脂质过氧化诱导培养的内皮细胞表达巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α和血管细胞粘附分子1
作者:夏春枝 邓仲端
单位:夏春枝(同济医科大学基础医学院病理学教研室, 湖北省武汉市 430030);邓仲端(同济医科大学基础医学院病理学教研室, 湖北省武汉市 430030)
关键词:内皮, 血管;脂质过氧化;血管细胞粘附分子1;动脉粥样硬化
中国动脉硬化杂志000304[摘 要] 为了解脂质过氧化损伤能否诱导内皮细胞表达巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α和血管细胞粘附分子1 mRNA,将培养的内皮细胞随机分为实验组(在培养液中分别加入1 μmol/L、5 μmol/L及10 μmol/L联胺)和对照组(不加联胺)。用地高辛随机引物标记的人巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α和血管细胞粘附分子1 cDNA探针与各组内皮细胞进行核酸原位杂交。用异硫氰酸胍法提取各组细胞的总RNA,与上述探针进行斑点杂交。原位杂交显示,正常内皮细胞的胞浆和胞核均表达巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α和血管细胞粘附分子1 mRNA,为蓝色颗粒。加联胺后,上述两种细胞因子的表达明显增强(P<0.05),并与所加联胺的浓度呈正相关。斑点杂交显示,1 μmol/L联胺组巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α和血管细胞粘附分子1 mRNA的表达分别为对照组的1.40倍和1.22倍;5 μmol/L联胺组为对照组的1.90倍和1.56倍;10 μmol/L联胺组为对照组的2.50倍和2.04倍,与联胺的浓度呈正相关。结果提示,脂质过氧化可通过刺激内皮细胞产生血管细胞粘附分子1和巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α诱导单核细胞粘附于内皮,并向内皮下间隙迁移,在动脉粥样硬化发生过程中单核细胞的募集可能起重要作用。
, http://www.100md.com
[中图分类号] R392.12 [文献标识码] A
[文章编号] 1007-3949(2000)-03-0202-04
Lipid Peroxidation Induces the Expression of Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1α and Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 in Cultured Human Endothelial Cells
XIA Chun-Zhi,DENG Zhong-Duan
(Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Tongji Medical University, Wuhan 430030, China)
, 百拇医药
ABSTRACT Aim To understand whether lipid peroxidation in endothelial cells (EC) induces the expression of macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α)and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1). Methods The cultured human umbilical vein EC were divided at random into experimental groups (cultured in the media containing 1 μmol/L, 5 μmol/L and 10 μmol/L diamide, respectively) and control group (cultured in standard medium without diamide). The EC of all groups were hybridized, insitu, with the digoxigenin-labeled MIP-1α and VCAM-1 cDNA probes. In addition , the total RNA in EC of all groups extracted by the single-step method, and MIP-1α and VCAM-1 mRNA expression in EC was determined by dot blotting analysis. Results Insitu hybridization showed that both the cytoplasm and nuclei of the normal EC expressed MIP-1α and VCAM-1 mRNA, that were granular blue substances. Diamide induced stronger expression of cytokines in a dose dependent manner. Of which, the expression of MIP-1α and VCAM-1 mRNA in EC in 1 μmol/L diamide group was 1.28- and 1.26-fold, in 5 μmol/L diamide group, 1.87- and 1.54-fold, and in 10 μmol/L diamide group, 2.41- and 2.01-fold as much as that in control group, respectively. The analysis of variance showed that there were significant differences between groups (P<0.05). Dot blotting showed that the expression of MIP-1α and VCAM-1 mRNA in 1 μmol/L diamide group was 1.40- and 1.22-fold, in 5 μmol/L diamide group, 1.90- and 1.56-fold , and in 10 μmol/L diamide group, 2.50- and 2.04-fold as much as that of the control group, and the increased expression of both cytokine mRNA was positively correlated with the diamide concentrations. Conclusions Lipid peroxidation injury might induce adhesion of monocytes to the endothelium and migration into subendothelial space through stimulating EC to produce increased MIP-1α and VCAM-1 and may play an important role in the recruitment of monocytes into the intima in atherogenesis.
