大鼠中枢运动核团内谷氨酸受体、GABAA受体、甘氨酸受体和阿片μ受体的定位分布
作者:高蓉 李云庆 施际武
单位:高蓉 李云庆 施际武 第四军医大学解剖学教研室、梁琚脑研究中心,西安 710032
关键词:谷氨酸受体;GABAA受体;甘氨酸受体;阿片μ受体;运动核;大鼠
解剖学报990207 【摘要】 目的 观察大鼠中枢运动核团内谷氨酸受体、γ-氨基丁酸受体(GABAAR)、甘氨酸受体(GlyR)和阿片μ受体(MOR)的定位分布,搞清谷氨酸、GABA、甘氨酸和脑啡肽在中枢运动核团内的作用部位。 方法 免疫组织化学染色技术。 结果 在动眼神经核、滑车神经核、三叉神经运动核、展神经核、面神经核、疑核、舌下神经核、E-W核、上涎核、迷走神经背核和脊髓前角内均可见NMDAR1样和GluR2/3样阳性胞体,但NMDAR1样和GluR2/3样阳性纤维和终末仅见于动眼神经核、E-W核、滑车神经核、三叉神经运动核和迷走神经背核,除三叉神经运动核、疑核和脊髓前角能见到少量GABAAR β亚单位样阳性胞体外,上述各核团也可见GABAAR β亚单位样阳性的纤维和终末,而GABAARα亚单位样阳性胞体主要见于疑核、舌下神经核、迷走神经背核和脊髓前角;中枢运动核团内均可见GlyR和MOR样阳性的纤维和终末。 结论 谷氨酸、GABA、甘氨酸和脑啡肽在中枢运动核团可能通过突触前和突触后机制,对中枢运动神经元发挥调控作用。
, 百拇医药
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL LOCALIZATION OF GLUTAMATERECEPTOR,GABAA RECEPTOR,GLYCINE RECEPTORAND μ-OPIOID RECEPTOR IN THE CENTRALMOTOR NUCLEI OF THE RAT
Gao Rong, Li YunqingΔ, Shi Jiwu
(Department of Anatomy,K.K.Leung Brain Research Centre,The Fourth Military Medical University,Xi'an)
【Abstract】 Objective To observe the locations of glutamate receptor(NMDAR1,GluR2/3),GABAA receptor(α and β subunits of GABAAR),glycine receptor(GlyR)and μ-opioid receptor(MOR) in the somatic motor nuclei and parasympathetic motor nuclei of the brainstem and the ventral horn of the spinal cord in the rat and to investigate the binding sites of glutamate,GABA,glycine and enkephalin on the motoneurons of the motor nuclei in the central nervous system(CNS).Methods Immunohistochemical staining method was used in the present study.Results NMDAR1- and GluR2/3-like immunoreactive(LI) neurons were found in the oculomotor nucleus,trochlear nucleus,trigeminal motor nucleus,abducens nucleus,facial nucleus,ambiguus nucleus,hypoglossal nucleus,Edinger- Westphal(E-W) nucleus,superior salivary nucleus,dorsal motor nucleus of vagus and the ventral horn of the spinal cord;but NMDAR1-LI and GluR2/3-LI fibers and terminals were found in oculomotor nucleus,Edinger-Westphal (E-W) nucleus,trochlear nucleus,trigeminal motor nucleus and dorsal motor nucleus of vagus.GABAARβ subunit-LI fibers and terminals could be seen at all of nuclei as mentioned above,in the trigeminal motor nucleus,ambiguus nucleus and ventral horn of the spinal cord,GABAARβ subunit-LI neurons were observed.GABAA R α subunit-LI neurons were mainly encounted in ambiguus nucleus,hypoglossal nucleus,dorsal motor nucleus of vagus and ventral horn of the spinal cord;GlyR-LI and MOR-LI fibers and terminals were observed in all of the central motor nuclei.Conclusion Glutmate,GABA, glycine and enkephalin may regulate the activities of motoneurons in the CNS through the way of presynaptic and/or postsynaptic mechanism.
