右房房性心动过速的导管标测和消融
作者:王业松 马虹 唐安丽 廖新学 柳俊 何建桂 吴素华
单位:中山医科大学附属第一医院内科, 广东 广州 510080
关键词:心房;心动过速;治疗;导管消融术;方法
中山医科大学学报000117
摘 要:目的 探讨右房房速的导管标测和消融方法。方法 常规电生理检查确诊3例右房房速后,多极标测导管在右房内弯曲、旋转粗标右房的不同面,寻找较体表心电图P波提前的相对较早的心房内电图,以此电图的电极对作为参考点,消融导管通过Swartz鞘在该点附近仔细标测,寻找最早心房激动点消融。射频消融的能量从15 W开始逐渐递增至25 W。结果 3例右房房速消融成功。消融成功部位的心房内电图较P波提前40~50 ms。终止房速初始放电能量为15 W,时间在5 s内。放电次数2~4次。X线暴光时间28~36 min。结论 多极标测导管粗标,消融导管经Swartz鞘细标寻找最早心房激动消融右房房速的方法简单有效。
, http://www.100md.com
分类号:R 541.7 文献标识码:A
文章编号:1000-257X(2000)01-0057-03
Catheter Mapping and Ablation of Right Atrial Tachycardias
WANG Ye-song
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
MA Hong
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
, http://www.100md.com
TANG An-li
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
LIAO Xin-xue
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
LIU Jun
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
, http://www.100md.com
HE Jian-gui
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
WU Su-hua
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
Abstract:Objective To investigate the methods of mapping and ablation of right atrial tachycardia. Methods Three cases of right atrial tachycardia were confirmed by routine electrophysilogic examination. Multipolar mapping catheter was curved and rotated in the right atrium to map the atrial wall for exploring the site of relative early atrial electrogram preceded the P wave in the surface electrocardiogram. Ablative catheter was used to map carefully near this site through Swartz sheath to locate the earliest site of atrial activation where radiofrequency energy was delivered. The energy was titrated from 15 W to 25 W. Results Ablation was successful in all three patients. The local atrial electrograme preceded the onset of the P wave by 40~50 ms at the successful ablation site. The atrial tachycardias were terminated by using 15 W of power for less than 5 s. Successful ablation in the three patients required 2~4 radiofrequcency energy applications and 28~36 min fluoroscopy time. Conclusion It is simple and effective that radiofrequency ablation of right atrial tachycardia was guided by general mapping of multipolar catheter and careful mapping of ablative catheter through Swartz sheath to locate the site of earliest atrial activation.
, 百拇医药
Key words:heart atrium; tachycardia/therapy; catheter ablation/methods▲
在室上性心动过速中,房性心动过速(简称房速)远较房室折返性心动过速及房室结折返性心动过速少见,但射频消融的难度却大得多。房速的导管标测和消融各家报道的方法不一[1~4],我们采用多极标测导管粗标,消融导管借助Swartz鞘细标的方法消融右房房速3例,均获得成功。现将方法和结果报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例选择
自1995年以来,165例室上性心动过速病人来我院行心内电生理检查及射频消融治疗,3例证实为房速,男2例,女1例,年龄15~42岁,反复心动过速发作史2~13年,常规检查未发现有器质性心脏病。
, http://www.100md.com
1.2 电生理检查
常规置高位右房(HRA)、希氏束(HBE)、冠状窦(CS)及右心室(RV)电极,同步记录心腔双极电图和体表心电图(Ⅰ、AVF及V1)。分别在RVA、HRA两个部位行程序早搏刺激(S1S2)及递增起搏(S1S1),如不能诱发心动过速则静滴异丙肾上腺素后再行电刺激。诱发房速后,根据上述电极记录的心房激动顺序初步确定房速的起源,3例均为右房房速。电生理检查采用德国Hellige Midas 5500型24导生理记录仪。
