养殖牙鲆淋巴囊肿病病原的研究
作者:徐洪涛 姜忠良 朴春爱 王文兴
单位:徐洪涛 姜忠良(中国科学院海洋研究所,山东 青岛 266071);朴春爱(TAMU,TX77843,USA);王文兴(国家海洋局第一海洋研究所,山东 青岛 266003)
关键词:牙鲆;虹彩病毒;淋巴囊肿病;DNA序列测定
病毒学报000307 摘要:近几年我国海水养殖鱼类发生病毒性传染病,病鱼鳍、鳃及体表皮肤出现乳头瘤样赘生物。将发病牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)表皮瘤组织进行超薄切片,电镜下在病变组织明显肥大的细胞胞浆内发现大量球状病毒,呈二十面体对称,具包膜,直径约210nm。根据虹彩病毒主要衣壳蛋白(major capsid protein,MCP)基因中间保守区序列设计简并引物,应用PCR方法从病变组织中扩增出长636bp的片段。经DNA序列测定及同源性分析表明,该段核苷酸序列与欧洲分离的淋巴囊肿病病毒1型(lymphocystic disease virus type 1,LCDV-1)MCP基因相应序列有77%的同源性,表明该病毒属虹彩病毒科(Iridoviridae)淋巴囊肿病毒属(Lymphocystivirus),但与欧洲分离株有一定差异。将该病毒暂命名为淋巴囊肿病病毒中国分离株(lymphocystis disease virus-Chinese isolate,LCDV-cn)。
, 百拇医药
中图分类号:S852.65+9.1;Q523+.8 文献标识码:A
文章编号:1000-8721(2000)03-0223-04
Study on the Causative Agent of Lymphocystic Disease in Cultured Flounder, Paralichthys Olivaceus, in Mainland China
XU Hong-tao,JIANG Zhong-liang
(Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shandong, Qingdao 266071, China)
PIAO Chun-ai
, 百拇医药
(TAMU, TX 77843, USA)
WANG Wen-xing
(First Institute of Oceanography, National Bureau of Ocean, Shandong, Qingdao 266003, China)
Abstract: Viral epizootic causing papilloma-like lesions on the skin, gill and fin of factory-cultivated flatfish, Paralichthys olivaceus, occurred in mainland China and caused great economic loss in the past few years. Electron microscopy showed large amount of enveloped icosehedral, hexogonal viruses in the cytoplasm of hypertrophied cells. The diameter of the virus averages in 210 nm (side to side) . A pair of degenerate primers based on the conserved sequence of the major capsid protein (MCP) gene of iridovirus amplified a 636bp fragment using DNA extracted from the virus purified from diseased fish tissues as the template. The nucleotide sequence of the amplified fragment showed 77% homology with the corresponding region of the MCP gene of lymphocystic disease virus type 1 (LCDV-1) . Both elcectron microscopy and DNA sequencing results showed that this virus belongs to genus Lymphocystivirus, family Iridoviridae. The virus reported here was named temporally the Chinese flounder isolate of lymphocystic disease virus (LCDV-cn) . This is the first report on the partial DNA sequencing of the MCP gene of piscine iridovirus isolated in mainland China.
