例患者的3D-SCTA检查资料,具体评价3D-SCTA的临床应用价值。
1 材料和方法
本文11例颅内动脉瘤破裂造成蛛网膜下腔出血的患者全部先接受了DSA检查,由于瘤颈、载瘤动脉及瘤体立体形态显示不满意等原因继之又进行SCTA检查,后者通过三维重建进行评价,男6例,女5例,共计15个动脉瘤,年龄31~55岁,平均49岁。所有患者均在我院住院经手术治疗。本文以术中所见作为评价两种检查方法的标准。
, 百拇医药
SCTA检查:采用东芝Xpress/Gx螺旋CT机,工作站:Sun工作站;三维图像软件:Xtension。检查步骤:①常规平扫定位片,病人仰卧于检查台上,120kV,100mA,视野S场,确定检查范围以听眦线为基准,以鞍底为扫描中心,向上和向下各扩展约30mm。②增强螺旋CT扫描,120kV,200mA,1秒曝光,视野S场,螺距为1,进床速度2mm/s,扫描层厚2mm,用高压注射器经前臂静脉团注优维显,流速为2.5~3ml/s,延迟时间为15~20s,扫描时间20~30s从颅底向顶部扫描,扫描结束后用0.6mm间隔重建成有部分重叠的图像。③三维图像重建:将平滑重建后的数据传输到Sun工作站,应用Xtension软件,选用MIP、SSD法重建图像。
DSA检查:采用德国西门子MULTISTART.O.T数字血管造影机,常规股动脉途径行脑血管造影,通过放大技术获取后前位、侧位及斜位像。
2 结果
, 百拇医药
本组11例患者术中探查发现15个动脉瘤,3D-SCTA与DSA均检出14个,检出率为93.3%(14/15),1个脉络膜前动脉瘤3D-SCTA与DSA均未发现(见表1)。经x2检验3D-SCTA与DSA之间及二者对颅内动脉瘤的检出与术中所见之间的差异无统计学上的显著性(P>0.05)。3D-SCTAMIP图像测得动脉瘤最大径范围2~20mm,平均8.8mm,瘤颈宽度范围2~10mm,平均为5mm,MIP对颅内动脉瘤瘤体大小的显示与术中所见之间的差异经成对t检验无显著性(P>0.05)。对于DSA检出的14个动脉瘤中,12个瘤颈显示不满意,在3D-SCTASSD图像上均可清晰显示,10个动脉瘤载瘤动脉DSA显示不理想,其中8个SSD图像可清晰显示,一个后交通动脉起始部动脉瘤的载瘤动脉和1个脉络膜前动脉起始部动脉瘤的载瘤动脉SSD图像也未能显示。另外,SSD多角度多方位图像能比较清晰的显示动脉瘤完整的立体形态、生长方向、体部大小以及与邻近血管、颅骨的空间解剖关系(图1~6),但对小血管显示不良,例如正常CT阈值范围内约30%的后交通动脉未见显影。
, http://www.100md.com
图1 DSA颈内动脉侧位图像,示前交通动脉瘤、后交通动脉瘤和
脉络膜前动脉起始部动脉瘤,但前交通动脉瘤瘤颈显示不佳。
图2 同一病例,CTASSD+伪彩色图像示前交通动脉瘤瘤体最大径、瘤颈及载瘤动脉。
图3 同一病例,CTASSD正位图像,除较大的前交通动脉瘤外,还可见颈内动脉有两个小隆起,正常阈值范围载瘤动脉未见显示,术中证实分别为后交通动脉起始部动脉瘤和脉络膜前动脉起始部动脉瘤。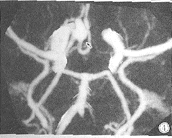
图4 同一病例,CTAMIP图像。
, http://www.100md.com
图5 DSA示较大类葫芦形动脉瘤,但载瘤动脉显示不佳。
图6 3D-SCTASSD图像,清晰显示为大脑前动脉起始部动脉瘤,并可见瘤体的立体形态和周围结构的关系。
表1 3D-SCTA、DSA与术中对颅内动脉瘤的检出数比较
3D-SCTA
DSA
术中所见
前交通动脉瘤
6
6
, 百拇医药 6
后交通动脉瘤
3
4
4
大脑前动脉瘤
1
1
1
大脑中动脉瘤
1
1
1
颈内动脉瘤
, 百拇医药
3
1
1
脉络膜前动脉瘤
0
1
2
总计
14
14
15
3 讨论
据文献报道,尸检约5%的人颅内有动脉瘤,动脉瘤破裂造成蛛网膜下腔出血是其最危险的并发症,常危及患者的生命。寻求有效的检测手段,尽早准确的检出动脉瘤具有重要临床意义。在螺旋CT问世以前,DSA广泛应用于临床诊断颅内动脉瘤,并被视为金标准〔1〕。然而,作为一种创伤性的检测手段,有血管并发症的危险,如血肿、血管痉挛、中风等。此外,如本组病例,DSA因必须在显影前确定投照方向,又不能无限制调整投照方向,所以在血管关系复杂的部位,如Willis环动脉瘤的载瘤动脉、瘤颈、瘤体生长方向等往往不易清晰显示。
, 百拇医药