1.3 标测和消融
20级Daig电极经股静脉送入右房,弯曲电极导管并旋转,粗标右房波不同的面,比较各电极对所记录心房内电图的激动顺序,寻找较体表心电图的心房波(P波)提前的最早的心房内电图,以此心房内电图对应的电极对所在部位作为消融导管标测的参考点。经股静脉送相应型号的Swartz鞘(美国Daig公司生产)进右房,4极Daig消融电极在Swartz鞘支撑下于粗标的参考点的附近进行仔细标测,寻找最早的心房激动(A波)作为消融的靶点。初始放电15 W,5~10 s房速不终止重新标测,如终止,则能量逐渐递增至25 W,持续放电60~90 s。消融终点:静脉滴注异丙肾上腺素前、后,重复右房电生理检查不能诱发心动过速,观察15~20 min后再重复上述检查仍不能诱发心动过速。射频消融采用中国科学仪器研制中心生产的RFG-Ⅱ射频消融仪。
, http://www.100md.com
2 结 果
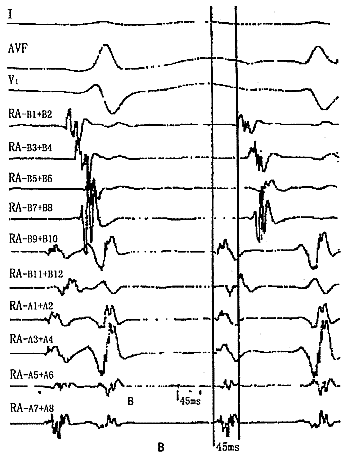
3例病人常规置管的电生理检查显示:心室S1S1起搏3例分别于600、500以及450 ms显示室房分离;右房电刺激均可诱发和终止心动过速;心动过速的P波周长分别为300、340及280 ms,PⅡ、Ⅲ、AVF倒置,QRS波形态正常;心动过速显示的心房激动顺序与窦性心律完全不同,最早心房激动均位于冠状窦口,伴有2度Ⅰ型房室传导阻滞。20极电极粗标的消融参考点分别在右房后面中下部、房间隔的中上部及冠状窦口。消融电极在SR0型Swartz鞘的支撑下于参考点的电极对附近仔细标测,分别寻找到最早的心房激动较体表心电图的P波提前40、50及45 ms,均以15 W放电,5 s内终止心动过速。3例放电的次数分别为3次、4次及2次;X线曝光时间分别为32、36及28 min。图1显示成功部位的右房多极电极及消融电极导管标测与X线的影像。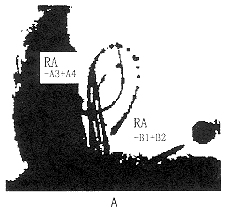
, http://www.100md.com
v(paper speet)/mm.s-1=200
图1 成功消融的局部电图与X线影像(病例1)
Fig.1 Local electrograms and fluoroscopic picture duing successful catheter ablation sessiom(in patient 1)
A: Left anterior oblique 45° fluoroscopic picture of the multipolar mapping catheter and the successful catheter ablation site. B: Local electrogram of multipolar catheter mapping and the successful catheter ablation. The local electrogram (RA-A3+A4) of the multipolar mapping catheter electrode 15 and 16 was 40 ms before P wave. The ablation catheter(ABL) was used to map carefully near the site of the mapping electrode 15 and 16 through Swartz sheath to find the successful ablation site where the local electrogram (ABL-A7+A8) was 45 ms before P wave
, 百拇医药
3 讨 论
本文报道的3例心动过速均可被右房电刺激诱发和终止,提示心动过速机制为折返可能性最大;心动过速时,PⅡ、Ⅲ、AVF倒置,P波周期长度分别为280~340 ms,QRS形态正常,故为阵发性室上性心动过速;心动过速时P波形态及心房激动顺序与窦性心律完全不同,可排除窦房折返性心动过速;心室S1S1起搏于450~600 ms显示室房分离,而心动过速的周长为280~340 ms,以及心动过速伴2度Ⅰ型房室传导阻滞,可排除旁路折返性心动过速;右房电生理检查未见房室结双通道,以及心动过速伴2度Ⅰ型房室传导阻滞,不支持房室结折返性心动过速。故本文3例可诊断为房内折返性心动过速。
右房房速的导管标测和消融方法有:① 一根消融导管分别在4个平面(上腔静脉开口水平至下腔静脉开口水平,每隔1 cm为1个平面)旋转导管,分别从前中隔、前壁、前侧壁、侧壁、后侧壁、后壁、后中壁至间隔,并在右心耳、卵圆窝以及冠状窦口附近仔细标测。寻找相对提前的心房激动部位,并在该部位行起搏拖带,以伴有起搏至P波间期最短的隐匿性拖带起搏部位作为慢传导区的出口部位,以此部位作为消融的靶点[1];或以消融电极在初定的部位进行起搏,寻找能重复出房速发作时的心房激动顺序的部位为消融靶点[2]。② 两根消融导管交替标测,在初定部位上、下2 cm水平面旋转导管,即从房间隔至外侧壁标侧,当寻找到心房激动比初定房速部位还早,将该导管作为参照电极,另一根消融导管在参照电极附近移动标测,寻找更早的心房激动部位。如此两根大头导管交替、移动标测,直至标测到最早心房激动,以此部位作为消融靶点[3~4]。这些方法使房速消融成功率达90%~95%。本文报道的3例右房房速经多极导管粗标及消融导管通过Swartz鞘细标寻找最早心房激动消融均获成功,说明此方法是可行的。由于病例少,其结果尚不能与上述文献报道的结果比较。我们的初步体会是:此方法简单可行;多极导管在右房内粗标可缩小消融导管标测的范围,有助于减少导管标测时的X线暴光时间,3例X线暴光时间为28~36 min;消融导管通过Swartz鞘支撑可与心房紧密接触,避免初始放电用较高能量以及放电过程中导管的移位,3例放电终止心动过速的初始能量均为15 W,时间均在5 s内;消融导管经Swartz鞘推送和回抽可在粗标参考电极附近进行线性连续标测,容易比较和正确识别最早心房激动的消融靶点图,避免过多的无效放电,3例放电次数2~4次。
, http://www.100md.com
房速的射频消融病例较少,方法尚不成熟,射频消融治疗房速仍有待经验积累和最佳方法的探索。■
作者简介:王业松(1962-),男,安徽人,硕士,讲师.
参考文献:
[1]Chen S A, Chiang C E, Yang C J, et al. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of sustained intra-atrial reentrant tachycardia in adult patients[J]. Circulation, 1993,88(2):578.
[2]Tracy C M, Swartz J F, Fletcher R D, et al. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of ectopic atrial tachycardia using paced activation sequency mapping[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1993,21(4):910.
[3]Kay C N, Chong F, Epstein A E,et al. Radiofrequency ablation for treatment of primary atrial tachycardias[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1993,21(4):901.
[4]吴书林,李海杰,郑祥生,等. 射频消融治疗房性心动过速[J]. 中华心血管杂志,1993,23(1):25.
收稿日期:1999-08-28, 百拇医药
单位:中山医科大学附属第一医院内科, 广东 广州 510080
关键词:心房;心动过速;治疗;导管消融术;方法
中山医科大学学报000117
摘 要:目的 探讨右房房速的导管标测和消融方法。方法 常规电生理检查确诊3例右房房速后,多极标测导管在右房内弯曲、旋转粗标右房的不同面,寻找较体表心电图P波提前的相对较早的心房内电图,以此电图的电极对作为参考点,消融导管通过Swartz鞘在该点附近仔细标测,寻找最早心房激动点消融。射频消融的能量从15 W开始逐渐递增至25 W。结果 3例右房房速消融成功。消融成功部位的心房内电图较P波提前40~50 ms。终止房速初始放电能量为15 W,时间在5 s内。放电次数2~4次。X线暴光时间28~36 min。结论 多极标测导管粗标,消融导管经Swartz鞘细标寻找最早心房激动消融右房房速的方法简单有效。
, http://www.100md.com
分类号:R 541.7 文献标识码:A
文章编号:1000-257X(2000)01-0057-03
Catheter Mapping and Ablation of Right Atrial Tachycardias
WANG Ye-song
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
MA Hong
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
, http://www.100md.com
TANG An-li
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
LIAO Xin-xue
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
LIU Jun
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
, http://www.100md.com
HE Jian-gui
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
WU Su-hua
(Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China)
Abstract:Objective To investigate the methods of mapping and ablation of right atrial tachycardia. Methods Three cases of right atrial tachycardia were confirmed by routine electrophysilogic examination. Multipolar mapping catheter was curved and rotated in the right atrium to map the atrial wall for exploring the site of relative early atrial electrogram preceded the P wave in the surface electrocardiogram. Ablative catheter was used to map carefully near this site through Swartz sheath to locate the earliest site of atrial activation where radiofrequency energy was delivered. The energy was titrated from 15 W to 25 W. Results Ablation was successful in all three patients. The local atrial electrograme preceded the onset of the P wave by 40~50 ms at the successful ablation site. The atrial tachycardias were terminated by using 15 W of power for less than 5 s. Successful ablation in the three patients required 2~4 radiofrequcency energy applications and 28~36 min fluoroscopy time. Conclusion It is simple and effective that radiofrequency ablation of right atrial tachycardia was guided by general mapping of multipolar catheter and careful mapping of ablative catheter through Swartz sheath to locate the site of earliest atrial activation.