, 百拇医药
MeSH Endothelium,Vascular; Lipid Peroxidation; Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1; Atherosclerosis
外周血单核细胞粘附于内皮并迁入内皮下间隙是动脉粥样硬化(atherosclerosis,As)的早期变化。该过程与内皮细胞(endothelial cell, EC)受刺激后分泌增多的某些粘附分子和趋化因子有关。血管细胞粘附分子-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, VCAM-1)是内皮细胞分泌的粘附分子之一,对单核细胞有选择性粘附作用。脂质过氧化与As密切相关,且脂质过氧化损伤后单核细胞粘附于内皮增多,但是否由于内皮细胞脂质过氧化损伤后VCAM-1分泌增多引起尚有待证实。另一方面,同属于C-C型趋化因子家族的巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α(macrophage inflammatory protein-1α,MIP-1α)对单核细胞亦有趋化作用。本实验旨在观察脂质过氧化损伤能否诱导内皮细胞为表达高水平的VCAM-1及MIP-1α,为单核细胞粘附和迁入内膜提供实验依据。
, 百拇医药
1 材料和方法
1.1 人脐静脉内皮细胞培养和分组
将传代培养的人脐静脉内皮细胞株(购自武汉大学中国典型物保藏中心)培养于含10%小牛血清(Gibco公司)的M199培养基(Sigma公司)。将生长在盖玻片表面的细胞随机分成实验组和对照组,实验组再分为三组,分别加入含1 μmol/L、5 μmol/L及10 μmol/L联胺的培养基,对照组不加联胺。培养4 h后,取出盖玻片,固定,-70℃保存备用。
1.2 原位杂交
培养于盖玻片上的各组EC经D-Hanks液洗涤两次后,用4%多聚甲醛(pH 7.4)室温固定20 min,再经D-Hanks液洗两次,逐级乙醇脱水,吹干后置-70℃保存备用。探针标记及原位杂交操作步骤参照德国Boehringer公司的地高辛标记及检测试剂盒的使用说明。人VCAM-1 cDNA探针(由阮秋蓉博士馈赠)和MIP-1 cDNA探针(由黄晓珠博士馈赠)的长度分别为3.03 kb 和0.27 kb。用TJTY-300型全自动分析仪测定细胞内杂交颗粒的平均吸光度值,用SAS软件对各组数据进行方差分析。
, 百拇医药
1.3 斑点杂交
人脐静脉内皮细胞株培养及分组同前。培养4 h后,收获细胞,用异硫氰酸胍法[1]提取细胞总RNA。取每个RNA样本20 μg点样于硝酸纤维素膜上,80℃干烤2 h。将点好样本的硝酸纤维素膜置于杂交袋内,加入少量预杂交液[含5×SSC(1×SSC: 0.15 mol/L NaCl、15 mmol/L枸椽酸钠)、50%去离子甲酰胺、0.1% N-十二烷基肌氨酸、0.02%SDS、1/5体积阻断液],封口。68℃预杂交30 min(摇床摇动),倾去预杂交液,加入含已变性的地高辛标记的MIP-1α和VCAM-1 cDNA探针的杂交液,68℃杂交6 h。杂交膜经洗膜、显色后,用TJTY-300型自动图像分析系统扫描,测定每个斑点积分吸光度值。
2 结 果
2.1 核酸原位杂交
对照组EC的胞浆和胞核均表达MIP-1α mRNA及VCAM-1 mRNA,为蓝色颗粒。MIP-1α mRNA主要分布于胞浆,VCAM-1 mRNA主要分布于胞核。 实验组EC表达的MIP-1α mRNA及VCAM-1 mRNA阳性颗粒均较对照组增多,颜色加深(图1和2,Figure 1 and 2)。实验组EC表达的MIP-1α mRNA及VCAM-1 mRNA水平较对照组高,以10 μmol/L联胺组最为显著,分别是对照组的2.41倍和2.01倍,其次是5 μmol/L联胺组,分别是对照组的1.87倍和1.54倍,1 μmol/L联胺组EC表达的MIP-1α mRNA和VCAM-1 mRNA水平分别为对照组的1.28倍和1.26倍(表1和2, Table 1 and 2)。
, 百拇医药
表1 各组内皮细胞巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α mRNA的表达
Table 1 Expression of MIP-1α mRNA in endothelial cells in different groups (n=20,x ±s) Groups
±s) Groups
Mean absorbance values
Control
0.04901±0.0027
1 μmol/L diamide
0.06287±0.0049a
, 百拇医药 5 μmol/L diamide
0.09122±0.021b
10 μmol/L diamide
0.11769±0.045c
a: P<0.05, compared with control group; b:P<0.05, compared with 1 μmol/L diamide group;c: P<0.05, compared with 5 μmol/L diamide group.表2 各组内皮细胞血管细胞粘附分子1 mRNA的表达
Table 2 Expression of VCAM-1 mRNA in endothelial cells in different groups (n=20,x ±s) Groups
±s) Groups
, 百拇医药
Mean absorbance values
Control
0.12896±0.039
1 μmol/L diamide
0.16294±0.062a
5 μmol/L diamide
0.19882±0.067b
10 μmol/L diamide
0.25991±0.092c
a: P<0.05, compared with control group; b: P<0.05, compared with 1 μmol/L diamide group; c: P<0.05, compared with 5 μmol/L diamide group.