, http://www.100md.com
Key words: Paralichthys olivaceus; Iridovirus; lymphocystic disease; DNA sequencing
海水养殖业一直是我国国民经济的支柱产业之一。近几年养殖的牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)、鲈鱼、真鲷、石斑鱼等名贵鱼种发生一种病毒性传染病,病鱼体表呈现乳头瘤样赘生物,感染率在80%以上,死亡率近30%[1,2],严重影响其市场价值,造成重大经济损失。牙鲆是我国工厂化养殖的主要鱼类品种,为查明该病的病原特征,我们对发病牙鲆进行了电镜观察,在病变组织细胞浆内发现虹彩病毒样颗粒。根据虹彩病毒主要衣壳蛋白(major capsid protein,MCP)基因中间保守区序列设计引物,从病变组织中扩增出长为636bp的DNA片段,并进行了序列测定。
材料与方法
1 标本 患病牙鲆于1997年9月10日取自山东荣成邱家养殖场,由国家海洋局第一海洋研究所王文兴教授提供,冻存于-70℃。健康牙鲆为国家海洋局第一海洋研究所存养。
, http://www.100md.com
2 电镜标本制备 取自然发病牙鲆的表皮瘤组织经2.5%戊二醛固定、1%锇酸后固定、乙醇脱水、Epon812树脂包埋后,进行常规超薄切片,醋酸铀染色,透射电镜观察、拍照。
3 病毒分离纯化及基因组DNA提取 病毒纯化参照文献[3-6]的方法并加以改进:取5g表皮瘤组织,于50ml TNE[7]缓冲液中匀浆,3?000r/min离心20min,上清铺于30%蔗糖垫层,25?000r/min(Beckman SW27转子)。4℃离心120min,沉淀用适量TNE缓冲液重悬,上10%~35%氯化铯密度梯度,30?000r/min(Beckman SW40转子)10℃离心24h,取乳白色病毒带对TNE缓冲液4℃透析36h。纯化病毒核衣壳悬液加蛋白酶K及Sarkosyl分别至0.1mg/ml及0.5%,56℃孵育2h,酚、酚:氯仿及氯仿各抽提1次,乙醇沉淀,溶于TE用作PCR反应模板。
4 健康牙鲆表皮组织DNA提取 按文献[7]所述真核细胞基因组DNA提取方法进行,用作PCR反应阴性对照模板。
, 百拇医药
5 PCR扩增反应 简并引物系依据虹彩病毒MCP中间保守区序列[8-11]设计,由中国科学院微生物研究所合成:
正向引物:5′ATGAT(T/C)GG(T/A)AAT(A/G)C(A/T)(A/T)(T/C)T3′
反向引物:5′CA(C/G)CAAA(A/G)AATAATA(T/A)TCA(C/G)(T/A)AC3′
50μl PCR反应混合物内含:引物各50pmol,dNTPs各250μmol/L,MgCl2 1.5mmol/L,Taq DNA聚合酶2U,DNA模板适量。反应在PE-2400热循环仪上进行,循环参数为:94℃变性5min;94℃45s,45℃45s,72℃45s,循环30次;72℃延伸7min。
6 PCR产物克隆及DNA序列测定 PCR产物经纯化后连接到pGEM-T载体(Promega产品),转化致敏菌DH5α,提取质粒DNA。序列测定由宝生物(大连)生物工程有限公司完成。
, http://www.100md.com
7 DNA序列同源性分析 应用Dnasis序列分析软件进行。
结 果
1 发病牙鲆病变特征
在发病牙鲆体表皮肤、鳃、鳍等部位出现灰白色乳头瘤样赘生物,部分肿瘤组织聚集成桑椹状(图1)。严重者赘生物遍布全身,甚至挤出病鱼眼球。病变也可见于咽部、肠系膜、肝、脾和卵巢。
图1 患病牙鲆表皮瘤
Figure 1 Epidermic tumor of diseased Paralichthys olivaceus
2 电子显微镜观察
, http://www.100md.com
病变组织细胞浆内可见大量六角形立体对称病毒颗粒,有包膜,完整毒粒直径约为210nm(边-边),大量毒粒堆积可呈晶格状排列(图2)。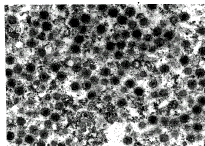
图2 患病牙鲆病变组织超薄切片的电镜照片(×41?340)
Figure 2 Electron micrograph of the tumor tissue from diseased Paralichthys olivaceus(×41,340)
3 PCR扩增产物序列测定
以纯化病毒DNA为模板扩增出长约0.6kb的DNA片段,扩增片段经纯化、克隆和序列测定获得长为636bp的核苷酸序列(图3)。健康牙鲆组织DNA无相应扩增产物。
, http://www.100md.com
4 核苷酸序列同源性分析
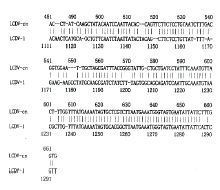
本文报道的病毒(以LCDV-cn表示)基因序列与淋巴囊肿病病毒1型(LCDV-1)MCP基因[9]631~1?266位核苷酸同源性为77%(图4)。
图3 PCR扩增产物DNA序列
划线部分示引物区
Figure3 DNA sequence of the PCR amplification product
The primer regions are underlined.