, 百拇医药
【Key words】 Glutamate receptor; GABAA receptor; Glycine Receptor, μ-Opioid receptor; Immunohistochemistry; Motor nuclei; Rat
氨基酸类神经递质广泛分布于中枢神经系统(CNS)内,在CNS感觉信息传导和完成运动指令等突触传递过程中发挥重要作用,所以研究它们的受体在CNS的作用部位具有重要意义。根据氨基酸类物质对突触后神经元作用的不同,可将它们分为兴奋性及抑制性氨基酸,分别以谷氨酸(Glu)、γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)和甘氨酸(Gly)为代表。中枢运动核团内均有密集的Glu样、GABA样、Gly样和脑啡肽样阳性纤维和终末,这些阳性纤维和终末主要来自脑干的运动前神经元[1~4]。Glu受体(GluR)有代谢型GluR和离子型GluR两种,离子型GluR又可分为NMDA受体和非NMDA受体两种,而非NMDA受体还可进一步分为AMPA受体(GluR1~4)和KA受体(GluR5~7)[5];GABA受体有GABAA受体、GABAB受体和GABAC受体3种类型[6]。大量的研究结果都证明阿片受体(至少包括3种亚型)中的μ亚型不但参与吗啡的镇痛过程,而且对中枢运动神经元的活动具有调控作用[7]。以往的研究对GluR、GABAAR的α和β亚单位、GlyR和MOR在大鼠CNS内的分布已有一些报道[8~11],但尚缺乏关于GluR、GABAAR、GlyR和MOR在运动核团内精确定位分布的系统资料,所以本研究采用免疫组织化学方法观察了NMDAR1、GluR2/3、GABAAR的α和β亚单位、GlyR和MOR在大鼠中枢运动核团内的定位分布。
, 百拇医药
材料和方法
雄性SD大鼠8只,体重200~250g。戊巴比妥钠经腹腔麻醉(40mg/kg),开胸后插管至升主动脉,先以0.9%盐水100ml冲洗血液,再用500ml含4%多聚甲醛和0.2%苦味酸的0.1mol/L磷酸盐缓冲液(PB,pH7.4)灌注固定,持续约45min。取脑及脊髓入上述新鲜固定液中后固定2~4h(4℃),再移入含30%庶糖的PB液中至沉底。恒冷箱切片机冰冻横切脑干及脊髓,片厚30μm。切片隔6张取1张,分7套收集,将第1~6套切片按ABC法行免疫组织化学染色(表1)。在第1抗体和第2抗体中分别孵育18~24h和3~5h,其浓度分别为1∶1 000和1∶200,ABC混合液(1∶50,Vector)中孵育1h后用二甲基联苯胺(DAB)和H2O2呈色。抗体和复合物的稀释均用含0.3% Triton X-100和2%正常羊血清的PBS。孵育均在室温下进行,各步骤之间均用PBS彻底清洗切片。对照试验选择第7套的部分切片,并将其分为6组,除用正常兔血清或小鼠血清代替第1抗体孵育切片外,其余处理同上;将第7套的其他切片行Nissl染色,以便对照观察和定位免疫组织化学的染色结果。
, 百拇医药
免疫组织化学染色阳性结果的评判:(1)阳性神经元的相对密度:为随机选取各运动核200μm2面积内阳性神经元的数量,大量(+++):10~15个;中等量(++):6~10个;少量(+):3~5个;偶见(±):1~2个;阴性-:0。(2)阳性纤维和终末的相对密度:为随机选取各运动核100μm2面积内阳性纤维和终末的数量,大量(+++):10~15根纤维,终末密集;中等量(++):6~10根纤维,终末略少;少量(+):3~5根纤维,终末较少;偶见(±):1~2根纤维,终末稀疏;阴性(-):无纤维和终末。
表1 抗体种类、来源和生产厂家
Table 1 Antibody,host and producer 第1抗体primary antibody
来源
host
, 百拇医药
生产厂家
producer
第2抗体
secondary antibody
生产厂家
producer
N-甲基-D-门冬氨酸受体1型
NMDAR1
兔
rabbit
Chemicon
Biotin-羊抗兔IgG
, 百拇医药
Biotin-Goat Anti-rabbit IgG
Vector
谷氨酸受体2/3型
GluR2/3
兔
rabbit
RBI
Biotin-羊抗兔IgG
Biotin-Goat Anti-rabbit IgG
Vector
γ-氨基丁酸A受体α亚单位
, 百拇医药
GABAARα
小鼠
mouse
Boehringer
Biotin-羊抗小鼠IgG
Biotin-Goat Anti-mouse IgG
Jackson
γ-氨基丁酸A受体β亚单位
GABAARβ
小鼠
mouse
, 百拇医药
Boehringer
Biotin-羊抗小鼠IgG
Biotin-Goat Anti-mouse IgG
Jackson
甘氨酸受体
GlyR
小鼠
mouse
Boehringer
Biotin-羊抗小鼠IgG
Biotin-Coat Anti-mouse IgG
, 百拇医药
Jackson
阿片μ受体
MOR
兔
rabbit
Ding等[11]
Biotin-羊抗兔IgG
Biotin-Goat Anti-rabbit IgG
Vector
结 果
本研究用免疫组织化学方法所染出的几种受体大多位于中枢运动神经元胞体和突起的膜上,但NMDAR1样、GluR2/3样、GABAAR的α和β亚单位样阳性产物也见于胞浆,在大鼠中枢运动核团内未见GlyR样和MOR样阳性神经元胞体,仅见GlyR样和MOR样阳性纤维和终末(图1~8)。GlyR样和MOR样阳性纤维和终末常呈篮状包绕在运动神经元的胞体和突起的周围(图5,8)。中枢运动核团内的NMDAR1样和GABAARα亚单位样阳性神经元常呈强阳性(图1,6,7),而GluR2/3样阳性神经元常略弱(图2,3)。几种受体阳性运动神经元胞体的长径多为≤40μm。对照试验的切片上,均未观察到免疫组织化学阳性染色结果。
, http://www.100md.com
表2 Glu受体、GABAA受体、Gly受体、阿片受体样阳性神经元在中枢运动核团内的分布和相对密度
Table 2 Distribution and relative density of GluR-,GABAAR-,GlyR- and μ-opioid
receptor-like immunoreactive neurons in the central motor nuclei
NMDAR1
GluR2/3
GABAARα
GABAARβ
, 百拇医药
GlyR
MOR
动眼神经核(oculomotor nucleus)