, http://www.100md.com
图1 各组内皮细胞的巨噬细胞炎性蛋白-1α mRNA表达
Figure 1 Expression of MIP-1α mRNA in endothelial cells in different groups (×57). A: control group; B: 1 μmol/L diamide group; C: 5 μmol/L diamide group; D: 10 μmol/L diamide group.
图2 各组内皮细胞的血管细胞粘附分子-1 mRNA表达
Figure 2 Expression of VCAM-1 mRNA in endothelial cells in different groups (×266). A: control group; B: 1 μmol/L diamide group; C: 5 μmol/L diamide group; D: 10 μmol/L diamide group.
, 百拇医药
2.2 斑点杂交
培养的EC不暴露或暴露于联胺后,其RNA与MIP-1α mRNA和VCAM-1 cDNA探针杂交后,均呈现出具有不同积分吸光度的斑点(图3和4,Figure 3 and 4)。EC暴露于1 μmol/L、5 μmol/L及10 μmol/L联胺后,MIP-1α mRNA的表达水平分别为对照组的1.40倍、1.90倍和2.50倍,VCAM-1 mRNA的表达水平分别为对照组的1.22倍、1.56倍和2.04倍(表3和4,Table 3 and 4)。结果提示,联胺可促进EC表达高水平MIP-1α mRNA和VCAM-1 mRNA,且二者的表达均与联胺的浓度成正比。
表3 各组巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α mRNA斑点的吸光度扫描
Table 3 Densitometry scans of the dot blots of MIP-1α mRNA expressed by EC Groups
, 百拇医药
Relative integral absorbance values
Control
10.34
1 μmol/L diamide
14.48
5 μmol/L diamide
19.65
10 μmol/L diamide
25.85
表4 各组血管细胞粘附分子1 mRNA斑点的吸光度扫描
Table 4 Densitometry scans of the dot blots of VCAM-1 mRNA expressed by EC Groups
, http://www.100md.com
Relative integral absorbance values
Control
17.36
1 μmol/L diamide
21.11
5 μmol/L diamide
27.18
10 μmol/L diamide
35.54
图3 不同浓度的联胺对内皮细胞巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α mRNA表达的影响
, http://www.100md.com
Figure 3 The effects of diamide at different concentrations on the expression of MIP-1α mRNA by EC. A: control group; B: 1 μmol/L diamide group; C: 5 μmol/L diamide group; D: 10 μmol/L diamide group.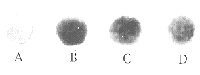
图4 不同浓度的联胺对内皮细胞血管细胞粘附分子1 mRNA表达的影响
Figure 4 The effects of diamide at different concentrations on the expression of VCAM-1 mRNA by EC. A: control group; B: 1 μmol/L diamide group; C: 5 μmol/L diamide group; D: 10 μmol/L diamide group.
