孕早期人母-胎免疫耐受机制的研究
作者:蔡琳 李大金 孙晓溪 王明雁
单位:蔡琳(上海医科大学妇产科医院生殖 免疫室,上海 200011);李大金(上海医科大学妇产科医院生殖 免疫室,上海 200011);孙晓溪(上海医科大学妇产科医院生殖 免疫室,上海 200011);王明雁(上海医科大学妇产科医院生殖 免疫室,上海 200011)
关键词:孕早期;滋养细胞;蜕膜;免疫耐受
中国免疫学杂志000410 摘 要 目的:探讨孕早期母胎免疫耐受调节机制。方法 :应用流式细胞仪分析(FACS)蜕膜及孕妇外周血淋巴细胞亚群;采用改进的乳酸脱 氢酶释放试验测定蜕膜淋巴细胞对K562的自然杀伤活性;同时以滋养细胞与蜕膜淋巴 细胞共同培养,研究母体免疫系统对滋养细胞抗原免疫应答状态。结果:蜕膜组织中CD56+NK细胞含量高于孕妇及对照组外周血CD56+细胞比例(P<0.05) ; 蜕膜组织中NK细胞杀伤活性明显低于孕妇及对照组外周血NK细胞杀伤活性(P<0.05); 滋 养细胞抑制母方淋巴细胞增殖反应(P<0.05)。结论:滋养细胞调 低蜕膜淋巴 细胞增殖反应,蜕膜CD56+NK细胞自然杀伤活性受抑制,可能是维持正常妊娠的重要机制 。
, 百拇医药
中国图书分类号 R371-34
Investigation of materno-fetal immunotolerance in human first trimester pregnancy
CAI Lin LI Da-Jin SUN Xiao-Xi
(Lab.for Reproductive Immunology,Ins tiute of Obs/Gyn,Shanghai Medical University,Shanghai 200011)
Abstract Objective:To investigate materno-fetal immunor egulation mechanism in human first trimester pregnancy.Methods:The subsets of decidual lymphocytes and periphera l blood lymphocytes(PBL) were analyzed by FACS test. The proliferative r eaction of a mix ed culture of decidual lymphocytes to trophocytes was investigated in an assay a nalogous to one way mixed lymphocytes reaction.Results:CD 56+ c ells of first trimester decidual were higher than those of PBL from the pregnant women and the healthy fertile women(P<0.05). The NK cytotoxici ty of first trimester decidual is lower than those of PBL from pregnant woman an d control woman (P<0.05). Trophocytes down-regulated the prolif eration of decidual lymphocytes (P<0.05).Conclusion: It is due to the interaction between trophocytes and CD56+ NK-cel ls in decidual that the materno-fetal immunotolerance is maintained.
, 百拇医药
Key words First trimester pregnancy Trophoblast decidual Immunotolerance
正常妊娠,母体对胚胎存在复杂的免疫应答和免疫调节机制。滋养 细胞侵袭 蜕膜化的子宫内膜及其血管形成胎儿胎盘单位,滋养层蜕膜局部的免疫学研究倍受关注。 本 研究分析蜕膜淋巴细胞亚群分布及自然杀伤活性,同时采用类似混合淋巴细胞培养的增殖试 验探讨母胎局部及系统免疫耐受调节机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料 8~12 w龄正常妊娠人流绒毛、蜕膜组织及外周血标本由本院门 诊手术室提供。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 蜕膜淋巴细胞、滋养细胞的分离 肉眼分离新鲜蜕膜及绒毛组织, 无菌操作,用PBS洗 3次,剪碎成直径 1mm大小,用0.25%胰蛋白酶、15 U/ml DNase-1 37℃消化1 h,离心后过100目筛,取细胞悬液进行5%~75% Percoll 非连 续密度梯度离心,收集界面细 胞(滋养细胞:35%~55%;蜕膜淋巴细胞:45%~60%),离心洗涤配成1×106浓度[1 ,2]。
, http://www.100md.com
1.2.2 外周血淋巴细胞的分离 用肝素抗凝的人外周血8~10 ml, 以Hank ’s液2∶1稀释,加至淋巴细胞分离液上,200 r/min离心20 min。收集界面细胞,洗涤离心 配成1×106浓度。
1.2.3 NK细胞杀伤活性测定 采用LDH释放试验测定杀伤效果[3] 。以K562细胞(上海细胞生物所提供)为靶细胞,按效靶比例10∶1加入蜕膜或外周血 淋巴细胞,在96孔培养板上按常规进行,每组均做3复孔。培养22 h后加LDH基质液,显色, 测定光吸收值(A)。
