鼻咽癌中浸润的淋巴类细胞与瘤细胞凋亡的关系
作者:宗永生 李智 刘克拉 买世娟 梁英杰
单位:中山医科大学病理学教研室, 广东 广州 510089
关键词:鼻咽肿瘤;病理学;淋巴细胞;病理学;凋亡
中山医科大学学报000102Correlation Between Infiltrating Lymphoid Cells and
Neoplastic Cell Apoptosis in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
ZONG Yong-sheng
(Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510089, China)
, http://www.100md.com
LI Zhi
(Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510089, China)
LIU Ke-la
(Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510089, China)
MAI Shi-juan
(Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510089, China)
, 百拇医药
LIANG Ying-jie
(Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510089, China)
Abstract:Objective To investigate the correlation between infiltrating lymphoid cells and neoplastic cell apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Methods 38 untreated NPC biopsies were collected from the Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences. TUNEL (TdT-mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling) method was performed for quantitating the apoptosis count (AC, numbers of apoptotic cell from among 5 000 NPC cells). DAKO LSAB kit (K 0681) and respective primary antibodies were used for detecting reactive T-lymphocyte, monocyte/macrophage, pan B-lymphocyte, and accessory dendritic cell immunohistochemically. The amount of infiltrating lymphoid cells was indicated in terms of TCI (T-cell index), MMI (monocyte/macrophage index), BCI (B-cell index), and DCI (dendritic cell index) by their cell numbers per one average high power field, respectively. Results ①The AC varied greatly from case to case in untreated NPCs, the mean value being (12.9±13.9)/5 000; ②The AC was both positively correlated with TCI (P<0.05) and MMI (P<0.05), but not with BCI (P>0.05) and DCI (P>0.05). Conclusions ①The infiltrating T-lymphocytes representing cell-mediated immunity are able to induce NPC cell apoptosis; ②The infiltrating monocytes/macrophages might principally be an apoptosis-inducer or as a consequence of degraded apoptotic debris; ③The infiltrating B-lymphocytes representing humoural immunity and antigen presenting dendritic cells as well are not directly correlated with NPC cell apoptosis.
, 百拇医药
Key words: nasopharyngeal neoplasms/pathology; lymphocytes/pathology; apoptosis
CLC number: R 739.6 Document code: A
Article ID:1000-257 X(2000)01-0006-05
摘 要:目的 研究鼻咽癌中浸润的淋巴类细胞与癌细胞凋亡间的相关性。方法 收集中山医科大学病理学教研室38例未经治疗的鼻咽癌活检标本。应用TUNEL (TdT-mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling)方法定量检测凋亡癌细胞计数(每5 000个鼻咽癌细胞中的凋亡细胞数)。以免疫组化法分别检测T细胞,单核/巨噬细胞,B细胞和树突状细胞。结果 ① 在未经治疗的鼻咽癌活检标本各例间癌细胞凋亡计数差异很大,平均为(12.9±13.9)/5 000; ② 凋亡癌细胞计数与T细胞指数(I,即平均每个高倍视野浸润的T淋巴细胞数)和单核/巨噬细胞指数(moncyte macro phage index,MMI,即平均每个高倍视野浸润的单核/巨噬细胞数)均呈正相关,P<0.05,但凋亡癌细胞计数与B细胞指数(平均每个高倍视野浸润的B淋巴细胞数)和树突状细胞指数(平均每个高倍视野浸润的树突状细胞数)无相关性,P>0.05。结论 ① 代表细胞介导免疫的浸润性T淋巴细胞可以诱导鼻咽癌细胞凋亡; ② 浸润的单核/巨噬细胞可能主要是癌细胞凋亡的诱导者也可能部分是凋亡的后果; ③ 代表体液免疫的浸润性B淋巴细胞和递呈抗原的树突状细胞与鼻咽癌细胞的凋亡无直接相关性。
, 百拇医药
分类号: R 739.6 文献标识码:A
文章编号: 1000-257X(2000)01-0006-05▲
Lymphoinfiltration is a pathognomonic feature of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC)[1], and the amount of infiltrating lymphoid cells including T lymphocyte, monocyte/macrophage, B lymphocyte, and dendritic cell could influence the patients' prognosis[2]. On the other hand, neoplastic cell apoptosis could always be found in human untreated NPC biopsies[3,4]as well as NPC cell line nude mice transplants[5,6]. Does correlation between infiltrating lymphoid cells and neoplastic cell apoptosis exist in untreated NPC? What kinds of infiltrating lymphoid cells are correlated with NPC cell apoptosis? What role do the infiltrating lymphoid cells play on NPC cell apoptosis? This research was aiming at the issues just mentioned above.