, 百拇医药
3 讨 论
众所周知,外周血单核细胞粘附于内皮并迁入内皮下间隙,转变为巨噬细胞,继而摄取氧化脂蛋白变为泡沫细胞是As的早期病变之一。近年来,As发病机制的炎症观点又重新被强调,白细胞的游出与动脉壁细胞分泌的粘附分子和趋化因子密切相关,内皮细胞分泌的粘附分子中,VCAM-1对As病变的形成和发展有重要作用[2]。因为第一,VCAM-1的配体 VLA-4仅在单核细胞和淋巴细胞表面表达,VCAM-1对单核细胞有选择性粘附作用[3]。第二,As早期病变区的内皮细胞表达VCAM-1[2],粘附于内皮的单核细胞受到动脉壁细胞分泌的趋化因子的作用而向内膜下迁移,以前的研究几乎将单核细胞的迁移都归功于甲基受体趋化蛋白(methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein, MCP-1)的趋化作用[4]。目前已有报道,在As斑块中单核/巨噬细胞表达CC型趋化因子(MCP-1、MCP-4、MIP-1α、MIP-1α 及RANTES),在人体As斑块中,T细胞表达 MIP-1α和MIP-1β[5] 。我们也曾观察到食饵性兔主动脉As斑块内巨噬细胞源性及肌源性泡沫细胞及斑块表面的EC表达MIP-1α(另文发表)。然而,对MIP-1在As发生中的作用仍然知之甚少。 脂质过氧化是一种氧自由基介导的细胞损伤机制[6],与As密切相关[7]。洪伟等[7]报道,联胺可诱导内皮细胞脂质过氧化损伤,并且联胺作用后,单核细胞粘附于内皮增多,表明脂质过氧化可诱导 内皮细胞产生一些粘附分子。本研究表明,正常的内皮细胞可表达VCAM-1,一定浓度的联胺引起脂质过氧化损伤后,内皮细胞的VCAM-1表达增强,并且在所加联胺浓度不致引起内皮细胞剥脱性损伤的情况下,VCAM-1的表达与所加联胺浓度呈正比。表明脂质过氧化损伤后单核细胞粘附于内皮增多与内皮细胞的VCAM-1的表达增多有关,但其机制尚未明了。据认为脂质过氧化可能通过激活NF-κB而促进内皮细胞VCAM-1表达增多,进而促进单核细胞附于内皮[8]。Uguccioni等[9]用钙离子脱敏实验证明,人单核细胞表面至少有两种不同的C-C型趋化因子受体,其中一个识别MCP-1(R1), 另一个除识别MIP-1α、MIP-1β、RANTES及MCP-3外,与MCP-1亦有一定的亲合力。并且证明,MIP-1α对单核细胞有趋化作用,尽管其趋化作用弱于RANTES和MCP-1。本研究表明,内皮细胞产生的MIP-1α对单核细胞的迁移有一定作用。总之,我们认为,脂质过氧化损伤所致内皮细胞VCAM-1和MIP-1α表达增强,在动脉粥样硬化病变形成中有重要的意义。
, 百拇医药
[基金项目] 国家自然科学基金资助项目(项目编号 39730220)
[作者简介] 夏春枝,女,1969年12月出生,医学博士研究生。邓仲端,男,1927年10月出生,病理学教授,博士研究生导师,是本文的通讯联系人。
参考文献
[1] Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction [J]. Anal Biochem, 1987, 162 (1): 156-159
[2] 张新超. 细胞粘附分子在动脉粥样硬化发生发展中的作用 [J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 1999, 7 (2): 6179-184
, http://www.100md.com
[3] Carlos TN, Kovach B, Schwartz M, et al. Human monocytes bind to two cytokine-induced adhesive ligands on cultured human endothelial cells: endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 [J]. Blood, 1991, 77 (10): 2 266-271
[4] Cushing SD, Berliner JA, Valente AJ. Minimally modified low density lipoprotein induces monocyte chemotactic protein 1 in human endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1990, 87 (13): 5 134-138
, http://www.100md.com
[5] Reape TJ, Groot PHE. Chemokines and atherosclerosis [J]. Atherosclerosis, 1999, 147 (2 ): 213-225
[6] Cheeseman KM. Mechanisms and effects of lipid peroxidation [J]. Molec Aspects Med, 1993, 14 (3): 191-197
[7] 洪 伟, 陈铁镇. 内皮细胞脂质过氧化损伤与单核细胞内皮下穿入 [J]. 中国医科大学学报, 1994, 23 (3): 189-193
[8] Marui N, Offermann MK, Swertick R, et al. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) gene transcription and expression are regulated through an antioxidant-sensitive mechanism in human vascular endothelial cells [J]. J Clin Invest, 1993, 92 (4): 1 866-874
[9] Uguccioni M, D'Apuzzo M, Loetscher M, et al. Actions of the chemotactic cytokines MCP-1, MCP-2, MCP-3, RANTES, MIP-1α and MIP-1β on human monocytes [J]. Eur J Immunol, 1995, 25 (1): 64-68
(此文2000-01-10收到,2000-07-15修回), http://www.100md.com
单位:夏春枝(同济医科大学基础医学院病理学教研室, 湖北省武汉市 430030);邓仲端(同济医科大学基础医学院病理学教研室, 湖北省武汉市 430030)
关键词:内皮, 血管;脂质过氧化;血管细胞粘附分子1;动脉粥样硬化