, 百拇医药
Key words:heart atrium; tachycardia/therapy; catheter ablation/methods▲
在室上性心动过速中,房性心动过速(简称房速)远较房室折返性心动过速及房室结折返性心动过速少见,但射频消融的难度却大得多。房速的导管标测和消融各家报道的方法不一[1~4],我们采用多极标测导管粗标,消融导管借助Swartz鞘细标的方法消融右房房速3例,均获得成功。现将方法和结果报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例选择
自1995年以来,165例室上性心动过速病人来我院行心内电生理检查及射频消融治疗,3例证实为房速,男2例,女1例,年龄15~42岁,反复心动过速发作史2~13年,常规检查未发现有器质性心脏病。
, http://www.100md.com
1.2 电生理检查
常规置高位右房(HRA)、希氏束(HBE)、冠状窦(CS)及右心室(RV)电极,同步记录心腔双极电图和体表心电图(Ⅰ、AVF及V1)。分别在RVA、HRA两个部位行程序早搏刺激(S1S2)及递增起搏(S1S1),如不能诱发心动过速则静滴异丙肾上腺素后再行电刺激。诱发房速后,根据上述电极记录的心房激动顺序初步确定房速的起源,3例均为右房房速。电生理检查采用德国Hellige Midas 5500型24导生理记录仪。
1.3 标测和消融
20级Daig电极经股静脉送入右房,弯曲电极导管并旋转,粗标右房波不同的面,比较各电极对所记录心房内电图的激动顺序,寻找较体表心电图的心房波(P波)提前的最早的心房内电图,以此心房内电图对应的电极对所在部位作为消融导管标测的参考点。经股静脉送相应型号的Swartz鞘(美国Daig公司生产)进右房,4极Daig消融电极在Swartz鞘支撑下于粗标的参考点的附近进行仔细标测,寻找最早的心房激动(A波)作为消融的靶点。初始放电15 W,5~10 s房速不终止重新标测,如终止,则能量逐渐递增至25 W,持续放电60~90 s。消融终点:静脉滴注异丙肾上腺素前、后,重复右房电生理检查不能诱发心动过速,观察15~20 min后再重复上述检查仍不能诱发心动过速。射频消融采用中国科学仪器研制中心生产的RFG-Ⅱ射频消融仪。
, http://www.100md.com
2 结 果
3例病人常规置管的电生理检查显示:心室S1S1起搏3例分别于600、500以及450 ms显示室房分离;右房电刺激均可诱发和终止心动过速;心动过速的P波周长分别为300、340及280 ms,PⅡ、Ⅲ、AVF倒置,QRS波形态正常;心动过速显示的心房激动顺序与窦性心律完全不同,最早心房激动均位于冠状窦口,伴有2度Ⅰ型房室传导阻滞。20极电极粗标的消融参考点分别在右房后面中下部、房间隔的中上部及冠状窦口。消融电极在SR0型Swartz鞘的支撑下于参考点的电极对附近仔细标测,分别寻找到最早的心房激动较体表心电图的P波提前40、50及45 ms,均以15 W放电,5 s内终止心动过速。3例放电的次数分别为3次、4次及2次;X线曝光时间分别为32、36及28 min。图1显示成功部位的右房多极电极及消融电极导管标测与X线的影像。


, http://www.100md.com
v(paper speet)/mm.s-1=200
图1 成功消融的局部电图与X线影像(病例1)
Fig.1 Local electrograms and fluoroscopic picture duing successful catheter ablation sessiom(in patient 1)
A: Left anterior oblique 45° fluoroscopic picture of the multipolar mapping catheter and the successful catheter ablation site. B: Local electrogram of multipolar catheter mapping and the successful catheter ablation. The local electrogram (RA-A3+A4) of the multipolar mapping catheter electrode 15 and 16 was 40 ms before P wave. The ablation catheter(ABL) was used to map carefully near the site of the mapping electrode 15 and 16 through Swartz sheath to find the successful ablation site where the local electrogram (ABL-A7+A8) was 45 ms before P wave