, 百拇医药
图4 LCDV-cn及LCDV-1 MCP基因部分核苷酸序列同源性分析
Figure 4 Nucleotide homology analysis of partial DNA sequence of MCP gene of LCDV-cn and LCDV-1
讨 论
虹彩病毒科(Iridoviridae)是一组从多种昆虫及脊椎动物宿主中分离到的二十面体对称的胞浆内DNA病毒,分为五个病毒属[12],即:虹彩病毒属(Iridovirus)、绿虹彩病毒属(Chloriridovirus)、蛙病毒属(Ranavirus)、淋巴囊肿病毒属(Lymphocystivirus)和金鱼病毒1型样病毒属(Goldfish virus 1-like viruses)。该科病毒具有独特的形态学特征,病毒呈六角形、二十面体对称,有包膜,在细胞浆内装配。根据本文报道的发病牙鲆病变组织超薄切片的电子显微镜观察结果,该病毒符合上述典型的形态学特征,属虹彩病毒科。尽管仅仅根据形态学特征很容易确定一种病毒是否为虹彩病毒,但不能确定病毒属于何种病毒属,也不能确定从不同宿主或不同地域内的同类宿主中分离的病毒是否为同一种病毒或变异株,本文依据MCP是虹彩病毒的主要结构蛋白,在胞浆内双链DNA病毒,如虹彩病毒、藻类DNA病毒及非洲猪瘟病毒中具有高度保守性,是研究病毒进化及分类的良好对象[11],目前广泛应用于新分离的脊椎动物虹彩病毒的分类鉴定。通过MCP基因序列同源性分析,最近已发现新分离的引起鱼类系统性感染的虹彩病毒属于蛙病毒属。我们根据虹彩病毒MCP基因中间高度保守区设计引物,从国内养殖的发病牙鲆病变组织中扩增出长为636bp的片段,经序列测定及同源性分析表明,其核苷酸序列与欧洲分离的淋巴囊肿病病毒1型(LCDV-1)MCP基因631~1266位核苷酸序列同源性为77%,表明扩增产物确为病毒的基因序列而非非特异性扩增产物。LCDV-1是淋巴囊肿病病毒属的代表株,因此可以确定本文研究的病毒属于淋巴囊肿病病毒属,但与LCDV-1存在差异,是不同的分离株,提示相同病毒在不同地域内的相似宿主中存在变异株。为别于欧洲分离的LCDV-1,暂将其命名为淋巴囊肿病病毒中国分离株(lymphocystic disease virus-Chinese isolate,LCDV-cn)。
, http://www.100md.com
本文对我国养殖牙鲆淋巴囊肿病病毒进行了电子显微镜观察,并测定了其MCP中间保守区636bp的核苷酸序列,不仅明确了该病毒的基本特征,同时表明LCDV-cn与欧洲分离的LCDV-1存在一定差异,说明从不同地域中同类宿主中分离的病毒毒株不同。根据该段DNA序列设计特异性引物,建立了LCDV-cn的PCR检测技术(结果另文报道),可以为国内该病毒病的诊断及检疫提供良好的手段。同时,可以用作DNA探针进行LCDV-cn MCP全基因的克隆及鉴定,进而为研制基因工程疫苗打下基础。
作者简介:徐洪涛(1965-),男,医学博士,研究海洋病毒学。
本文报道的序列已由GenBank发布,录入号BankIt 252036。
参考文献:
[1]周丽,宫庆礼,编著.海水鱼虾蟹贝病害防治技术[M].青岛:青岛海洋大学出版社,1998.
, 百拇医药
[2]孟庄显,俞开康,编著.鱼虾蟹贝疾病诊断和防治[M].北京:中国农业出版社,1996.
[3] Darai G, Anders K, Koch H G, et al. Analysis of the genome of fish lymphocystic disease virus isolated directly from epidermal tumours of pleuronectes [J] . Virology, 1983, 126 (2) : 466-479.