中国动脉硬化杂志000304[摘 要] 为了解脂质过氧化损伤能否诱导内皮细胞表达巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α和血管细胞粘附分子1 mRNA,将培养的内皮细胞随机分为实验组(在培养液中分别加入1 μmol/L、5 μmol/L及10 μmol/L联胺)和对照组(不加联胺)。用地高辛随机引物标记的人巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α和血管细胞粘附分子1 cDNA探针与各组内皮细胞进行核酸原位杂交。用异硫氰酸胍法提取各组细胞的总RNA,与上述探针进行斑点杂交。原位杂交显示,正常内皮细胞的胞浆和胞核均表达巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α和血管细胞粘附分子1 mRNA,为蓝色颗粒。加联胺后,上述两种细胞因子的表达明显增强(P<0.05),并与所加联胺的浓度呈正相关。斑点杂交显示,1 μmol/L联胺组巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α和血管细胞粘附分子1 mRNA的表达分别为对照组的1.40倍和1.22倍;5 μmol/L联胺组为对照组的1.90倍和1.56倍;10 μmol/L联胺组为对照组的2.50倍和2.04倍,与联胺的浓度呈正相关。结果提示,脂质过氧化可通过刺激内皮细胞产生血管细胞粘附分子1和巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α诱导单核细胞粘附于内皮,并向内皮下间隙迁移,在动脉粥样硬化发生过程中单核细胞的募集可能起重要作用。
, http://www.100md.com
[中图分类号] R392.12 [文献标识码] A
[文章编号] 1007-3949(2000)-03-0202-04
Lipid Peroxidation Induces the Expression of Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1α and Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 in Cultured Human Endothelial Cells
XIA Chun-Zhi,DENG Zhong-Duan
(Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Tongji Medical University, Wuhan 430030, China)
, 百拇医药
ABSTRACT Aim To understand whether lipid peroxidation in endothelial cells (EC) induces the expression of macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α)and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1). Methods The cultured human umbilical vein EC were divided at random into experimental groups (cultured in the media containing 1 μmol/L, 5 μmol/L and 10 μmol/L diamide, respectively) and control group (cultured in standard medium without diamide). The EC of all groups were hybridized, insitu, with the digoxigenin-labeled MIP-1α and VCAM-1 cDNA probes. In addition , the total RNA in EC of all groups extracted by the single-step method, and MIP-1α and VCAM-1 mRNA expression in EC was determined by dot blotting analysis. Results Insitu hybridization showed that both the cytoplasm and nuclei of the normal EC expressed MIP-1α and VCAM-1 mRNA, that were granular blue substances. Diamide induced stronger expression of cytokines in a dose dependent manner. Of which, the expression of MIP-1α and VCAM-1 mRNA in EC in 1 μmol/L diamide group was 1.28- and 1.26-fold, in 5 μmol/L diamide group, 1.87- and 1.54-fold, and in 10 μmol/L diamide group, 2.41- and 2.01-fold as much as that in control group, respectively. The analysis of variance showed that there were significant differences between groups (P<0.05). Dot blotting showed that the expression of MIP-1α and VCAM-1 mRNA in 1 μmol/L diamide group was 1.40- and 1.22-fold, in 5 μmol/L diamide group, 1.90- and 1.56-fold , and in 10 μmol/L diamide group, 2.50- and 2.04-fold as much as that of the control group, and the increased expression of both cytokine mRNA was positively correlated with the diamide concentrations. Conclusions Lipid peroxidation injury might induce adhesion of monocytes to the endothelium and migration into subendothelial space through stimulating EC to produce increased MIP-1α and VCAM-1 and may play an important role in the recruitment of monocytes into the intima in atherogenesis.