近年来,3D-SCTA作为一种相对无创而又有效的血管检查技术,越来越多的应用于颅内动脉瘤的诊断。3D-SCTA即经周围静脉借助高压注射器团注造影剂后于靶血管内造影剂浓度达峰值时行螺旋CT薄层扫描,平滑处理后数据进行三维重建,从而显示血管立体图像〔2〕。目前国内外文献中3D-SCTA多采用表面遮盖成像(SSD)或SSD+最大密度投影(MIP)方法,本组病例均采用MIP+SSD两种方法检查颅内动脉瘤。SSD方法用来显示颅内动脉瘤的立体形态及与周围结构解剖关系,术中发现的15个动脉瘤中,3D-SCTA对瘤体的检出率为93.3%(14/15),一个脉络膜前动脉瘤由于太小(约2mm)而漏诊。3D-SCTA对动脉瘤瘤颈、载瘤动脉的显示优于DSA,对载瘤动脉的显示不及瘤颈,原因可能是由于瘤体比较小或位于载瘤动脉的起始处及动脉瘤的优势供血效应,使其远端的血管痉挛、变细,逸出CT阈值范围而不显示,因而3D-SCTA因不能显示载瘤动脉而误将1个脉络膜前动脉起始处动脉瘤和1个后交通支起始处动脉瘤诊为颈内动脉瘤。国内外文献认为3D-SCTA对诊断Willis环周围瘤体大于4mm以上的动脉瘤检出率高,显示效果好〔3,4〕。本组结果符合上述观点。
, http://www.100md.com
另外,3D-SCTA一次注药既可多视向、多角度观察图像3D-SCTASSD图像能直观、立体让血管与颅骨同时显示,又可单独显示血管,减掉颅骨影像,通过模拟手术入路成像,有助于外科医生选择最佳术式及手术入路,进行术前评估〔3,4〕,以缩短手术时间,降低术中意外的发生率,深受神经外科医生的喜欢。同时,在动脉瘤的栓塞术介入治疗中,动脉瘤的立体形态、瘤颈宽窄、载瘤动脉直径及二者关系直接影响了栓塞技术及栓塞药物的选择〔5,6〕,3D-SCTA在此方面必将有更大的临床应用价值。
由于SSD具有夸大效应,故在MIP图像上测量瘤体的大小和瘤颈宽窄。Dillon〔7〕和Rubin〔8〕等认为MIP重建图像类似血管造影,能可靠显示管腔狭窄、动脉瘤等病变,可弥补横断面CT和MRA的不足,在某种程度上可替代血管造影或DSA。本组资料结果符合上述结论,但3D-SCTA也有其自身的局限性,无法分清血流方向,动静脉同时显影,CT阈值设定过宽则干扰因素增加,过窄则丢失信息,我们还发现常规显示Willis环血管时,后交通动脉常显示不良,并且Willis环以远的血管及病变显示也不理想,对较小及接近颅底的动脉瘤显示比较困难。
, http://www.100md.com
总之,3D-SCTA在诊断颅内动脉瘤方面是对DSA的重要补充。
关丽明:中国医科大学附属第一临床学院放射科医师
〔参考文献〕
〔 1〕 詹炯,戴建平,高培毅,等.三维CT血管造影在诊断颅内动脉瘤中的应用.中华放射学杂志,1999,33(4):235~ 238
〔 2〕 周康荣主编.螺旋CT.上海:上海医科大学出版社,1998,262~ 263
〔 3〕 Ogawa T,Okudera T,Noguchi K,et al.Cerebral aneurysms:evaluation with three- dimensional CT angiography.AJNR,1996,17(3):447~ 454
, 百拇医药
〔 4〕 Hope JK,Wilson JL,Thomson FJ,et al,Three- dimensional CT angiography in the detection and characterization of intracranial berry aneurysms.AJNR,1996,17(3):437~ 445
〔 5〕 Martin D,Rodesch G,Alvarez H,et al.Preliminary results of embolisation of nonsurgical intracranial aneurysms with GD coils:the 1st year of their use.Neuroradiology,1996;38(suppl):S142~ S150
〔 6〕 Cognard C,Pierot L,Boulin A,et al.Intracranial aneurysm:endovascular treatment with mechanical detachable spirals in aneurysm.Radiology,1997,202(3):783~ 792
〔 7〕 Dillon EH,Van Leeuwen MS,Fernandez MA,et al.Spiral CT angiography.AJR,1993,160(6):1273~ 1278
〔 8〕 Rubin GD,Dake MD,Napel SA,et al.Three- dimensional spiral CT angiography of the abdomen:initial clinical experience.Radiology,1993,186(1):147~ 152
(1999-12-31收稿), 百拇医药
单位:关丽明 高思佳 曲海源 王强 李松柏 徐克(中国医科大学附属第一临床学院放射科,辽宁沈阳110001);王晓峰(沈阳市第四人民医院放射科,辽宁沈阳110031)
关键词:脑动脉瘤;体层摄影术;X线计算机;血管造影术;数字减影
中国临床医学影像杂志000102