[4] Samalecos C P. Analysis of the structure of fish lymphocystic disease virions from skin tumours of pleuronectes [J] . Arch Virol, 1986, 91 (1-2) : 1-10.
, 百拇医药 [5] Robin J, Berthiaume L. Purification of lymphocystic disease virus (LCDV) grown in tissue culture. Evidences for the presence of two types of viral particles [J] . Rev Can Biol, 1981, 40 (4) : 323-329.
[6] Berthiaume L, Alain R, Robin J. Morphology and ultrastructure of lymphocystisc disease virus, a fish iridovirus, grown in tissue culture [J] . Virology, 1984, 135 (1) : 10-19.
[7] Sambrook J, Fritsch E F, Maniatis T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual [M] . 2nd ed. New York, USA: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989.
, http://www.100md.com
[8] Mao J, Tham T N, Gentry G A, et al. Cloning, sequence analysis and expression of the major capsid protein of the iridovirus frog virus 3 [J] . Virology, 1996, 216 (2) : 431-436.
[9] Schnitzler P, Darai G. Identification of the gene encoding the major capsid protein of fish lymphocystic disease virus [J] . J Gen Virol, 1993, 74 (10) : 2143-2150.
[10] Stohwasser R, Raab K, Schnitzler P, et al. Identification of the gene encoding the major capsid protein of insect iridescent virus type 6 by polymerase chain reaction [J] . J Gen Virol, 1993, 74 (5) : 873-879.
, 百拇医药
[11] Tidona C A, Schnitzler P, Kehm R, et al. Is the major capsid protein of iridoviruses a suitable target for the study of viral evolution [J] ? Virus Genes, 1998, 16 (1) : 59-66.
[12] Murphy F A, Fanquet C M, Bishop D H L, et al. Virus taxonomy, 6th report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses [C]. Arch Virol, 1995, Suppl. 10: 208-239.
[13] Mao J, Hedrick R P. Chinchar V G. Molecular characterization, sequence analysis, and taxonomic position of newly isolated fish iridoviruses [C] . Virology, 1997, 229 (1) : 212-220.
收稿日期:1999-03-03;修回日期:1999-05-11, 百拇医药
单位:徐洪涛 姜忠良(中国科学院海洋研究所,山东 青岛 266071);朴春爱(TAMU,TX77843,USA);王文兴(国家海洋局第一海洋研究所,山东 青岛 266003)
关键词:牙鲆;虹彩病毒;淋巴囊肿病;DNA序列测定
病毒学报000307 摘要:近几年我国海水养殖鱼类发生病毒性传染病,病鱼鳍、鳃及体表皮肤出现乳头瘤样赘生物。将发病牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)表皮瘤组织进行超薄切片,电镜下在病变组织明显肥大的细胞胞浆内发现大量球状病毒,呈二十面体对称,具包膜,直径约210nm。根据虹彩病毒主要衣壳蛋白(major capsid protein,MCP)基因中间保守区序列设计简并引物,应用PCR方法从病变组织中扩增出长636bp的片段。经DNA序列测定及同源性分析表明,该段核苷酸序列与欧洲分离的淋巴囊肿病病毒1型(lymphocystic disease virus type 1,LCDV-1)MCP基因相应序列有77%的同源性,表明该病毒属虹彩病毒科(Iridoviridae)淋巴囊肿病毒属(Lymphocystivirus),但与欧洲分离株有一定差异。将该病毒暂命名为淋巴囊肿病病毒中国分离株(lymphocystis disease virus-Chinese isolate,LCDV-cn)。
, 百拇医药
中图分类号:S852.65+9.1;Q523+.8 文献标识码:A
文章编号:1000-8721(2000)03-0223-04
Study on the Causative Agent of Lymphocystic Disease in Cultured Flounder, Paralichthys Olivaceus, in Mainland China
XU Hong-tao,JIANG Zhong-liang
(Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shandong, Qingdao 266071, China)
PIAO Chun-ai
, 百拇医药
(TAMU, TX 77843, USA)
WANG Wen-xing
(First Institute of Oceanography, National Bureau of Ocean, Shandong, Qingdao 266003, China)
Abstract: Viral epizootic causing papilloma-like lesions on the skin, gill and fin of factory-cultivated flatfish, Paralichthys olivaceus, occurred in mainland China and caused great economic loss in the past few years. Electron microscopy showed large amount of enveloped icosehedral, hexogonal viruses in the cytoplasm of hypertrophied cells. The diameter of the virus averages in 210 nm (side to side) . A pair of degenerate primers based on the conserved sequence of the major capsid protein (MCP) gene of iridovirus amplified a 636bp fragment using DNA extracted from the virus purified from diseased fish tissues as the template. The nucleotide sequence of the amplified fragment showed 77% homology with the corresponding region of the MCP gene of lymphocystic disease virus type 1 (LCDV-1) . Both elcectron microscopy and DNA sequencing results showed that this virus belongs to genus Lymphocystivirus, family Iridoviridae. The virus reported here was named temporally the Chinese flounder isolate of lymphocystic disease virus (LCDV-cn) . This is the first report on the partial DNA sequencing of the MCP gene of piscine iridovirus isolated in mainland China.