, 百拇医药
MeSH Endothelium,Vascular; Lipid Peroxidation; Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1; Atherosclerosis
外周血单核细胞粘附于内皮并迁入内皮下间隙是动脉粥样硬化(atherosclerosis,As)的早期变化。该过程与内皮细胞(endothelial cell, EC)受刺激后分泌增多的某些粘附分子和趋化因子有关。血管细胞粘附分子-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, VCAM-1)是内皮细胞分泌的粘附分子之一,对单核细胞有选择性粘附作用。脂质过氧化与As密切相关,且脂质过氧化损伤后单核细胞粘附于内皮增多,但是否由于内皮细胞脂质过氧化损伤后VCAM-1分泌增多引起尚有待证实。另一方面,同属于C-C型趋化因子家族的巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α(macrophage inflammatory protein-1α,MIP-1α)对单核细胞亦有趋化作用。本实验旨在观察脂质过氧化损伤能否诱导内皮细胞为表达高水平的VCAM-1及MIP-1α,为单核细胞粘附和迁入内膜提供实验依据。
, 百拇医药
1 材料和方法
1.1 人脐静脉内皮细胞培养和分组
将传代培养的人脐静脉内皮细胞株(购自武汉大学中国典型物保藏中心)培养于含10%小牛血清(Gibco公司)的M199培养基(Sigma公司)。将生长在盖玻片表面的细胞随机分成实验组和对照组,实验组再分为三组,分别加入含1 μmol/L、5 μmol/L及10 μmol/L联胺的培养基,对照组不加联胺。培养4 h后,取出盖玻片,固定,-70℃保存备用。
1.2 原位杂交
培养于盖玻片上的各组EC经D-Hanks液洗涤两次后,用4%多聚甲醛(pH 7.4)室温固定20 min,再经D-Hanks液洗两次,逐级乙醇脱水,吹干后置-70℃保存备用。探针标记及原位杂交操作步骤参照德国Boehringer公司的地高辛标记及检测试剂盒的使用说明。人VCAM-1 cDNA探针(由阮秋蓉博士馈赠)和MIP-1 cDNA探针(由黄晓珠博士馈赠)的长度分别为3.03 kb 和0.27 kb。用TJTY-300型全自动分析仪测定细胞内杂交颗粒的平均吸光度值,用SAS软件对各组数据进行方差分析。
, 百拇医药
1.3 斑点杂交
人脐静脉内皮细胞株培养及分组同前。培养4 h后,收获细胞,用异硫氰酸胍法[1]提取细胞总RNA。取每个RNA样本20 μg点样于硝酸纤维素膜上,80℃干烤2 h。将点好样本的硝酸纤维素膜置于杂交袋内,加入少量预杂交液[含5×SSC(1×SSC: 0.15 mol/L NaCl、15 mmol/L枸椽酸钠)、50%去离子甲酰胺、0.1% N-十二烷基肌氨酸、0.02%SDS、1/5体积阻断液],封口。68℃预杂交30 min(摇床摇动),倾去预杂交液,加入含已变性的地高辛标记的MIP-1α和VCAM-1 cDNA探针的杂交液,68℃杂交6 h。杂交膜经洗膜、显色后,用TJTY-300型自动图像分析系统扫描,测定每个斑点积分吸光度值。
2 结 果
2.1 核酸原位杂交
对照组EC的胞浆和胞核均表达MIP-1α mRNA及VCAM-1 mRNA,为蓝色颗粒。MIP-1α mRNA主要分布于胞浆,VCAM-1 mRNA主要分布于胞核。 实验组EC表达的MIP-1α mRNA及VCAM-1 mRNA阳性颗粒均较对照组增多,颜色加深(图1和2,Figure 1 and 2)。实验组EC表达的MIP-1α mRNA及VCAM-1 mRNA水平较对照组高,以10 μmol/L联胺组最为显著,分别是对照组的2.41倍和2.01倍,其次是5 μmol/L联胺组,分别是对照组的1.87倍和1.54倍,1 μmol/L联胺组EC表达的MIP-1α mRNA和VCAM-1 mRNA水平分别为对照组的1.28倍和1.26倍(表1和2, Table 1 and 2)。
, 百拇医药
表1 各组内皮细胞巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α mRNA的表达
Table 1 Expression of MIP-1α mRNA in endothelial cells in different groups (n=20,x
 ±s) Groups
±s) GroupsMean absorbance values
Control
0.04901±0.0027
1 μmol/L diamide
0.06287±0.0049a
, 百拇医药 5 μmol/L diamide
0.09122±0.021b
10 μmol/L diamide
0.11769±0.045c
a: P<0.05, compared with control group; b:P<0.05, compared with 1 μmol/L diamide group;c: P<0.05, compared with 5 μmol/L diamide group.表2 各组内皮细胞血管细胞粘附分子1 mRNA的表达
Table 2 Expression of VCAM-1 mRNA in endothelial cells in different groups (n=20,x
 ±s) Groups
±s) Groups, 百拇医药
Mean absorbance values
Control
0.12896±0.039
1 μmol/L diamide
0.16294±0.062a
5 μmol/L diamide
0.19882±0.067b
10 μmol/L diamide
0.25991±0.092c
a: P<0.05, compared with control group; b: P<0.05, compared with 1 μmol/L diamide group; c: P<0.05, compared with 5 μmol/L diamide group.