[摘要]目的:评价3D-SCTA对颅内动脉瘤的临床应用价值。方法:DSA检查诊为颅内动脉瘤,但瘤颈、载瘤动脉或瘤体立体形态显示不满意的患者11例,行3D-SCTA检查,重建方法采用最大强度投影(MIP)和表面遮盖成像(SSD)。全部病例均经手术证实。结果:11例术中共发现15个动脉瘤,螺旋CT血管造影及三维重建与DSA均检出14个动脉瘤,漏诊1个脉络膜前动脉瘤,检出率为933%。在DSA检出的14个动脉瘤中,12个动脉瘤的瘤颈显示不满意,3D-SCTASSD图像全部得以明确;10个动脉瘤的载瘤动脉显示不理想,在3D-SCTASSD上可清晰显示8个,1个脉络膜前动脉起始部动脉瘤和1个后交通动脉起始部动脉瘤未能明确显示。SSD图像可使血管和颅骨同时显示,但对小血管的显示不及DSA,DSA正常显示的后交通动脉约30%在3D-SCTA上未显示。SSD图像可清晰显示动脉瘤颈部的解剖关系、载瘤动脉、邻近血管及周围骨结构。结论:螺旋CT血管造影及三维重建对Willis环周围瘤体大于4mm的颅内动脉瘤可达到与DSA同样的检出率,可以明确DSA显示不理想的动脉瘤的瘤颈、载瘤动脉情况,但对瘤周小血管的显示不及DSA。
, 百拇医药
[中图分类号]R739.41 [文献标识码]A [文章编号]1008-1062(2000)01-0004-03
Assessment of intracranial aneurysms by three- dimensional spiral CT angiography
GUAN Li-ming,GAO Si-jia,QV Hai-yuan,WANG Qiang,LI Song-bai,XU Ke,WANG Xiao-feng
Department of Radiology,the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University,Shenyang 110001,China
Abstract:Objective:To evaluate the diagnostic value of Three- dimensional Spiral CT Angiography(3D- SCTA)for intracranial aneurysms.Methods:For dissatisfied with the display of the aneurysm s neck and loading artery examined by Digital Subtraction Angiography(DSA),3D- SCTA study was performed in 11 patients with intracranial aneurysm.After all data transferred to computer workstation,Maximum Intensity projection(MIP)、 Surface Shaded Display(SSD)and pseudo color encoding techniques were used to reconstruct 3D images.Aneurysms were analyzed for size of the neck and relationship of the aneurysm with surrounding arteries,and neighboring bone structure.Results:In eleven patients,15 cerebral aneurysms ranging from 2 to 20mm in maximum diameter were found on operation,1 aneurysm in anterior choroidal artery was located outside the imaging volume of 3D- SCTA and DSA.The detection rate of the two techniques for the remaining 14 aneurysms was 93 3% .12(86% )of the 14 aneurysms and 8 of the 10 aneurysms,which neck and/or the loading artery was shown poorly on DSA,were identified on 3D- SCTA.The remaining 2 aneurysms were not also displayed clearly on 3D- SCTA.However,3D- SCTA is not as good at displaying the small arteries such as posterior