++
++
±
-
-
-
滑车神经核(trochlear nucleus)
++
++
, http://www.100md.com ±
-
-
-
三叉神经运动核(trigeminal motor nucleus)
+++
+++
±
+
-
-
展神经核(abducens nucleus)
++
, 百拇医药
++
±
-
-
-
面神经核(facial nucleus)
++
++
±
-
-
-
疑核(ambiguus nucleus)
, 百拇医药
++
++
++
+
-
-
舌下神经核(hypoglossal nucleus)
+++
+++
+++
-
-
-
, http://www.100md.com
E\|W核(Edinger\|Westphal nucleus)
++
++
±
-
-
-
上涎核(superior salivary nucleus)
++
++
±
-
, 百拇医药
-
-
迷走神经背核(dorsal motor nucleus of vagus)
++
++
++
-
-
-
脊髓前角(ventral horn of spinal cord)
+++
+++
, http://www.100md.com
++
+
-
-
相对密度:-.阴性 ±.偶见 +.少量 ++.中等量 +++.大量
Relative density:-:negative ±:occasionally observed +:low density ++:medium density +++:high density表3 Glu受体、GABAA受体、Gly受体、阿片μ受体样阳性纤维和终末在中枢运动核团内的分布和相对密度
Table 3 Distribution and relative density of GluR-,GABAAR-,GlyR- and μ-opioid
, 百拇医药
receptor-like immunoreactive fibers and terminals in the central motor nuclei
NMDAR1
GluR2/3
GABAARα
GABAARβ
GlyR
MOR
动眼神经核(oculomotor nucleus)
+
+
, 百拇医药
±
+
++
+
滑车神经核(trochlear nucleus)
+
+
±
+
++
+
三叉神经运动核(trigeminal motor nucleus)
, 百拇医药 +
+
±
+
+++
+
展神经核(abducens nucleus)
-
-
±
+
++
+
, http://www.100md.com 面神经核(facial nucleus)
-
-
±
+
+++
++
疑核(ambiguus nucleus)
-
-
±
++
++
, 百拇医药
++
舌下神经核(hypoglossal nucleus)
-
±
+
+
+++
++
E-W核(Edinger-Westphal nucleus)
++
+
±
, http://www.100md.com ++
++
+
上涎核(superior salivary nucleus)
-
±
±
+
+
+
迷走神经背核(dorsal motor nucleus of vagus)
+
, 百拇医药
+
++
+
+
++
脊髓前角(ventral horn of spinal cord)
-
-
±
++
++
+++
相对密度:-~+++同表2 Relative density:-~+++ same as table 2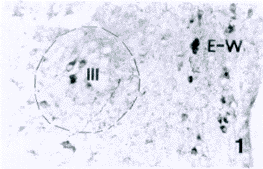
, 百拇医药
图1 示动眼神经核(Ⅲ)和动眼神经副交感核(E-W核)内的NMDAR1样阳性神经元(标尺示80μm,图2~7同)
Fig.1 Showing NMDAR1-like immunoreactive (NMDA1-LI) neurons in the oculomotor nucleus(Ⅲ) and Edinger-Westphal(E-W) nucleus.
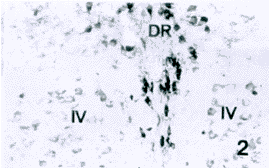
图2 示滑车神经核(Ⅳ)内的GluR2/3样阳性神经元。DR.中缝背核
Fig.2 Showing GluR2/3-LI neurons in the trochlear nucleus (Ⅳ).DR:dorsal raphe nucleus.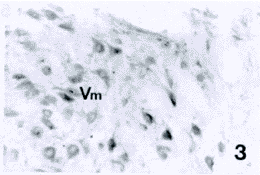
, 百拇医药
图3 示三叉神经运动核(Vm)内的GluR2/3样阳性神经元
Fig.3 Showing GluR2/3-LI neurons in the trigeminal motor nucleus(Vm).
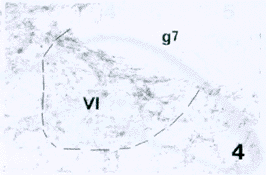
图4 示展神经核(Ⅵ)内的GlyR样阳性纤维和终末。g7.面神经膝
Fig.4 Showing GlyR-LI fibers and terminals in the abducens nucleus(Ⅵ).g7:genu of facial nerve.

图5 示面神经核(Ⅶ)内密集的Gly R样阳性纤维和终末
, 百拇医药
Fig.5 Showing GlyR-LI fibers and terminals in the facial nucleus(Ⅶ).
图6 示疑核(Amb)内的GABAARα样阳性神经元
Fig.6 Showing strong positive GABAARα subunit-LI neurons in the ambiguous(Amb)nucleus.

图7 示迷走神经背核(X)和舌下神经核(Ⅹ Ⅱ)内的GABAAR α样阳性神经元。NTS.孤束核
, 百拇医药 Fig.7 GABAARα subunit-LI neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of vagus(Ⅹ)and hypoglossal nucleus(Ⅹ Ⅱ).NTS:nucleus tractus solitarri.
图8 示颈髓前角内的MOR样阳性纤维和终末
Fig.8 Showing MOR-LI fibers and terminals in the ventral horn of the cervical spinal cord.Bar=80μm for all Figs.1~8.