, http://www.100md.com
1 MATERIAL & METHODS
1.1 Material
Thirty-eight untreated NPC biopsies were collected from the Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences in the year 1997. All the biopsy specimens were fixed in 10% formalin and embedded with paraffin. The paraffin blocks were consecutively sectioned.
1.2 H&E stain
Routine haematoxylin and eosin staining (H&E) was performed on every NPC biopsy slide.
, http://www.100md.com
1.3 In-situ cell death detection
TUNEL [TdT (Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase)-mediated fluorescein-dUTP Nick End Labeling]method was performed for detection and quantification of apoptosis count by use of Boehringer Mannheim “in-situ cell death detection kit, AP (Cat. No. 1684809)". The working procedure was carried out following the enclosed instruction in the kit. The positive signals showed dark purple color.
1.4 Immunohistochemistry
, 百拇医药
LSAB immunohistochemistry and respective primary antibodies were performed for detection of reactive T-lymphocyte, monocyte/macrophage, B-lymphocyte and accessory dendritic cell using DAKO LSAB kit (K 0681) and primary antibodies. The primary antibodies used were UCHL1, Lysozyme EC 3.2.1.17 (Muramidase), L26 and S-100 for reactive T cell, monocyte/macrophage, pan B cell and accessory dendritic cell, respectively. The working dilutions of these antibodies were 1/100, 1/300, 1/100 and 1/150 for UCHL 1, Lysozyme EC 3.2.1.17, L26, and S-100, respectively. Microwave pretreatment using pH6.0 citrate buffer was done before adding the UCHL1 or L26 diluted antibody solution. Trypsin pretreatment was adopted for immunohistochemical detection of S-100 and Lysozyme EC 3.2.1.17.
, 百拇医药
1.5 Apoptosis count of NPC cells
Apoptosis count (AC) of NPC cells was indicated as the numbers of apoptotic cell from among 5 000 NPC cells demonstrated on TUNEL slide by the use of “in-situ cell death detection kit". TCI(T cell index), MMI (monocyte/macrophage index), BCI (B cell index), and DCI (dendritic cell index) were shown as the numbers of positive cell per one average high power field (10×40) by counting at least 5 appropriate fields on their respective immunohistochemically stained slides.
, 百拇医药
1.6 Statistical analysis
Spearman rank correlation was used for statistical analysis.
2 RESULTS
2.1 Morphology of neoplastic cell apoptosis and infiltrating lymphoid cells
According to the criteria of WHO's histological classification, all of the 38 NPC biopsies were of the non-keratinizing carcinoma in type. Among them, 30 belong to undifferentiated subtype (undifferentiated carcinoma of nasopharyngeal type), and 8 belong to differentiated subtype (differentiated non-keratinizing carcinoma). The neoplastic cell AC varied greatly from case to case, the mean value was (12.9±13.2)/5 000. On H&E stained slides, the typically morphological changes of apoptotic cells, such as condensed nucleus and eosinophilic cytoplasm (Fig.1), apoptotic bodies (Fig.2) and apoptotic bodies phagocytosed by neighboring neoplastic cell or macrophage (Fig.3) could be found. These apoptotic cells and bodies showed end-labeling signals on TUNEL slide (Fig.4). The reactive T-lymphocytes (Fig.5), monocytes/macrophages (Fig.6), pan B-lymphocytes (Fig.7) and accessory dendritic cells (Fig.8) infiltrating within the NPC tissues could be clearly distinguished on their specifically stained slides.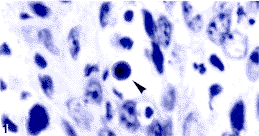 图1 鼻咽未分化癌 示核固缩的调亡细胞;Fig.1 Undifferentiated carcinoma of the nasopharynxShowing an apoptotic cell with condensed nucleus ( H&E 5×100)
图1 鼻咽未分化癌 示核固缩的调亡细胞;Fig.1 Undifferentiated carcinoma of the nasopharynxShowing an apoptotic cell with condensed nucleus ( H&E 5×100)  图2 鼻咽未分化癌 示调亡小体;Fig.2 Undifferenb`ated carcinoma of the nasopharyiixShowing apoptoiic bodies (H&E 5×100)
图2 鼻咽未分化癌 示调亡小体;Fig.2 Undifferenb`ated carcinoma of the nasopharyiixShowing apoptoiic bodies (H&E 5×100)  图3鼻咽未分化癌 示被邻近的瘤细胞所吞噬的调亡小体;Fig.3 Undifferentiated carcinoma of thf nasopharynxShowing an apoptotic body phagocytosed by a neighboring neoplastic cell(H&E 5×100)
图3鼻咽未分化癌 示被邻近的瘤细胞所吞噬的调亡小体;Fig.3 Undifferentiated carcinoma of thf nasopharynxShowing an apoptotic body phagocytosed by a neighboring neoplastic cell(H&E 5×100) 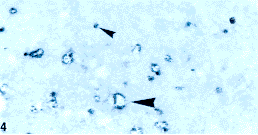 图4调亡中的TUNEL阳性尽咽癌细胞和调亡小体;Fig. 4 TUNEL-positive NPC cells undergoing apoptosis and apoptotic bodies(TUNEL 5×100)