communicating artery as DSA.Conclusions:3D- SCTA is comparable to DSA in detecting cerebral aneurysms larger than 4mm in diameter located around the circle of Willis and is more accurate and direct for the neck of aneurysm,loading artery,surrounding artery and neighboring bone structure which are identified poorly on DSA the same as the image of small vessels on 3D- SCTA is not so distinguished as on DSA. - dimensional Spiral CT Angiography(3D- SCTA)for intracranial aneurysms.Methods:For dissatisfied with the display of the aneurysm s neck and loading artery examined by Digital Subtraction Angiography(DSA),3D- SCTA study was performed in 11 patients with intracranial aneurysm.After all data transferred to computer workstation,Maximum Intensity projection(MIP)、 Surface Shaded Display(SSD)and pseudo color encoding techniques were used to reconstruct 3D images.Aneurysms were analyzed for size of the neck and relationship of the aneurysm with surrounding arteries,and neighboring bone structure.Results:In eleven patients,15 cerebral aneurysms ranging from 2 to 20mm in maximum diameter were found on operation,1 aneurysm in anterior choroidal artery was located outside the imaging volume of 3D- SCTA and DSA.The detection rate of the two techniques for the remaining 14 aneurysms was 93 3% .12(86% )of the 14 aneurysms and 8 of the 10 aneurysms,which neck and/or the loading artery was shown poorly on DSA,were identified on 3D- SCTA.The remaining 2 aneurysms were not also displayed clearly on 3D- SCTA.However,3D- SCTA is not as good at displaying the small arteries such as posterior communicating artery as DSA.Conclusions:3D- SCTA is comparable to DSA in detecting cerebral aneurysms larger than 4mm in diameter located around the circle of Willis and is more accurate and direct for the neck of aneurysm,loading artery,surrounding artery and neighboring bone structure which are identified poorly on DSA the same as the image of small vessels on 3D- SCTA is not so distinguished as on DSA.
, 百拇医药
Key words:cerebral aneurysm;tomography,X-ray computed;angiography,digital subtraction