讨 论
大量的生理学实验都证明谷氨酸(Glu)是对中枢神经元具有兴奋作用的氨基酸之一,Glu作用于突触后受体,可能直接与膜去极化的通路偶联[5]。Glu的两类离子型受体——NMDA受体和非NMD受体(AMPA受体和KA受体)是同一受体-通道复合物的组成部分,主要参与Glu对神经元的兴奋作用。Glu将离子型受体激活后,使Ca2+向细胞内的流动增加和细胞的兴奋性增强,从而产生兴奋性反应,而且是一种河豚毒素不能阻断的快兴奋作用[5]。本研究在大鼠中枢的动眼神经核、滑车神经核、三叉神经运动核、展神经核、面神经核、疑核、舌下神经核、E-W核、上涎核、迷走神经背核和脊髓前角均观察到了NMDAR1样和GluR2/3样阳性的神经元胞体,并在动眼神经核、E-W核、滑车神经核、三叉神经运动核和迷走神经背核分别观察到NMDAR1样和GluR2/3样阳性的纤维和终末,从而说明对离子型受体具有激活作用的Glu是影响上述核团内运动神经元活动的兴奋性递质。
, 百拇医药
GABA和Gly均为典型的抑制性神经递质。GABA和Gly与GABAAR和GlyR结合后,出现短暂的阴离子(Cl-)内向通透性增加,使Cl-在细胞内的浓度上升,导致细胞膜的超极化和兴奋性降低,产生抑制效应[6,12]。本研究观察到GABAARα亚单位样阳性胞体主要见于疑核、舌下神经核、迷走神经背核和脊髓前角;除三叉神经运动核、疑核和迷走神经背核内能见到GABAARβ亚单位样阳性胞体外,中枢运动核团也可见GABAARβ亚单位样阳性纤维和终末;除上涎核和迷走神经背核较稀疏外,较密集的GlyR样阳性纤维和终末见于动眼神经核、滑车神经核、三叉神经运动核、展神经核、面神经核、疑核、舌下神经核、E-W核和脊髓前角;说明GABAAR和GlyR对于GABA和Gly在上述运动核团内不同运动神经元间的功能协调方面,可能扮演着重要的角色。
尽管大量的研究都证明MOR主要参与吗啡的镇痛作用,但也有许多证据表明MOR在躯体运动和内脏活动中具有调控效应[7,13]。向大鼠小脑延髓池内注入大剂量的脑啡肽除抑制心血管活动和呼吸外,还可使运动减少、木僵和肌肉强直。本研究在面神经核、疑核、舌下神经核、迷走神经背核和脊髓前角等与上述躯体运动和内脏活动有关的中枢运动核团内观察到较密集的MOR样阳性纤维和终末,为以往的机能学研究提供了可靠的形态学依据。
, http://www.100md.com
以往的研究观察到阿片类物质对脊髓后角的伤害性感受神经元的抑制存在突触前和突触后两种机制[6,14],阿片类物质还可通过突触前机制在脊髓后角内抑制外周来源的P物质(SP)能终末释放SP[15]。本研究在与躯体运动和内脏活动有关的中枢运动核团内观察到NMDAR1样、GABAAR样、GlyR样和MOR样阳性终末,提示GluR、GABAAR、GlyR和MOR的突触前调控机制在上述运动核团内可能也发挥重要的作用。
国家杰出青年科学基金资助课题(No.39625011)
感谢丁玉强同志提供MOR抗体及张淼丽技师和原悦萍同志在图片制作过程中的帮助。
参考文献
[1]Li YQ,Takada M,Kaneko T,et al.GABAergic and glycinergic neurons projecting to the trigeminal motor nucleus:a double labeling study in the rat.J Comp Neurol,1996,373(3):498
, 百拇医药
[2]Li YQ,Takada M,Kaneko T,et al.Distribution of GABA ergic and glycinergic premotor neurons projecting to the facial and hypoglossal nuclei in the rat.J Comp Neurol,1997,378(2):283
[3]李云庆,王智明,施际武.大鼠脑干向面口部运动核的P物质能和脑啡肽能投射.解剖学报,1999,30(1):11
[4]李云庆,王智明,施际武.大鼠脑干面口部运动神经元与5-HT样、SP样、L-ENK样、GABA样和Gly样阳性终末间的突触联系.解剖学报,1998,29(4):351
[5]Monaghan DT,Bridges RJ,Cotman CW,The excitatory amino acid receptors:their classes,pharmacology,and distinct properties in the function of the central nervous system.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol,1989,29:365
, 百拇医药
[6]Luddens H,Korpi ER,Seeburg PH.GABAA/Benzodiazepine receptor heterogeneity:neurophysiolgical implications.Neuropharmacology,1995,34(2):245
[7]Minami M,Satoh M.Molecular biology of the opioid receptors:structure,functions and distributions.Neurosci Res,1995,23(1):121
[8]李云庆,王智明,施际武.大鼠三叉神经尾侧亚核和脊髓内离子型谷氨酸受体、GABAA受体和甘氨酸受体的分布.解剖学报,1997,28(2):118
[9]Moreno JI,Piva MA,Miralles CP,et al.Immunocytochemical localization of the β2 subunit of the gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor in the rat brain.J Comp Neurol,1994,350(2):260
, 百拇医药
[10]Araki T,Yamano M,Marakami T,et al.Localization of glycine receptors in the rat central nervous system:an immunocytochemical analysis using monoclonal antibody.Neuroscience,1988,25(2):613
[11]Ding Y-Q,Kaneko T,Nomura S,et al.Immunohistochemical localization of μ-opioid receptors in the central nervous system of the rat.J Comp Neurol,1996,367(3):375
[12]Chase MH,Soja PJ,Morales FR.Evidence that glycine mediates the postsynaptic potentials that inhibit lumbar motoneurons during the atonia of active sleep.J Neurosci,1989,9(4):743