1.2.4 CD56+、CD3+细胞百分含量测定 将蜕膜或外周血淋巴细胞先与 NK、CD3FITC和抗小鼠IgG的FITC 37℃孵育30 min,洗涤后,用美国BECTON DICKINSON流 式细胞仪分析,每个样品含4 000个细胞[4]。
, 百拇医药
1.2.5 类似混合淋巴细胞反应试验(MLR) 滋养细胞作为刺激细胞,蜕膜淋 巴细胞、母方外周血淋巴细胞为反应细胞,调节细胞浓度1×106,各取0.1 ml加入96孔培 养板,每组3复孔(刺激细胞先经50 μg/ml丝裂霉素37℃处理30 min),5% 37℃温箱孵 育5 d,培养结束前18 h加3H-TdR 0.6 mu/孔。收集细胞于净化滤纸片,加闪烁液,置β射 线计数仪测定CPM值[5]。
1.3 统计学处理 测定数据采用均数±标准差(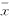 ±s),组间比较采用t检验及配对t检测。
±s),组间比较采用t检验及配对t检测。
2 结果
2.1 流式细胞仪分析蜕膜及外周血淋巴细胞亚群 孕早期蜕膜组织中NK样 细胞比例高于其外周血及对照组外周血比例(P<0.05)。早孕妇女与非孕妇女外周血比较无显著性差异(见表1)。
, 百拇医药
表1 FACS分析淋巴细胞亚群(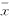 ±s ,%)
±s ,%)
Tab.1 FACE analysis of lymphocyte subsets(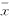 ±s,%) Group
±s,%) Group
Case
CD56+
CD3+
decidual lymphocyte
3
46.08±9.891)
, http://www.100md.com
41.61±2.272)
PBL of pregnant woman
3
16.71±2.19
69.82±13.50
PBL of unpregnant woman
4
14.88±9.11
67.89±5.82
Note:1),2)compared with the other two groups, P<0.052.2 NK细胞杀伤活性的测定 孕早期蜕膜组织NK细胞杀伤活性明显低于 其外周血及对照组外周血NK细胞杀伤活性(P<0.05),孕妇外周血与非孕 妇女外周血无显著性差异(见表2)。
, http://www.100md.com
表2 蜕膜淋巴细胞杀伤活性(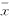 ±s ,%)
±s ,%)
Tab.2 NK cytotoxity of decidual lymphocyte(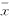 ±s,%) Group
±s,%) Group
Case
cytotoxity
decidual
5
5.14±2.421)
PBL of pregnant woman
, http://www.100md.com
5
123.64±7.11
PBL of unpregnant woman
5
20.34±5.65
Note:1)compared with the other two groups,P<0.052.3 蜕膜淋巴细胞反应性 滋养细胞及母方外周血淋巴细胞不能刺激蜕膜 淋 巴细胞产生增殖反应(P>0.05),父方外周血淋巴细胞能有效刺激蜕膜淋 巴细胞及母方外周血淋巴细胞的增殖(P<0.01);但对后者的刺激强 度明显高于前者(见表3)。
表3 蜕膜淋巴细胞反应性(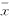 ±s,%)
±s,%)
, 百拇医药
Tab.3 response of decidual lymphocytes (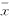 ±s, %) Group
±s, %) Group
Case
CPM
trophocytes(s)/decidual lymohocytes(r)
4
904.77±790.20
maternal PBL(s)/decidual lymohocytes(r)
4
595.60±385.21
, 百拇医药
fartherly PBL(s)/decidual lymohocytes(r)
4
7700±13711)
fartherly PBL(s)/maternal PBL
3
12791±5802)
decidual lymohocytes(control)
3
620.40±73.27
Note:s.stands for stimulating,r.stands for responsive cells,PBL.stands fo r peripheral blood lymphocytes.1),2)compared with decidual lymphocytes control, P<0.012.4 滋养细胞抗原刺激性 滋养细胞不能有效刺激父方淋巴细胞增殖反应( P>0.05),对母方外周血淋巴细胞则抑制其增殖反应(P<0.05)(见表4)。
, 百拇医药
表4 滋养细胞抗原刺激性 (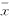 ±s,%)
±s,%)