, http://www.100md.com
图1 各组内皮细胞的巨噬细胞炎性蛋白-1α mRNA表达
Figure 1 Expression of MIP-1α mRNA in endothelial cells in different groups (×57). A: control group; B: 1 μmol/L diamide group; C: 5 μmol/L diamide group; D: 10 μmol/L diamide group.
图2 各组内皮细胞的血管细胞粘附分子-1 mRNA表达
Figure 2 Expression of VCAM-1 mRNA in endothelial cells in different groups (×266). A: control group; B: 1 μmol/L diamide group; C: 5 μmol/L diamide group; D: 10 μmol/L diamide group.
, 百拇医药
2.2 斑点杂交
培养的EC不暴露或暴露于联胺后,其RNA与MIP-1α mRNA和VCAM-1 cDNA探针杂交后,均呈现出具有不同积分吸光度的斑点(图3和4,Figure 3 and 4)。EC暴露于1 μmol/L、5 μmol/L及10 μmol/L联胺后,MIP-1α mRNA的表达水平分别为对照组的1.40倍、1.90倍和2.50倍,VCAM-1 mRNA的表达水平分别为对照组的1.22倍、1.56倍和2.04倍(表3和4,Table 3 and 4)。结果提示,联胺可促进EC表达高水平MIP-1α mRNA和VCAM-1 mRNA,且二者的表达均与联胺的浓度成正比。
表3 各组巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α mRNA斑点的吸光度扫描
Table 3 Densitometry scans of the dot blots of MIP-1α mRNA expressed by EC Groups
, 百拇医药
Relative integral absorbance values
Control
10.34
1 μmol/L diamide
14.48
5 μmol/L diamide
19.65
10 μmol/L diamide
25.85
表4 各组血管细胞粘附分子1 mRNA斑点的吸光度扫描
Table 4 Densitometry scans of the dot blots of VCAM-1 mRNA expressed by EC Groups
, http://www.100md.com
Relative integral absorbance values
Control
17.36
1 μmol/L diamide
21.11
5 μmol/L diamide
27.18
10 μmol/L diamide
35.54

图3 不同浓度的联胺对内皮细胞巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α mRNA表达的影响
, http://www.100md.com
Figure 3 The effects of diamide at different concentrations on the expression of MIP-1α mRNA by EC. A: control group; B: 1 μmol/L diamide group; C: 5 μmol/L diamide group; D: 10 μmol/L diamide group.

图4 不同浓度的联胺对内皮细胞血管细胞粘附分子1 mRNA表达的影响
Figure 4 The effects of diamide at different concentrations on the expression of VCAM-1 mRNA by EC. A: control group; B: 1 μmol/L diamide group; C: 5 μmol/L diamide group; D: 10 μmol/L diamide group.