, http://www.100md.com
Key words: Paralichthys olivaceus; Iridovirus; lymphocystic disease; DNA sequencing
海水养殖业一直是我国国民经济的支柱产业之一。近几年养殖的牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)、鲈鱼、真鲷、石斑鱼等名贵鱼种发生一种病毒性传染病,病鱼体表呈现乳头瘤样赘生物,感染率在80%以上,死亡率近30%[1,2],严重影响其市场价值,造成重大经济损失。牙鲆是我国工厂化养殖的主要鱼类品种,为查明该病的病原特征,我们对发病牙鲆进行了电镜观察,在病变组织细胞浆内发现虹彩病毒样颗粒。根据虹彩病毒主要衣壳蛋白(major capsid protein,MCP)基因中间保守区序列设计引物,从病变组织中扩增出长为636bp的DNA片段,并进行了序列测定。
材料与方法
1 标本 患病牙鲆于1997年9月10日取自山东荣成邱家养殖场,由国家海洋局第一海洋研究所王文兴教授提供,冻存于-70℃。健康牙鲆为国家海洋局第一海洋研究所存养。
, http://www.100md.com
2 电镜标本制备 取自然发病牙鲆的表皮瘤组织经2.5%戊二醛固定、1%锇酸后固定、乙醇脱水、Epon812树脂包埋后,进行常规超薄切片,醋酸铀染色,透射电镜观察、拍照。
3 病毒分离纯化及基因组DNA提取 病毒纯化参照文献[3-6]的方法并加以改进:取5g表皮瘤组织,于50ml TNE[7]缓冲液中匀浆,3?000r/min离心20min,上清铺于30%蔗糖垫层,25?000r/min(Beckman SW27转子)。4℃离心120min,沉淀用适量TNE缓冲液重悬,上10%~35%氯化铯密度梯度,30?000r/min(Beckman SW40转子)10℃离心24h,取乳白色病毒带对TNE缓冲液4℃透析36h。纯化病毒核衣壳悬液加蛋白酶K及Sarkosyl分别至0.1mg/ml及0.5%,56℃孵育2h,酚、酚:氯仿及氯仿各抽提1次,乙醇沉淀,溶于TE用作PCR反应模板。
4 健康牙鲆表皮组织DNA提取 按文献[7]所述真核细胞基因组DNA提取方法进行,用作PCR反应阴性对照模板。
, 百拇医药
5 PCR扩增反应 简并引物系依据虹彩病毒MCP中间保守区序列[8-11]设计,由中国科学院微生物研究所合成:
正向引物:5′ATGAT(T/C)GG(T/A)AAT(A/G)C(A/T)(A/T)(T/C)T3′
反向引物:5′CA(C/G)CAAA(A/G)AATAATA(T/A)TCA(C/G)(T/A)AC3′
50μl PCR反应混合物内含:引物各50pmol,dNTPs各250μmol/L,MgCl2 1.5mmol/L,Taq DNA聚合酶2U,DNA模板适量。反应在PE-2400热循环仪上进行,循环参数为:94℃变性5min;94℃45s,45℃45s,72℃45s,循环30次;72℃延伸7min。
6 PCR产物克隆及DNA序列测定 PCR产物经纯化后连接到pGEM-T载体(Promega产品),转化致敏菌DH5α,提取质粒DNA。序列测定由宝生物(大连)生物工程有限公司完成。
, http://www.100md.com
7 DNA序列同源性分析 应用Dnasis序列分析软件进行。
结 果
1 发病牙鲆病变特征
在发病牙鲆体表皮肤、鳃、鳍等部位出现灰白色乳头瘤样赘生物,部分肿瘤组织聚集成桑椹状(图1)。严重者赘生物遍布全身,甚至挤出病鱼眼球。病变也可见于咽部、肠系膜、肝、脾和卵巢。

图1 患病牙鲆表皮瘤
Figure 1 Epidermic tumor of diseased Paralichthys olivaceus
2 电子显微镜观察
, http://www.100md.com
病变组织细胞浆内可见大量六角形立体对称病毒颗粒,有包膜,完整毒粒直径约为210nm(边-边),大量毒粒堆积可呈晶格状排列(图2)。

图2 患病牙鲆病变组织超薄切片的电镜照片(×41?340)
Figure 2 Electron micrograph of the tumor tissue from diseased Paralichthys olivaceus(×41,340)
3 PCR扩增产物序列测定
以纯化病毒DNA为模板扩增出长约0.6kb的DNA片段,扩增片段经纯化、克隆和序列测定获得长为636bp的核苷酸序列(图3)。健康牙鲆组织DNA无相应扩增产物。