Tab.4 antigenicity of trophocytes (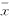 ±s,%) Group
±s,%) Group
Case
CPM
trophocytes(s)/matemal PBL(r)
3
1018.67±907.081)
trophcytes(s)/fartherly PBL(r)
, 百拇医药
3
3410.29±1597.16
matemal PBL(control)
3
3736.40±938.62
fartherly PBL(control)
3
4148.00±1007.50
Note:s.stands for stimulating cells,r.stands for responsive cells. PBL.stands for peripheral blood lymphocytes;1)compared with maternal PBL contr ol, P<0.05
, 百拇医药
3 讨论
3.1 早孕蜕膜CD56+NK样细胞自然活性 本研究采用FACS分析妊娠早期 蜕膜局部和外周血CD3+和CD56+细胞亚群分布情况,结果与有关文献报道基本一致:孕早期蜕膜局部淋巴细胞以CD56+细胞为主,而外周血以CD 3+细胞为主。提示蜕膜局部聚集的CD56+NK细胞可能在母胎免疫调节中起重要作用 。蜕膜局部与外周血细胞自然杀伤性的比较,前者明显低于后者,与King等人试验结果一致 。蜕膜局部自然杀伤活性被抑制,可能是维持正常母胎界面免疫耐受的机制之一[6,7]。
3.2 滋养细胞-蜕膜淋巴细胞混合淋巴细胞反应 本研究发现滋养细胞对蜕膜淋巴细胞和母方外周血淋巴细胞体外实验不具抗原刺激性,因此 ,母体在全身和蜕膜局部不存在针对滋养层细胞的经典免疫应答,此与King等人研究一致 [5,8]。滋养细胞抑制母方外周血淋巴细胞的增殖反应,可能因为滋养细胞提供了降 调节信号,推测与滋养细胞表面表达的限制性HLA-G有关[9]。体外培养,母方外 周血淋巴细胞再度接触滋养细胞抗原产生对抗原不敏感状态;而父方未接触过胚胎抗原,表 现为滋养细胞不刺激也不抑制其增殖反应。
, http://www.100md.com
蜕膜淋巴细胞对父方外周血淋巴细胞的反应性远低于母方外周血淋巴细胞的增殖反应,此项 结果与King[5],Mincheva和Deniz等一致[10,11]。推测蜕膜淋 巴细胞类似其他粘膜上皮细胞,如小肠,同种抗原信号不能刺激免疫活性细胞克隆增殖。其 机制可能是克隆无反应性或者抑制作用被活化。蜕膜淋巴细胞低反应还可能与γδ+T细胞 表面TCR/CD3复合物低表达有关[10,12]。滋养细胞与蜕膜淋巴细胞之间复杂的 相互作用,可能是胎儿免受母体免疫攻击的重要机制。
作者简介:蔡琳,女,26岁,硕士,住院医师,现在上海市第六人民医院工作
李大金 通讯作者,43岁,教授,博士导师,主要从事生殖免疫等研究
4 参考文献
1,Shimonovitz S,Yagel S,Anteby E et al. Interleukin-1 stim ulates prostaglandin E production by Human trophoblast cells from first and thir d trimesters.J Clin Endocrino Metab,1995;80:1641
, 百拇医药
2,Fiedl P L,Romero J R,Ramirez M et al. Interleukin-1 receptor a nt agonist(IL-lra)production by human amnion,chorion,and decidua. Am J Reprod Immu nol,1995;32:1
3,徐根林,胡延仪,罗丽萍 et al.人外周血天然杀伤细胞活性的测定方法 .中华劳动卫生职业病杂志,1991;9(3):173
4,Hoffman R A,Kung P C,Hansen W P. Goldstein simple and rapid measureme nt of hum an T lymphocytes and their subclasses in peripheral blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci US A,1980;77:4914
, 百拇医药
5,King A,Gardner L,Loke Y W.Human decidual leukocytes do not proliferate in r e sponse to eigher extravillous trophoblast or allogeneic peripheral blood lymphoc ytes.J Reprod Immunol,1996;30:67
6,King A,Birkby C,Loke Y W.Early human decidual cells exhibit NK activity aga i nst the K562 cell line but not against first trimester trophoblast. Cell I mmunol,1989;118:337
7,Manaseki S, Searle R F. Natural killer(NK) cell activity of first trimester human decidua. Cell Immunol,1989;12:166
, 百拇医药