螺旋CT血管造影及三维重建是近年来新发展起来的扫描技术,有关其在颅内动脉瘤诊断方面的应用,国内已有报道,但这些文章大都侧重介绍3D-SCTA的成像原理、方法及临床应用,对3D-SCTA与DSA的比较方面则不够深入,本文收集了我院1998年12月~1999年8月DSA检查诊为颅内动脉瘤,但瘤颈、载瘤动脉或瘤体立体形态显示不满意的11例患者的3D-SCTA检查资料,具体评价3D-SCTA的临床应用价值。
1 材料和方法
本文11例颅内动脉瘤破裂造成蛛网膜下腔出血的患者全部先接受了DSA检查,由于瘤颈、载瘤动脉及瘤体立体形态显示不满意等原因继之又进行SCTA检查,后者通过三维重建进行评价,男6例,女5例,共计15个动脉瘤,年龄31~55岁,平均49岁。所有患者均在我院住院经手术治疗。本文以术中所见作为评价两种检查方法的标准。
, 百拇医药
SCTA检查:采用东芝Xpress/Gx螺旋CT机,工作站:Sun工作站;三维图像软件:Xtension。检查步骤:①常规平扫定位片,病人仰卧于检查台上,120kV,100mA,视野S场,确定检查范围以听眦线为基准,以鞍底为扫描中心,向上和向下各扩展约30mm。②增强螺旋CT扫描,120kV,200mA,1秒曝光,视野S场,螺距为1,进床速度2mm/s,扫描层厚2mm,用高压注射器经前臂静脉团注优维显,流速为2.5~3ml/s,延迟时间为15~20s,扫描时间20~30s从颅底向顶部扫描,扫描结束后用0.6mm间隔重建成有部分重叠的图像。③三维图像重建:将平滑重建后的数据传输到Sun工作站,应用Xtension软件,选用MIP、SSD法重建图像。
DSA检查:采用德国西门子MULTISTART.O.T数字血管造影机,常规股动脉途径行脑血管造影,通过放大技术获取后前位、侧位及斜位像。
2 结果
, 百拇医药
本组11例患者术中探查发现15个动脉瘤,3D-SCTA与DSA均检出14个,检出率为93.3%(14/15),1个脉络膜前动脉瘤3D-SCTA与DSA均未发现(见表1)。经x2检验3D-SCTA与DSA之间及二者对颅内动脉瘤的检出与术中所见之间的差异无统计学上的显著性(P>0.05)。3D-SCTAMIP图像测得动脉瘤最大径范围2~20mm,平均8.8mm,瘤颈宽度范围2~10mm,平均为5mm,MIP对颅内动脉瘤瘤体大小的显示与术中所见之间的差异经成对t检验无显著性(P>0.05)。对于DSA检出的14个动脉瘤中,12个瘤颈显示不满意,在3D-SCTASSD图像上均可清晰显示,10个动脉瘤载瘤动脉DSA显示不理想,其中8个SSD图像可清晰显示,一个后交通动脉起始部动脉瘤的载瘤动脉和1个脉络膜前动脉起始部动脉瘤的载瘤动脉SSD图像也未能显示。另外,SSD多角度多方位图像能比较清晰的显示动脉瘤完整的立体形态、生长方向、体部大小以及与邻近血管、颅骨的空间解剖关系(图1~6),但对小血管显示不良,例如正常CT阈值范围内约30%的后交通动脉未见显影。

, http://www.100md.com
图1 DSA颈内动脉侧位图像,示前交通动脉瘤、后交通动脉瘤和
脉络膜前动脉起始部动脉瘤,但前交通动脉瘤瘤颈显示不佳。

图2 同一病例,CTASSD+伪彩色图像示前交通动脉瘤瘤体最大径、瘤颈及载瘤动脉。

图3 同一病例,CTASSD正位图像,除较大的前交通动脉瘤外,还可见颈内动脉有两个小隆起,正常阈值范围载瘤动脉未见显示,术中证实分别为后交通动脉起始部动脉瘤和脉络膜前动脉起始部动脉瘤。

图4 同一病例,CTAMIP图像。

, http://www.100md.com
图5 DSA示较大类葫芦形动脉瘤,但载瘤动脉显示不佳。

图6 3D-SCTASSD图像,清晰显示为大脑前动脉起始部动脉瘤,并可见瘤体的立体形态和周围结构的关系。
表1 3D-SCTA、DSA与术中对颅内动脉瘤的检出数比较
3D-SCTA
DSA
术中所见
前交通动脉瘤
6
6
, 百拇医药 6
后交通动脉瘤
3
4
4
大脑前动脉瘤
1
1
1
大脑中动脉瘤
1
1
1
颈内动脉瘤
, 百拇医药
3
1
1
脉络膜前动脉瘤
0
1
2
总计
14
14
15
3 讨论
据文献报道,尸检约5%的人颅内有动脉瘤,动脉瘤破裂造成蛛网膜下腔出血是其最危险的并发症,常危及患者的生命。寻求有效的检测手段,尽早准确的检出动脉瘤具有重要临床意义。在螺旋CT问世以前,DSA广泛应用于临床诊断颅内动脉瘤,并被视为金标准〔1〕。然而,作为一种创伤性的检测手段,有血管并发症的危险,如血肿、血管痉挛、中风等。此外,如本组病例,DSA因必须在显影前确定投照方向,又不能无限制调整投照方向,所以在血管关系复杂的部位,如Willis环动脉瘤的载瘤动脉、瘤颈、瘤体生长方向等往往不易清晰显示。
, 百拇医药