, 百拇医药
[13]史密斯,罗浩.阿片受体与阿片肽.见韩济生主编.神经科学纲要.北京:北京医科大学中国协和医科大学联合出版社,1993:458~470
[14]赵志奇.痛觉及其调制.见韩济生主编.神经科学纲要.北京:北京医科大学中国协和医科大学联合出版社,1993:535~553
[15]Ding Y-Q,Nomura S,Kaneko T,et al.Co-localization of μ-opioid receptor-like and subtance P-like immunoreactivities in axon terminals within the superficial layers of the medullary and spinal dorsal horns of the rat.Neurosci Lett,1995,198(1):45, 百拇医药
单位:高蓉 李云庆 施际武 第四军医大学解剖学教研室、梁琚脑研究中心,西安 710032
关键词:谷氨酸受体;GABAA受体;甘氨酸受体;阿片μ受体;运动核;大鼠
解剖学报990207 【摘要】 目的 观察大鼠中枢运动核团内谷氨酸受体、γ-氨基丁酸受体(GABAAR)、甘氨酸受体(GlyR)和阿片μ受体(MOR)的定位分布,搞清谷氨酸、GABA、甘氨酸和脑啡肽在中枢运动核团内的作用部位。 方法 免疫组织化学染色技术。 结果 在动眼神经核、滑车神经核、三叉神经运动核、展神经核、面神经核、疑核、舌下神经核、E-W核、上涎核、迷走神经背核和脊髓前角内均可见NMDAR1样和GluR2/3样阳性胞体,但NMDAR1样和GluR2/3样阳性纤维和终末仅见于动眼神经核、E-W核、滑车神经核、三叉神经运动核和迷走神经背核,除三叉神经运动核、疑核和脊髓前角能见到少量GABAAR β亚单位样阳性胞体外,上述各核团也可见GABAAR β亚单位样阳性的纤维和终末,而GABAARα亚单位样阳性胞体主要见于疑核、舌下神经核、迷走神经背核和脊髓前角;中枢运动核团内均可见GlyR和MOR样阳性的纤维和终末。 结论 谷氨酸、GABA、甘氨酸和脑啡肽在中枢运动核团可能通过突触前和突触后机制,对中枢运动神经元发挥调控作用。
, 百拇医药
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL LOCALIZATION OF GLUTAMATERECEPTOR,GABAA RECEPTOR,GLYCINE RECEPTORAND μ-OPIOID RECEPTOR IN THE CENTRALMOTOR NUCLEI OF THE RAT
Gao Rong, Li YunqingΔ, Shi Jiwu
(Department of Anatomy,K.K.Leung Brain Research Centre,The Fourth Military Medical University,Xi'an)
【Abstract】 Objective To observe the locations of glutamate receptor(NMDAR1,GluR2/3),GABAA receptor(α and β subunits of GABAAR),glycine receptor(GlyR)and μ-opioid receptor(MOR) in the somatic motor nuclei and parasympathetic motor nuclei of the brainstem and the ventral horn of the spinal cord in the rat and to investigate the binding sites of glutamate,GABA,glycine and enkephalin on the motoneurons of the motor nuclei in the central nervous system(CNS).Methods Immunohistochemical staining method was used in the present study.Results NMDAR1- and GluR2/3-like immunoreactive(LI) neurons were found in the oculomotor nucleus,trochlear nucleus,trigeminal motor nucleus,abducens nucleus,facial nucleus,ambiguus nucleus,hypoglossal nucleus,Edinger- Westphal(E-W) nucleus,superior salivary nucleus,dorsal motor nucleus of vagus and the ventral horn of the spinal cord;but NMDAR1-LI and GluR2/3-LI fibers and terminals were found in oculomotor nucleus,Edinger-Westphal (E-W) nucleus,trochlear nucleus,trigeminal motor nucleus and dorsal motor nucleus of vagus.GABAARβ subunit-LI fibers and terminals could be seen at all of nuclei as mentioned above,in the trigeminal motor nucleus,ambiguus nucleus and ventral horn of the spinal cord,GABAARβ subunit-LI neurons were observed.GABAA R α subunit-LI neurons were mainly encounted in ambiguus nucleus,hypoglossal nucleus,dorsal motor nucleus of vagus and ventral horn of the spinal cord;GlyR-LI and MOR-LI fibers and terminals were observed in all of the central motor nuclei.Conclusion Glutmate,GABA, glycine and enkephalin may regulate the activities of motoneurons in the CNS through the way of presynaptic and/or postsynaptic mechanism.