8,Loke Y W,King A,Tanya D B. Decidua in human implantation.Human Reproduction ,1995;suppl 2:15
9,Pazmang L,Mandelboim O,Vales G M. Protection from natural killer cell-medi ated lysis by HLA-G expression on target cell.Science,1996;274:792
10,Mincheva N L, Hammarstrom S,Hammarstrom M L. Human decidual leukocyt es from early pregnancy contain high numbers of γδ+ cells and show selective d own-regulation of alloreactivity. J Immunol,1992;149:2203
, 百拇医药
11,Deniz G,Christmas S E,Brow R et al.PHenotypic and functional c e llular differences between human CD3- decidual and peripheral blood lymphoct es. J Immunol,1994;152:4255
12,Heyborne K D,Cranfill R L, Carding S R et al. Character ization of γδ T lymphocytes at the maternal-fetal interface.J Immunol,1992;149:2872
[收稿1998-12-12 修回1999-06-10], 百拇医药
单位:蔡琳(上海医科大学妇产科医院生殖 免疫室,上海 200011);李大金(上海医科大学妇产科医院生殖 免疫室,上海 200011);孙晓溪(上海医科大学妇产科医院生殖 免疫室,上海 200011);王明雁(上海医科大学妇产科医院生殖 免疫室,上海 200011)
关键词:孕早期;滋养细胞;蜕膜;免疫耐受
中国免疫学杂志000410 摘 要 目的:探讨孕早期母胎免疫耐受调节机制。方法 :应用流式细胞仪分析(FACS)蜕膜及孕妇外周血淋巴细胞亚群;采用改进的乳酸脱 氢酶释放试验测定蜕膜淋巴细胞对K562的自然杀伤活性;同时以滋养细胞与蜕膜淋巴 细胞共同培养,研究母体免疫系统对滋养细胞抗原免疫应答状态。结果:蜕膜组织中CD56+NK细胞含量高于孕妇及对照组外周血CD56+细胞比例(P<0.05) ; 蜕膜组织中NK细胞杀伤活性明显低于孕妇及对照组外周血NK细胞杀伤活性(P<0.05); 滋 养细胞抑制母方淋巴细胞增殖反应(P<0.05)。结论:滋养细胞调 低蜕膜淋巴 细胞增殖反应,蜕膜CD56+NK细胞自然杀伤活性受抑制,可能是维持正常妊娠的重要机制 。
, 百拇医药
中国图书分类号 R371-34
Investigation of materno-fetal immunotolerance in human first trimester pregnancy
CAI Lin LI Da-Jin SUN Xiao-Xi
(Lab.for Reproductive Immunology,Ins tiute of Obs/Gyn,Shanghai Medical University,Shanghai 200011)
Abstract Objective:To investigate materno-fetal immunor egulation mechanism in human first trimester pregnancy.Methods:The subsets of decidual lymphocytes and periphera l blood lymphocytes(PBL) were analyzed by FACS test. The proliferative r eaction of a mix ed culture of decidual lymphocytes to trophocytes was investigated in an assay a nalogous to one way mixed lymphocytes reaction.Results:CD 56+ c ells of first trimester decidual were higher than those of PBL from the pregnant women and the healthy fertile women(P<0.05). The NK cytotoxici ty of first trimester decidual is lower than those of PBL from pregnant woman an d control woman (P<0.05). Trophocytes down-regulated the prolif eration of decidual lymphocytes (P<0.05).Conclusion: It is due to the interaction between trophocytes and CD56+ NK-cel ls in decidual that the materno-fetal immunotolerance is maintained.