, 百拇医药
3 讨 论
本文报道的3例心动过速均可被右房电刺激诱发和终止,提示心动过速机制为折返可能性最大;心动过速时,PⅡ、Ⅲ、AVF倒置,P波周期长度分别为280~340 ms,QRS形态正常,故为阵发性室上性心动过速;心动过速时P波形态及心房激动顺序与窦性心律完全不同,可排除窦房折返性心动过速;心室S1S1起搏于450~600 ms显示室房分离,而心动过速的周长为280~340 ms,以及心动过速伴2度Ⅰ型房室传导阻滞,可排除旁路折返性心动过速;右房电生理检查未见房室结双通道,以及心动过速伴2度Ⅰ型房室传导阻滞,不支持房室结折返性心动过速。故本文3例可诊断为房内折返性心动过速。
右房房速的导管标测和消融方法有:① 一根消融导管分别在4个平面(上腔静脉开口水平至下腔静脉开口水平,每隔1 cm为1个平面)旋转导管,分别从前中隔、前壁、前侧壁、侧壁、后侧壁、后壁、后中壁至间隔,并在右心耳、卵圆窝以及冠状窦口附近仔细标测。寻找相对提前的心房激动部位,并在该部位行起搏拖带,以伴有起搏至P波间期最短的隐匿性拖带起搏部位作为慢传导区的出口部位,以此部位作为消融的靶点[1];或以消融电极在初定的部位进行起搏,寻找能重复出房速发作时的心房激动顺序的部位为消融靶点[2]。② 两根消融导管交替标测,在初定部位上、下2 cm水平面旋转导管,即从房间隔至外侧壁标侧,当寻找到心房激动比初定房速部位还早,将该导管作为参照电极,另一根消融导管在参照电极附近移动标测,寻找更早的心房激动部位。如此两根大头导管交替、移动标测,直至标测到最早心房激动,以此部位作为消融靶点[3~4]。这些方法使房速消融成功率达90%~95%。本文报道的3例右房房速经多极导管粗标及消融导管通过Swartz鞘细标寻找最早心房激动消融均获成功,说明此方法是可行的。由于病例少,其结果尚不能与上述文献报道的结果比较。我们的初步体会是:此方法简单可行;多极导管在右房内粗标可缩小消融导管标测的范围,有助于减少导管标测时的X线暴光时间,3例X线暴光时间为28~36 min;消融导管通过Swartz鞘支撑可与心房紧密接触,避免初始放电用较高能量以及放电过程中导管的移位,3例放电终止心动过速的初始能量均为15 W,时间均在5 s内;消融导管经Swartz鞘推送和回抽可在粗标参考电极附近进行线性连续标测,容易比较和正确识别最早心房激动的消融靶点图,避免过多的无效放电,3例放电次数2~4次。
, http://www.100md.com
房速的射频消融病例较少,方法尚不成熟,射频消融治疗房速仍有待经验积累和最佳方法的探索。■
作者简介:王业松(1962-),男,安徽人,硕士,讲师.
参考文献:
[1]Chen S A, Chiang C E, Yang C J, et al. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of sustained intra-atrial reentrant tachycardia in adult patients[J]. Circulation, 1993,88(2):578.
[2]Tracy C M, Swartz J F, Fletcher R D, et al. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of ectopic atrial tachycardia using paced activation sequency mapping[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1993,21(4):910.
[3]Kay C N, Chong F, Epstein A E,et al. Radiofrequency ablation for treatment of primary atrial tachycardias[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1993,21(4):901.
[4]吴书林,李海杰,郑祥生,等. 射频消融治疗房性心动过速[J]. 中华心血管杂志,1993,23(1):25.
收稿日期:1999-08-28, 百拇医药