图4调亡中的TUNEL阳性尽咽癌细胞和调亡小体;Fig. 4 TUNEL-positive NPC cells undergoing apoptosis and apoptotic bodies(TUNEL 5×100) 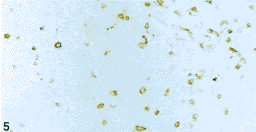 图5鼻咽癌组织中浸润的T淋巴细胞:Fig. 5 T-lymphi)cytes infiltrati`ng in NPC tissue(UCHLI IHC 5×20)
图5鼻咽癌组织中浸润的T淋巴细胞:Fig. 5 T-lymphi)cytes infiltrati`ng in NPC tissue(UCHLI IHC 5×20)  图6鼻咽癌组织中浸润的单核/巨噬细胞;Fig. 6 Monocytes/macrophages infiltrating in NPC tissiie(Lysozyme IHC 5×20)
图6鼻咽癌组织中浸润的单核/巨噬细胞;Fig. 6 Monocytes/macrophages infiltrating in NPC tissiie(Lysozyme IHC 5×20)  图7鼻咽癌组织中浸润的L淋巴细胞;Fig. 7 B-ly'nphocytes infiltrating in NPC tissue(M6 IHC 5×20)
图7鼻咽癌组织中浸润的L淋巴细胞;Fig. 7 B-ly'nphocytes infiltrating in NPC tissue(M6 IHC 5×20) 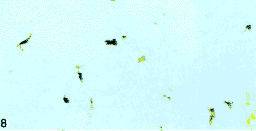 图8鼻咽癌组织中浸涧的树状突细胞Fig. 8 Dendritic cells iiifiltrating in NPC tissue(5100 IHC 5×20) 2.2 Correlation between neoplastic cell apoptosis count and the indexes of infiltrating lymphoid cells
图8鼻咽癌组织中浸涧的树状突细胞Fig. 8 Dendritic cells iiifiltrating in NPC tissue(5100 IHC 5×20) 2.2 Correlation between neoplastic cell apoptosis count and the indexes of infiltrating lymphoid cells
, 百拇医药
The mean values of AC, TCI, MMI, BCI and DCI were 12.9±13.2, 43.7±29.3, 41.4±29.7, 15.1±17.0 and 23.6±23.8, respectively. Rank correlation test was statistically calculated between these indexes by Spearman's formula. The data obtained showed that ①there was significant difference between AC and TCI (r=0.347, P<0.05) as well as AC and MMI (r=0.476, P<0.05); and ② no correlation existed between AC and BCI (r=-0.024,P>0.05) as well as AC and DCI (r=0.189, P>0.05).
, http://www.100md.com 3 DISCUSSION
NPC was formerly called lymphoepithelioma[7]because of a mixed appearance of epithelial and lymphoid cells presenting in tumour growth histopathologically. Since the report of Svoboda et al[8], it is popularly recognized that the lymphoinfiltration is representing an immunological response against epithelial neoplastic cells[9]. In 1993, Zong et al[2]. reported the effect of infiltrating lymphoid cells on NPC patients' prognosis; and recently Li and Zong described the apoptotic features of NPC cells in untreated NPC biopsies[3]and NPC cell line nude mice transplants[5,6]. These findings logically lead the authors to study the correlation between infiltrating lymphoid cells and neoplastic cell apoptosis in NPC. The authors think that to illustrate the basic molecular events involved in untreated NPC cell apoptosis will be of benefit for designing therapeutic research work because either radiotherapy or chemotherapy would play some therapeutic effects on NPC mainly through the pathway of apoptosis.
, 百拇医药
Though the AC and TCI were both varied greatly from case to case, there was a definite positive rank correlation between them as shown in the above result. Worthy to be noted is that a monoclonal antibody, clone UCHL1, was used for detecting infiltrating T-lymphocytes in this study. This antibody can recognize a 180 185ku determinant of reactive T-lymphocytes[10]and is not able to demonstrate pan T cells; and therefore it is an excellent marker for detecting reactive T cell or memory/effector cell[11]. Therefore, the reactive infiltrating T-lymphocytes might have the ability to induce neoplastic cell apoptosis in untreated NPC. According to the logical postulation, the authors further assume that the cell-mediated immunity represented by reactive T cells might exert its effect on NPC cell apoptosis. This finding is an additional evidence and theoretical basis for investigating therapeutic agents to enhance human cell-mediated immunity against NPC[12]. But however, though the authors had demonstrated a definite linkage of reactive T cells and neoplastic cell apoptosis, the interactions between tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and NPC cells would be very complex. On the one hand, NPC cells harbouring Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) could process and present EBV-encoded antigens onto cytotoxic T cells[13]; and on the other hand, the TILs could express T cell receptor gene[14]in NPC tissues. So, the issue concerning correlation of reactive T lymphocytes and NPC cell apoptosis is worthy to be further investigated.