, 百拇医药
【Key words】 Glutamate receptor; GABAA receptor; Glycine Receptor, μ-Opioid receptor; Immunohistochemistry; Motor nuclei; Rat
氨基酸类神经递质广泛分布于中枢神经系统(CNS)内,在CNS感觉信息传导和完成运动指令等突触传递过程中发挥重要作用,所以研究它们的受体在CNS的作用部位具有重要意义。根据氨基酸类物质对突触后神经元作用的不同,可将它们分为兴奋性及抑制性氨基酸,分别以谷氨酸(Glu)、γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)和甘氨酸(Gly)为代表。中枢运动核团内均有密集的Glu样、GABA样、Gly样和脑啡肽样阳性纤维和终末,这些阳性纤维和终末主要来自脑干的运动前神经元[1~4]。Glu受体(GluR)有代谢型GluR和离子型GluR两种,离子型GluR又可分为NMDA受体和非NMDA受体两种,而非NMDA受体还可进一步分为AMPA受体(GluR1~4)和KA受体(GluR5~7)[5];GABA受体有GABAA受体、GABAB受体和GABAC受体3种类型[6]。大量的研究结果都证明阿片受体(至少包括3种亚型)中的μ亚型不但参与吗啡的镇痛过程,而且对中枢运动神经元的活动具有调控作用[7]。以往的研究对GluR、GABAAR的α和β亚单位、GlyR和MOR在大鼠CNS内的分布已有一些报道[8~11],但尚缺乏关于GluR、GABAAR、GlyR和MOR在运动核团内精确定位分布的系统资料,所以本研究采用免疫组织化学方法观察了NMDAR1、GluR2/3、GABAAR的α和β亚单位、GlyR和MOR在大鼠中枢运动核团内的定位分布。
, 百拇医药
材料和方法
雄性SD大鼠8只,体重200~250g。戊巴比妥钠经腹腔麻醉(40mg/kg),开胸后插管至升主动脉,先以0.9%盐水100ml冲洗血液,再用500ml含4%多聚甲醛和0.2%苦味酸的0.1mol/L磷酸盐缓冲液(PB,pH7.4)灌注固定,持续约45min。取脑及脊髓入上述新鲜固定液中后固定2~4h(4℃),再移入含30%庶糖的PB液中至沉底。恒冷箱切片机冰冻横切脑干及脊髓,片厚30μm。切片隔6张取1张,分7套收集,将第1~6套切片按ABC法行免疫组织化学染色(表1)。在第1抗体和第2抗体中分别孵育18~24h和3~5h,其浓度分别为1∶1 000和1∶200,ABC混合液(1∶50,Vector)中孵育1h后用二甲基联苯胺(DAB)和H2O2呈色。抗体和复合物的稀释均用含0.3% Triton X-100和2%正常羊血清的PBS。孵育均在室温下进行,各步骤之间均用PBS彻底清洗切片。对照试验选择第7套的部分切片,并将其分为6组,除用正常兔血清或小鼠血清代替第1抗体孵育切片外,其余处理同上;将第7套的其他切片行Nissl染色,以便对照观察和定位免疫组织化学的染色结果。
, 百拇医药
免疫组织化学染色阳性结果的评判:(1)阳性神经元的相对密度:为随机选取各运动核200μm2面积内阳性神经元的数量,大量(+++):10~15个;中等量(++):6~10个;少量(+):3~5个;偶见(±):1~2个;阴性-:0。(2)阳性纤维和终末的相对密度:为随机选取各运动核100μm2面积内阳性纤维和终末的数量,大量(+++):10~15根纤维,终末密集;中等量(++):6~10根纤维,终末略少;少量(+):3~5根纤维,终末较少;偶见(±):1~2根纤维,终末稀疏;阴性(-):无纤维和终末。
表1 抗体种类、来源和生产厂家
Table 1 Antibody,host and producer 第1抗体primary antibody
来源
host
, 百拇医药
生产厂家
producer
第2抗体
secondary antibody
生产厂家
producer
N-甲基-D-门冬氨酸受体1型
NMDAR1
兔
rabbit
Chemicon
Biotin-羊抗兔IgG
, 百拇医药
Biotin-Goat Anti-rabbit IgG
Vector
谷氨酸受体2/3型
GluR2/3
兔
rabbit
RBI
Biotin-羊抗兔IgG
Biotin-Goat Anti-rabbit IgG
Vector
γ-氨基丁酸A受体α亚单位
, 百拇医药
GABAARα
小鼠
mouse
Boehringer
Biotin-羊抗小鼠IgG
Biotin-Goat Anti-mouse IgG
Jackson
γ-氨基丁酸A受体β亚单位
GABAARβ
小鼠
mouse
, 百拇医药
Boehringer
Biotin-羊抗小鼠IgG
Biotin-Goat Anti-mouse IgG
Jackson
甘氨酸受体
GlyR
小鼠
mouse
Boehringer
Biotin-羊抗小鼠IgG
Biotin-Coat Anti-mouse IgG
, 百拇医药
Jackson
阿片μ受体
MOR
兔
rabbit
Ding等[11]
Biotin-羊抗兔IgG
Biotin-Goat Anti-rabbit IgG
Vector
结 果
本研究用免疫组织化学方法所染出的几种受体大多位于中枢运动神经元胞体和突起的膜上,但NMDAR1样、GluR2/3样、GABAAR的α和β亚单位样阳性产物也见于胞浆,在大鼠中枢运动核团内未见GlyR样和MOR样阳性神经元胞体,仅见GlyR样和MOR样阳性纤维和终末(图1~8)。GlyR样和MOR样阳性纤维和终末常呈篮状包绕在运动神经元的胞体和突起的周围(图5,8)。中枢运动核团内的NMDAR1样和GABAARα亚单位样阳性神经元常呈强阳性(图1,6,7),而GluR2/3样阳性神经元常略弱(图2,3)。几种受体阳性运动神经元胞体的长径多为≤40μm。对照试验的切片上,均未观察到免疫组织化学阳性染色结果。
, http://www.100md.com
表2 Glu受体、GABAA受体、Gly受体、阿片受体样阳性神经元在中枢运动核团内的分布和相对密度
Table 2 Distribution and relative density of GluR-,GABAAR-,GlyR- and μ-opioid
receptor-like immunoreactive neurons in the central motor nuclei