, 百拇医药
3 讨 论
众所周知,外周血单核细胞粘附于内皮并迁入内皮下间隙,转变为巨噬细胞,继而摄取氧化脂蛋白变为泡沫细胞是As的早期病变之一。近年来,As发病机制的炎症观点又重新被强调,白细胞的游出与动脉壁细胞分泌的粘附分子和趋化因子密切相关,内皮细胞分泌的粘附分子中,VCAM-1对As病变的形成和发展有重要作用[2]。因为第一,VCAM-1的配体 VLA-4仅在单核细胞和淋巴细胞表面表达,VCAM-1对单核细胞有选择性粘附作用[3]。第二,As早期病变区的内皮细胞表达VCAM-1[2],粘附于内皮的单核细胞受到动脉壁细胞分泌的趋化因子的作用而向内膜下迁移,以前的研究几乎将单核细胞的迁移都归功于甲基受体趋化蛋白(methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein, MCP-1)的趋化作用[4]。目前已有报道,在As斑块中单核/巨噬细胞表达CC型趋化因子(MCP-1、MCP-4、MIP-1α、MIP-1α 及RANTES),在人体As斑块中,T细胞表达 MIP-1α和MIP-1β[5] 。我们也曾观察到食饵性兔主动脉As斑块内巨噬细胞源性及肌源性泡沫细胞及斑块表面的EC表达MIP-1α(另文发表)。然而,对MIP-1在As发生中的作用仍然知之甚少。 脂质过氧化是一种氧自由基介导的细胞损伤机制[6],与As密切相关[7]。洪伟等[7]报道,联胺可诱导内皮细胞脂质过氧化损伤,并且联胺作用后,单核细胞粘附于内皮增多,表明脂质过氧化可诱导 内皮细胞产生一些粘附分子。本研究表明,正常的内皮细胞可表达VCAM-1,一定浓度的联胺引起脂质过氧化损伤后,内皮细胞的VCAM-1表达增强,并且在所加联胺浓度不致引起内皮细胞剥脱性损伤的情况下,VCAM-1的表达与所加联胺浓度呈正比。表明脂质过氧化损伤后单核细胞粘附于内皮增多与内皮细胞的VCAM-1的表达增多有关,但其机制尚未明了。据认为脂质过氧化可能通过激活NF-κB而促进内皮细胞VCAM-1表达增多,进而促进单核细胞附于内皮[8]。Uguccioni等[9]用钙离子脱敏实验证明,人单核细胞表面至少有两种不同的C-C型趋化因子受体,其中一个识别MCP-1(R1), 另一个除识别MIP-1α、MIP-1β、RANTES及MCP-3外,与MCP-1亦有一定的亲合力。并且证明,MIP-1α对单核细胞有趋化作用,尽管其趋化作用弱于RANTES和MCP-1。本研究表明,内皮细胞产生的MIP-1α对单核细胞的迁移有一定作用。总之,我们认为,脂质过氧化损伤所致内皮细胞VCAM-1和MIP-1α表达增强,在动脉粥样硬化病变形成中有重要的意义。
, 百拇医药
[基金项目] 国家自然科学基金资助项目(项目编号 39730220)
[作者简介] 夏春枝,女,1969年12月出生,医学博士研究生。邓仲端,男,1927年10月出生,病理学教授,博士研究生导师,是本文的通讯联系人。
参考文献
[1] Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction [J]. Anal Biochem, 1987, 162 (1): 156-159
[2] 张新超. 细胞粘附分子在动脉粥样硬化发生发展中的作用 [J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 1999, 7 (2): 6179-184
, http://www.100md.com
[3] Carlos TN, Kovach B, Schwartz M, et al. Human monocytes bind to two cytokine-induced adhesive ligands on cultured human endothelial cells: endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 [J]. Blood, 1991, 77 (10): 2 266-271
[4] Cushing SD, Berliner JA, Valente AJ. Minimally modified low density lipoprotein induces monocyte chemotactic protein 1 in human endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1990, 87 (13): 5 134-138
, http://www.100md.com
[5] Reape TJ, Groot PHE. Chemokines and atherosclerosis [J]. Atherosclerosis, 1999, 147 (2 ): 213-225
[6] Cheeseman KM. Mechanisms and effects of lipid peroxidation [J]. Molec Aspects Med, 1993, 14 (3): 191-197
[7] 洪 伟, 陈铁镇. 内皮细胞脂质过氧化损伤与单核细胞内皮下穿入 [J]. 中国医科大学学报, 1994, 23 (3): 189-193
[8] Marui N, Offermann MK, Swertick R, et al. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) gene transcription and expression are regulated through an antioxidant-sensitive mechanism in human vascular endothelial cells [J]. J Clin Invest, 1993, 92 (4): 1 866-874
[9] Uguccioni M, D'Apuzzo M, Loetscher M, et al. Actions of the chemotactic cytokines MCP-1, MCP-2, MCP-3, RANTES, MIP-1α and MIP-1β on human monocytes [J]. Eur J Immunol, 1995, 25 (1): 64-68
(此文2000-01-10收到,2000-07-15修回), http://www.100md.com