, http://www.100md.com
4 核苷酸序列同源性分析
本文报道的病毒(以LCDV-cn表示)基因序列与淋巴囊肿病病毒1型(LCDV-1)MCP基因[9]631~1?266位核苷酸同源性为77%(图4)。

图3 PCR扩增产物DNA序列
划线部分示引物区
Figure3 DNA sequence of the PCR amplification product
The primer regions are underlined.


, 百拇医药
图4 LCDV-cn及LCDV-1 MCP基因部分核苷酸序列同源性分析
Figure 4 Nucleotide homology analysis of partial DNA sequence of MCP gene of LCDV-cn and LCDV-1
讨 论
虹彩病毒科(Iridoviridae)是一组从多种昆虫及脊椎动物宿主中分离到的二十面体对称的胞浆内DNA病毒,分为五个病毒属[12],即:虹彩病毒属(Iridovirus)、绿虹彩病毒属(Chloriridovirus)、蛙病毒属(Ranavirus)、淋巴囊肿病毒属(Lymphocystivirus)和金鱼病毒1型样病毒属(Goldfish virus 1-like viruses)。该科病毒具有独特的形态学特征,病毒呈六角形、二十面体对称,有包膜,在细胞浆内装配。根据本文报道的发病牙鲆病变组织超薄切片的电子显微镜观察结果,该病毒符合上述典型的形态学特征,属虹彩病毒科。尽管仅仅根据形态学特征很容易确定一种病毒是否为虹彩病毒,但不能确定病毒属于何种病毒属,也不能确定从不同宿主或不同地域内的同类宿主中分离的病毒是否为同一种病毒或变异株,本文依据MCP是虹彩病毒的主要结构蛋白,在胞浆内双链DNA病毒,如虹彩病毒、藻类DNA病毒及非洲猪瘟病毒中具有高度保守性,是研究病毒进化及分类的良好对象[11],目前广泛应用于新分离的脊椎动物虹彩病毒的分类鉴定。通过MCP基因序列同源性分析,最近已发现新分离的引起鱼类系统性感染的虹彩病毒属于蛙病毒属。我们根据虹彩病毒MCP基因中间高度保守区设计引物,从国内养殖的发病牙鲆病变组织中扩增出长为636bp的片段,经序列测定及同源性分析表明,其核苷酸序列与欧洲分离的淋巴囊肿病病毒1型(LCDV-1)MCP基因631~1266位核苷酸序列同源性为77%,表明扩增产物确为病毒的基因序列而非非特异性扩增产物。LCDV-1是淋巴囊肿病病毒属的代表株,因此可以确定本文研究的病毒属于淋巴囊肿病病毒属,但与LCDV-1存在差异,是不同的分离株,提示相同病毒在不同地域内的相似宿主中存在变异株。为别于欧洲分离的LCDV-1,暂将其命名为淋巴囊肿病病毒中国分离株(lymphocystic disease virus-Chinese isolate,LCDV-cn)。
, http://www.100md.com
本文对我国养殖牙鲆淋巴囊肿病病毒进行了电子显微镜观察,并测定了其MCP中间保守区636bp的核苷酸序列,不仅明确了该病毒的基本特征,同时表明LCDV-cn与欧洲分离的LCDV-1存在一定差异,说明从不同地域中同类宿主中分离的病毒毒株不同。根据该段DNA序列设计特异性引物,建立了LCDV-cn的PCR检测技术(结果另文报道),可以为国内该病毒病的诊断及检疫提供良好的手段。同时,可以用作DNA探针进行LCDV-cn MCP全基因的克隆及鉴定,进而为研制基因工程疫苗打下基础。
作者简介:徐洪涛(1965-),男,医学博士,研究海洋病毒学。
本文报道的序列已由GenBank发布,录入号BankIt 252036。
参考文献:
[1]周丽,宫庆礼,编著.海水鱼虾蟹贝病害防治技术[M].青岛:青岛海洋大学出版社,1998.
, 百拇医药
[2]孟庄显,俞开康,编著.鱼虾蟹贝疾病诊断和防治[M].北京:中国农业出版社,1996.
[3] Darai G, Anders K, Koch H G, et al. Analysis of the genome of fish lymphocystic disease virus isolated directly from epidermal tumours of pleuronectes [J] . Virology, 1983, 126 (2) : 466-479.