NMDAR1
GluR2/3
GABAARα
GABAARβ
, 百拇医药
GlyR
MOR
动眼神经核(oculomotor nucleus)
++
++
±
-
-
-
滑车神经核(trochlear nucleus)
++
++
, http://www.100md.com ±
-
-
-
三叉神经运动核(trigeminal motor nucleus)
+++
+++
±
+
-
-
展神经核(abducens nucleus)
++
, 百拇医药
++
±
-
-
-
面神经核(facial nucleus)
++
++
±
-
-
-
疑核(ambiguus nucleus)
, 百拇医药
++
++
++
+
-
-
舌下神经核(hypoglossal nucleus)
+++
+++
+++
-
-
-
, http://www.100md.com
E\|W核(Edinger\|Westphal nucleus)
++
++
±
-
-
-
上涎核(superior salivary nucleus)
++
++
±
-
, 百拇医药
-
-
迷走神经背核(dorsal motor nucleus of vagus)
++
++
++
-
-
-
脊髓前角(ventral horn of spinal cord)
+++
+++
, http://www.100md.com
++
+
-
-
相对密度:-.阴性 ±.偶见 +.少量 ++.中等量 +++.大量
Relative density:-:negative ±:occasionally observed +:low density ++:medium density +++:high density表3 Glu受体、GABAA受体、Gly受体、阿片μ受体样阳性纤维和终末在中枢运动核团内的分布和相对密度
Table 3 Distribution and relative density of GluR-,GABAAR-,GlyR- and μ-opioid
, 百拇医药
receptor-like immunoreactive fibers and terminals in the central motor nuclei
NMDAR1
GluR2/3
GABAARα
GABAARβ
GlyR
MOR
动眼神经核(oculomotor nucleus)
+
+
, 百拇医药
±
+
++
+
滑车神经核(trochlear nucleus)
+
+
±
+
++
+
三叉神经运动核(trigeminal motor nucleus)
, 百拇医药 +
+
±
+
+++
+
展神经核(abducens nucleus)
-
-
±
+
++
+
, http://www.100md.com 面神经核(facial nucleus)
-
-
±
+
+++
++
疑核(ambiguus nucleus)
-
-
±
++
++
, 百拇医药
++
舌下神经核(hypoglossal nucleus)
-
±
+
+
+++
++
E-W核(Edinger-Westphal nucleus)
++
+
±
, http://www.100md.com ++
++
+
上涎核(superior salivary nucleus)
-
±
±
+
+
+
迷走神经背核(dorsal motor nucleus of vagus)
+
, 百拇医药
+
++
+
+
++
脊髓前角(ventral horn of spinal cord)
-
-
±
++
++
+++
相对密度:-~+++同表2 Relative density:-~+++ same as table 2


, 百拇医药
图1 示动眼神经核(Ⅲ)和动眼神经副交感核(E-W核)内的NMDAR1样阳性神经元(标尺示80μm,图2~7同)
Fig.1 Showing NMDAR1-like immunoreactive (NMDA1-LI) neurons in the oculomotor nucleus(Ⅲ) and Edinger-Westphal(E-W) nucleus.
图2 示滑车神经核(Ⅳ)内的GluR2/3样阳性神经元。DR.中缝背核
Fig.2 Showing GluR2/3-LI neurons in the trochlear nucleus (Ⅳ).DR:dorsal raphe nucleus.


, 百拇医药
图3 示三叉神经运动核(Vm)内的GluR2/3样阳性神经元
Fig.3 Showing GluR2/3-LI neurons in the trigeminal motor nucleus(Vm).
图4 示展神经核(Ⅵ)内的GlyR样阳性纤维和终末。g7.面神经膝
Fig.4 Showing GlyR-LI fibers and terminals in the abducens nucleus(Ⅵ).g7:genu of facial nerve.


图5 示面神经核(Ⅶ)内密集的Gly R样阳性纤维和终末
, 百拇医药
Fig.5 Showing GlyR-LI fibers and terminals in the facial nucleus(Ⅶ).
图6 示疑核(Amb)内的GABAARα样阳性神经元
Fig.6 Showing strong positive GABAARα subunit-LI neurons in the ambiguous(Amb)nucleus.


图7 示迷走神经背核(X)和舌下神经核(Ⅹ Ⅱ)内的GABAAR α样阳性神经元。NTS.孤束核
, 百拇医药 Fig.7 GABAARα subunit-LI neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of vagus(Ⅹ)and hypoglossal nucleus(Ⅹ Ⅱ).NTS:nucleus tractus solitarri.
图8 示颈髓前角内的MOR样阳性纤维和终末
Fig.8 Showing MOR-LI fibers and terminals in the ventral horn of the cervical spinal cord.Bar=80μm for all Figs.1~8.