, 百拇医药
Key words First trimester pregnancy Trophoblast decidual Immunotolerance
正常妊娠,母体对胚胎存在复杂的免疫应答和免疫调节机制。滋养 细胞侵袭 蜕膜化的子宫内膜及其血管形成胎儿胎盘单位,滋养层蜕膜局部的免疫学研究倍受关注。 本 研究分析蜕膜淋巴细胞亚群分布及自然杀伤活性,同时采用类似混合淋巴细胞培养的增殖试 验探讨母胎局部及系统免疫耐受调节机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料 8~12 w龄正常妊娠人流绒毛、蜕膜组织及外周血标本由本院门 诊手术室提供。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 蜕膜淋巴细胞、滋养细胞的分离 肉眼分离新鲜蜕膜及绒毛组织, 无菌操作,用PBS洗 3次,剪碎成直径 1mm大小,用0.25%胰蛋白酶、15 U/ml DNase-1 37℃消化1 h,离心后过100目筛,取细胞悬液进行5%~75% Percoll 非连 续密度梯度离心,收集界面细 胞(滋养细胞:35%~55%;蜕膜淋巴细胞:45%~60%),离心洗涤配成1×106浓度[1 ,2]。
, http://www.100md.com
1.2.2 外周血淋巴细胞的分离 用肝素抗凝的人外周血8~10 ml, 以Hank ’s液2∶1稀释,加至淋巴细胞分离液上,200 r/min离心20 min。收集界面细胞,洗涤离心 配成1×106浓度。
1.2.3 NK细胞杀伤活性测定 采用LDH释放试验测定杀伤效果[3] 。以K562细胞(上海细胞生物所提供)为靶细胞,按效靶比例10∶1加入蜕膜或外周血 淋巴细胞,在96孔培养板上按常规进行,每组均做3复孔。培养22 h后加LDH基质液,显色, 测定光吸收值(A)。

1.2.4 CD56+、CD3+细胞百分含量测定 将蜕膜或外周血淋巴细胞先与 NK、CD3FITC和抗小鼠IgG的FITC 37℃孵育30 min,洗涤后,用美国BECTON DICKINSON流 式细胞仪分析,每个样品含4 000个细胞[4]。
, 百拇医药
1.2.5 类似混合淋巴细胞反应试验(MLR) 滋养细胞作为刺激细胞,蜕膜淋 巴细胞、母方外周血淋巴细胞为反应细胞,调节细胞浓度1×106,各取0.1 ml加入96孔培 养板,每组3复孔(刺激细胞先经50 μg/ml丝裂霉素37℃处理30 min),5% 37℃温箱孵 育5 d,培养结束前18 h加3H-TdR 0.6 mu/孔。收集细胞于净化滤纸片,加闪烁液,置β射 线计数仪测定CPM值[5]。
1.3 统计学处理 测定数据采用均数±标准差(
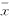 ±s),组间比较采用t检验及配对t检测。
±s),组间比较采用t检验及配对t检测。2 结果
2.1 流式细胞仪分析蜕膜及外周血淋巴细胞亚群 孕早期蜕膜组织中NK样 细胞比例高于其外周血及对照组外周血比例(P<0.05)。早孕妇女与非孕妇女外周血比较无显著性差异(见表1)。
, 百拇医药
表1 FACS分析淋巴细胞亚群(
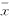 ±s ,%)
±s ,%)Tab.1 FACE analysis of lymphocyte subsets(
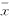 ±s,%) Group
±s,%) GroupCase
CD56+
CD3+
decidual lymphocyte
3
46.08±9.891)
, http://www.100md.com
41.61±2.272)
PBL of pregnant woman
3
16.71±2.19
69.82±13.50
PBL of unpregnant woman
4
14.88±9.11
67.89±5.82
Note:1),2)compared with the other two groups, P<0.052.2 NK细胞杀伤活性的测定 孕早期蜕膜组织NK细胞杀伤活性明显低于 其外周血及对照组外周血NK细胞杀伤活性(P<0.05),孕妇外周血与非孕 妇女外周血无显著性差异(见表2)。
, http://www.100md.com
表2 蜕膜淋巴细胞杀伤活性(
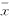 ±s ,%)
±s ,%)Tab.2 NK cytotoxity of decidual lymphocyte(
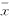 ±s,%) Group
±s,%) GroupCase
cytotoxity
decidual
5
5.14±2.421)
PBL of pregnant woman