[4] Samalecos C P. Analysis of the structure of fish lymphocystic disease virions from skin tumours of pleuronectes [J] . Arch Virol, 1986, 91 (1-2) : 1-10.
, 百拇医药 [5] Robin J, Berthiaume L. Purification of lymphocystic disease virus (LCDV) grown in tissue culture. Evidences for the presence of two types of viral particles [J] . Rev Can Biol, 1981, 40 (4) : 323-329.
[6] Berthiaume L, Alain R, Robin J. Morphology and ultrastructure of lymphocystisc disease virus, a fish iridovirus, grown in tissue culture [J] . Virology, 1984, 135 (1) : 10-19.
[7] Sambrook J, Fritsch E F, Maniatis T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual [M] . 2nd ed. New York, USA: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989.
, http://www.100md.com
[8] Mao J, Tham T N, Gentry G A, et al. Cloning, sequence analysis and expression of the major capsid protein of the iridovirus frog virus 3 [J] . Virology, 1996, 216 (2) : 431-436.
[9] Schnitzler P, Darai G. Identification of the gene encoding the major capsid protein of fish lymphocystic disease virus [J] . J Gen Virol, 1993, 74 (10) : 2143-2150.
[10] Stohwasser R, Raab K, Schnitzler P, et al. Identification of the gene encoding the major capsid protein of insect iridescent virus type 6 by polymerase chain reaction [J] . J Gen Virol, 1993, 74 (5) : 873-879.
, 百拇医药
[11] Tidona C A, Schnitzler P, Kehm R, et al. Is the major capsid protein of iridoviruses a suitable target for the study of viral evolution [J] ? Virus Genes, 1998, 16 (1) : 59-66.
[12] Murphy F A, Fanquet C M, Bishop D H L, et al. Virus taxonomy, 6th report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses [C]. Arch Virol, 1995, Suppl. 10: 208-239.
[13] Mao J, Hedrick R P. Chinchar V G. Molecular characterization, sequence analysis, and taxonomic position of newly isolated fish iridoviruses [C] . Virology, 1997, 229 (1) : 212-220.
收稿日期:1999-03-03;修回日期:1999-05-11, 百拇医药