近年来,3D-SCTA作为一种相对无创而又有效的血管检查技术,越来越多的应用于颅内动脉瘤的诊断。3D-SCTA即经周围静脉借助高压注射器团注造影剂后于靶血管内造影剂浓度达峰值时行螺旋CT薄层扫描,平滑处理后数据进行三维重建,从而显示血管立体图像〔2〕。目前国内外文献中3D-SCTA多采用表面遮盖成像(SSD)或SSD+最大密度投影(MIP)方法,本组病例均采用MIP+SSD两种方法检查颅内动脉瘤。SSD方法用来显示颅内动脉瘤的立体形态及与周围结构解剖关系,术中发现的15个动脉瘤中,3D-SCTA对瘤体的检出率为93.3%(14/15),一个脉络膜前动脉瘤由于太小(约2mm)而漏诊。3D-SCTA对动脉瘤瘤颈、载瘤动脉的显示优于DSA,对载瘤动脉的显示不及瘤颈,原因可能是由于瘤体比较小或位于载瘤动脉的起始处及动脉瘤的优势供血效应,使其远端的血管痉挛、变细,逸出CT阈值范围而不显示,因而3D-SCTA因不能显示载瘤动脉而误将1个脉络膜前动脉起始处动脉瘤和1个后交通支起始处动脉瘤诊为颈内动脉瘤。国内外文献认为3D-SCTA对诊断Willis环周围瘤体大于4mm以上的动脉瘤检出率高,显示效果好〔3,4〕。本组结果符合上述观点。
, http://www.100md.com
另外,3D-SCTA一次注药既可多视向、多角度观察图像3D-SCTASSD图像能直观、立体让血管与颅骨同时显示,又可单独显示血管,减掉颅骨影像,通过模拟手术入路成像,有助于外科医生选择最佳术式及手术入路,进行术前评估〔3,4〕,以缩短手术时间,降低术中意外的发生率,深受神经外科医生的喜欢。同时,在动脉瘤的栓塞术介入治疗中,动脉瘤的立体形态、瘤颈宽窄、载瘤动脉直径及二者关系直接影响了栓塞技术及栓塞药物的选择〔5,6〕,3D-SCTA在此方面必将有更大的临床应用价值。
由于SSD具有夸大效应,故在MIP图像上测量瘤体的大小和瘤颈宽窄。Dillon〔7〕和Rubin〔8〕等认为MIP重建图像类似血管造影,能可靠显示管腔狭窄、动脉瘤等病变,可弥补横断面CT和MRA的不足,在某种程度上可替代血管造影或DSA。本组资料结果符合上述结论,但3D-SCTA也有其自身的局限性,无法分清血流方向,动静脉同时显影,CT阈值设定过宽则干扰因素增加,过窄则丢失信息,我们还发现常规显示Willis环血管时,后交通动脉常显示不良,并且Willis环以远的血管及病变显示也不理想,对较小及接近颅底的动脉瘤显示比较困难。
, http://www.100md.com
总之,3D-SCTA在诊断颅内动脉瘤方面是对DSA的重要补充。
关丽明:中国医科大学附属第一临床学院放射科医师
〔参考文献〕
〔 1〕 詹炯,戴建平,高培毅,等.三维CT血管造影在诊断颅内动脉瘤中的应用.中华放射学杂志,1999,33(4):235~ 238
〔 2〕 周康荣主编.螺旋CT.上海:上海医科大学出版社,1998,262~ 263
〔 3〕 Ogawa T,Okudera T,Noguchi K,et al.Cerebral aneurysms:evaluation with three- dimensional CT angiography.AJNR,1996,17(3):447~ 454
, 百拇医药
〔 4〕 Hope JK,Wilson JL,Thomson FJ,et al,Three- dimensional CT angiography in the detection and characterization of intracranial berry aneurysms.AJNR,1996,17(3):437~ 445
〔 5〕 Martin D,Rodesch G,Alvarez H,et al.Preliminary results of embolisation of nonsurgical intracranial aneurysms with GD coils:the 1st year of their use.Neuroradiology,1996;38(suppl):S142~ S150
〔 6〕 Cognard C,Pierot L,Boulin A,et al.Intracranial aneurysm:endovascular treatment with mechanical detachable spirals in aneurysm.Radiology,1997,202(3):783~ 792
〔 7〕 Dillon EH,Van Leeuwen MS,Fernandez MA,et al.Spiral CT angiography.AJR,1993,160(6):1273~ 1278
〔 8〕 Rubin GD,Dake MD,Napel SA,et al.Three- dimensional spiral CT angiography of the abdomen:initial clinical experience.Radiology,1993,186(1):147~ 152
(1999-12-31收稿), 百拇医药