, http://www.100md.com
5
123.64±7.11
PBL of unpregnant woman
5
20.34±5.65
Note:1)compared with the other two groups,P<0.052.3 蜕膜淋巴细胞反应性 滋养细胞及母方外周血淋巴细胞不能刺激蜕膜 淋 巴细胞产生增殖反应(P>0.05),父方外周血淋巴细胞能有效刺激蜕膜淋 巴细胞及母方外周血淋巴细胞的增殖(P<0.01);但对后者的刺激强 度明显高于前者(见表3)。
表3 蜕膜淋巴细胞反应性(
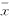 ±s,%)
±s,%), 百拇医药
Tab.3 response of decidual lymphocytes (
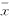 ±s, %) Group
±s, %) GroupCase
CPM
trophocytes(s)/decidual lymohocytes(r)
4
904.77±790.20
maternal PBL(s)/decidual lymohocytes(r)
4
595.60±385.21
, 百拇医药
fartherly PBL(s)/decidual lymohocytes(r)
4
7700±13711)
fartherly PBL(s)/maternal PBL
3
12791±5802)
decidual lymohocytes(control)
3
620.40±73.27
Note:s.stands for stimulating,r.stands for responsive cells,PBL.stands fo r peripheral blood lymphocytes.1),2)compared with decidual lymphocytes control, P<0.012.4 滋养细胞抗原刺激性 滋养细胞不能有效刺激父方淋巴细胞增殖反应( P>0.05),对母方外周血淋巴细胞则抑制其增殖反应(P<0.05)(见表4)。
, 百拇医药
表4 滋养细胞抗原刺激性 (
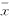 ±s,%)
±s,%)Tab.4 antigenicity of trophocytes (
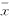 ±s,%) Group
±s,%) GroupCase
CPM
trophocytes(s)/matemal PBL(r)
3
1018.67±907.081)
trophcytes(s)/fartherly PBL(r)
, 百拇医药
3
3410.29±1597.16
matemal PBL(control)
3
3736.40±938.62
fartherly PBL(control)
3
4148.00±1007.50
Note:s.stands for stimulating cells,r.stands for responsive cells. PBL.stands for peripheral blood lymphocytes;1)compared with maternal PBL contr ol, P<0.05
, 百拇医药
3 讨论
3.1 早孕蜕膜CD56+NK样细胞自然活性 本研究采用FACS分析妊娠早期 蜕膜局部和外周血CD3+和CD56+细胞亚群分布情况,结果与有关文献报道基本一致:孕早期蜕膜局部淋巴细胞以CD56+细胞为主,而外周血以CD 3+细胞为主。提示蜕膜局部聚集的CD56+NK细胞可能在母胎免疫调节中起重要作用 。蜕膜局部与外周血细胞自然杀伤性的比较,前者明显低于后者,与King等人试验结果一致 。蜕膜局部自然杀伤活性被抑制,可能是维持正常母胎界面免疫耐受的机制之一[6,7]。
3.2 滋养细胞-蜕膜淋巴细胞混合淋巴细胞反应 本研究发现滋养细胞对蜕膜淋巴细胞和母方外周血淋巴细胞体外实验不具抗原刺激性,因此 ,母体在全身和蜕膜局部不存在针对滋养层细胞的经典免疫应答,此与King等人研究一致 [5,8]。滋养细胞抑制母方外周血淋巴细胞的增殖反应,可能因为滋养细胞提供了降 调节信号,推测与滋养细胞表面表达的限制性HLA-G有关[9]。体外培养,母方外 周血淋巴细胞再度接触滋养细胞抗原产生对抗原不敏感状态;而父方未接触过胚胎抗原,表 现为滋养细胞不刺激也不抑制其增殖反应。
, http://www.100md.com
蜕膜淋巴细胞对父方外周血淋巴细胞的反应性远低于母方外周血淋巴细胞的增殖反应,此项 结果与King[5],Mincheva和Deniz等一致[10,11]。推测蜕膜淋 巴细胞类似其他粘膜上皮细胞,如小肠,同种抗原信号不能刺激免疫活性细胞克隆增殖。其 机制可能是克隆无反应性或者抑制作用被活化。蜕膜淋巴细胞低反应还可能与γδ+T细胞 表面TCR/CD3复合物低表达有关[10,12]。滋养细胞与蜕膜淋巴细胞之间复杂的 相互作用,可能是胎儿免受母体免疫攻击的重要机制。