讨 论
大量的生理学实验都证明谷氨酸(Glu)是对中枢神经元具有兴奋作用的氨基酸之一,Glu作用于突触后受体,可能直接与膜去极化的通路偶联[5]。Glu的两类离子型受体——NMDA受体和非NMD受体(AMPA受体和KA受体)是同一受体-通道复合物的组成部分,主要参与Glu对神经元的兴奋作用。Glu将离子型受体激活后,使Ca2+向细胞内的流动增加和细胞的兴奋性增强,从而产生兴奋性反应,而且是一种河豚毒素不能阻断的快兴奋作用[5]。本研究在大鼠中枢的动眼神经核、滑车神经核、三叉神经运动核、展神经核、面神经核、疑核、舌下神经核、E-W核、上涎核、迷走神经背核和脊髓前角均观察到了NMDAR1样和GluR2/3样阳性的神经元胞体,并在动眼神经核、E-W核、滑车神经核、三叉神经运动核和迷走神经背核分别观察到NMDAR1样和GluR2/3样阳性的纤维和终末,从而说明对离子型受体具有激活作用的Glu是影响上述核团内运动神经元活动的兴奋性递质。
, 百拇医药
GABA和Gly均为典型的抑制性神经递质。GABA和Gly与GABAAR和GlyR结合后,出现短暂的阴离子(Cl-)内向通透性增加,使Cl-在细胞内的浓度上升,导致细胞膜的超极化和兴奋性降低,产生抑制效应[6,12]。本研究观察到GABAARα亚单位样阳性胞体主要见于疑核、舌下神经核、迷走神经背核和脊髓前角;除三叉神经运动核、疑核和迷走神经背核内能见到GABAARβ亚单位样阳性胞体外,中枢运动核团也可见GABAARβ亚单位样阳性纤维和终末;除上涎核和迷走神经背核较稀疏外,较密集的GlyR样阳性纤维和终末见于动眼神经核、滑车神经核、三叉神经运动核、展神经核、面神经核、疑核、舌下神经核、E-W核和脊髓前角;说明GABAAR和GlyR对于GABA和Gly在上述运动核团内不同运动神经元间的功能协调方面,可能扮演着重要的角色。
尽管大量的研究都证明MOR主要参与吗啡的镇痛作用,但也有许多证据表明MOR在躯体运动和内脏活动中具有调控效应[7,13]。向大鼠小脑延髓池内注入大剂量的脑啡肽除抑制心血管活动和呼吸外,还可使运动减少、木僵和肌肉强直。本研究在面神经核、疑核、舌下神经核、迷走神经背核和脊髓前角等与上述躯体运动和内脏活动有关的中枢运动核团内观察到较密集的MOR样阳性纤维和终末,为以往的机能学研究提供了可靠的形态学依据。
, http://www.100md.com
以往的研究观察到阿片类物质对脊髓后角的伤害性感受神经元的抑制存在突触前和突触后两种机制[6,14],阿片类物质还可通过突触前机制在脊髓后角内抑制外周来源的P物质(SP)能终末释放SP[15]。本研究在与躯体运动和内脏活动有关的中枢运动核团内观察到NMDAR1样、GABAAR样、GlyR样和MOR样阳性终末,提示GluR、GABAAR、GlyR和MOR的突触前调控机制在上述运动核团内可能也发挥重要的作用。
国家杰出青年科学基金资助课题(No.39625011)
感谢丁玉强同志提供MOR抗体及张淼丽技师和原悦萍同志在图片制作过程中的帮助。
参考文献
[1]Li YQ,Takada M,Kaneko T,et al.GABAergic and glycinergic neurons projecting to the trigeminal motor nucleus:a double labeling study in the rat.J Comp Neurol,1996,373(3):498
, 百拇医药
[2]Li YQ,Takada M,Kaneko T,et al.Distribution of GABA ergic and glycinergic premotor neurons projecting to the facial and hypoglossal nuclei in the rat.J Comp Neurol,1997,378(2):283
[3]李云庆,王智明,施际武.大鼠脑干向面口部运动核的P物质能和脑啡肽能投射.解剖学报,1999,30(1):11
[4]李云庆,王智明,施际武.大鼠脑干面口部运动神经元与5-HT样、SP样、L-ENK样、GABA样和Gly样阳性终末间的突触联系.解剖学报,1998,29(4):351
[5]Monaghan DT,Bridges RJ,Cotman CW,The excitatory amino acid receptors:their classes,pharmacology,and distinct properties in the function of the central nervous system.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol,1989,29:365
, 百拇医药
[6]Luddens H,Korpi ER,Seeburg PH.GABAA/Benzodiazepine receptor heterogeneity:neurophysiolgical implications.Neuropharmacology,1995,34(2):245
[7]Minami M,Satoh M.Molecular biology of the opioid receptors:structure,functions and distributions.Neurosci Res,1995,23(1):121
[8]李云庆,王智明,施际武.大鼠三叉神经尾侧亚核和脊髓内离子型谷氨酸受体、GABAA受体和甘氨酸受体的分布.解剖学报,1997,28(2):118
[9]Moreno JI,Piva MA,Miralles CP,et al.Immunocytochemical localization of the β2 subunit of the gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor in the rat brain.J Comp Neurol,1994,350(2):260
, 百拇医药
[10]Araki T,Yamano M,Marakami T,et al.Localization of glycine receptors in the rat central nervous system:an immunocytochemical analysis using monoclonal antibody.Neuroscience,1988,25(2):613
[11]Ding Y-Q,Kaneko T,Nomura S,et al.Immunohistochemical localization of μ-opioid receptors in the central nervous system of the rat.J Comp Neurol,1996,367(3):375
[12]Chase MH,Soja PJ,Morales FR.Evidence that glycine mediates the postsynaptic potentials that inhibit lumbar motoneurons during the atonia of active sleep.J Neurosci,1989,9(4):743
, 百拇医药
[13]史密斯,罗浩.阿片受体与阿片肽.见韩济生主编.神经科学纲要.北京:北京医科大学中国协和医科大学联合出版社,1993:458~470
[14]赵志奇.痛觉及其调制.见韩济生主编.神经科学纲要.北京:北京医科大学中国协和医科大学联合出版社,1993:535~553
[15]Ding Y-Q,Nomura S,Kaneko T,et al.Co-localization of μ-opioid receptor-like and subtance P-like immunoreactivities in axon terminals within the superficial layers of the medullary and spinal dorsal horns of the rat.Neurosci Lett,1995,198(1):45, 百拇医药