作者简介:蔡琳,女,26岁,硕士,住院医师,现在上海市第六人民医院工作
李大金 通讯作者,43岁,教授,博士导师,主要从事生殖免疫等研究
4 参考文献
1,Shimonovitz S,Yagel S,Anteby E et al. Interleukin-1 stim ulates prostaglandin E production by Human trophoblast cells from first and thir d trimesters.J Clin Endocrino Metab,1995;80:1641
, 百拇医药
2,Fiedl P L,Romero J R,Ramirez M et al. Interleukin-1 receptor a nt agonist(IL-lra)production by human amnion,chorion,and decidua. Am J Reprod Immu nol,1995;32:1
3,徐根林,胡延仪,罗丽萍 et al.人外周血天然杀伤细胞活性的测定方法 .中华劳动卫生职业病杂志,1991;9(3):173
4,Hoffman R A,Kung P C,Hansen W P. Goldstein simple and rapid measureme nt of hum an T lymphocytes and their subclasses in peripheral blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci US A,1980;77:4914
, 百拇医药
5,King A,Gardner L,Loke Y W.Human decidual leukocytes do not proliferate in r e sponse to eigher extravillous trophoblast or allogeneic peripheral blood lymphoc ytes.J Reprod Immunol,1996;30:67
6,King A,Birkby C,Loke Y W.Early human decidual cells exhibit NK activity aga i nst the K562 cell line but not against first trimester trophoblast. Cell I mmunol,1989;118:337
7,Manaseki S, Searle R F. Natural killer(NK) cell activity of first trimester human decidua. Cell Immunol,1989;12:166
, 百拇医药
8,Loke Y W,King A,Tanya D B. Decidua in human implantation.Human Reproduction ,1995;suppl 2:15
9,Pazmang L,Mandelboim O,Vales G M. Protection from natural killer cell-medi ated lysis by HLA-G expression on target cell.Science,1996;274:792
10,Mincheva N L, Hammarstrom S,Hammarstrom M L. Human decidual leukocyt es from early pregnancy contain high numbers of γδ+ cells and show selective d own-regulation of alloreactivity. J Immunol,1992;149:2203
, 百拇医药
11,Deniz G,Christmas S E,Brow R et al.PHenotypic and functional c e llular differences between human CD3- decidual and peripheral blood lymphoct es. J Immunol,1994;152:4255
12,Heyborne K D,Cranfill R L, Carding S R et al. Character ization of γδ T lymphocytes at the maternal-fetal interface.J Immunol,1992;149:2872
[收稿1998-12-12 修回1999-06-10], 百拇医药