, 百拇医药
How to interpret the positive correlation between AC and MMI? The macrophages can produce a whole array of cytokines including TNF-α(tumour necrosis factor-α) that will combine with TNFR (tumour necrosis factor receptor) expressed on NPC cell surface and trigger the TNF-α-mediated apoptosis[15]. The macrophages can process and present antigens, such as EBV-encoded LMP-1 onto the infiltrating CTLs (cytotoxic T-lymphocytes) in cooperation with HLA A2 antigen[15]. And then, the stimulated CTLs would undergo TCR (T cell receptor) gene rearrangements and become tumour-specific[15,16]. By clonal proliferation the tumour-specific CTLs will in their turn induce apoptosis. However, a few infiltrating monocytes/macrophages might be a consequence of phagocytosis initiated by degraded apoptotic cells (or secondary necrosis following apoptosis). Accordingly, besides reactive T cells, the infiltrating monocytes/macrophages might also play a role in inducing NPC cell apoptosis. It should be noted herein that besides apoptosis-inducing action, the macrophages might lyse the tumour cells by producing some toxic metabolites and proteolytic enzyme[15], therefore resulting in necrosis.
, 百拇医药
No correlation existed between AC and BCI. This revealed that the amount of infiltrating B-lymphocytes, which represent humoural immunity, could not directly influence neoplastic cell apoptosis. It should be pointed out that the humoural immunity might be indirectly even though very little related to apoptosis because, as it is popularly known, there are interactions between cell-mediated and humoural immunity.
The infiltrating dendritic cells might be originated from perivascular tissue as opposed to a derivation from the mononuclear phagocyte system[17]. Unlike monocytes/macrophages, the dendritic cells are poorly phagocytic and have large amount of class Ⅱ molecules on their cell surface[15]. So, the dendritic cells are much more associated with humoural immunity and thus reasonably showed no close correlation between DCI and AC in untreated NPC.
, http://www.100md.com
(本文图见插页1)■
Foundation item:This work was supported by the grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China(39730200-Ⅱ)
Biography: ZONG Yong-sheng (1927-), corresponding author, Jiangsu Province of China, Professor of Pathology.
References:
[1]Zong Y S, Lin H, Choy D T, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma and lymphoinfiltration [J]. Oncology, 1991, 48(4):290.
, http://www.100md.com
[2]Zong Y S, Zhang C Q, Zhang F, et al. Infiltrating lymphocytes and accessory cells in nasopharyngeal carcinoma [J]. Jpn J Cancer Res, 1993, 84(8):900.
[3]李 智,宗永生. 鼻咽癌组织中瘤细胞表达bc1-2、bax和p53及其与凋亡的关系[J].临床与实验病理学杂志, 1999, 15(2):127.
[4]Mutirangura A,Pornthanakasem W, Theamboonlers A, et al. Epstein-Barr viral DNA in serum of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma [J]. Clin Cancer Res, 1998,4(3):665.
, 百拇医药
[5]李 智,宗永生.鼻咽癌细胞株裸鼠移植瘤中癌细胞增生凋亡及其相关基因的表达[J]. 中山医科大学学报,1999,20(1):12.
[6]李 智,傅茂福,宗永生. 鼻咽癌细胞株裸鼠移植瘤中癌细胞的凋亡[J]. 癌症,1999,18(2):172.
[7]Chin K Y, Szutu C. Lymphoepithelioma, a pathological study of 97 cases [J]. Chinese Medical Journal, 1940, Supplement:94.
[8]Svoboda D J, Kirchiner F R, Shanmugaratnam K. The fine structure of nasopharyngeal carcinoma [A]. In:Muri C S, Shanmugaratnam K. Cancer of the Nasopharynx[H]. Copenhagen: UICC Monograph Series Publishing House, 1967,163~171.
, 百拇医药
[9]Kumar V, Cotran R S, Robbins S L. Basic Pathology [M]. 6th ed. Philadelphia:W B Saunders Company, 1997.82~83.
[10]Smith S H, Brown M H, Rowe D, et al.Functional subsets of human helper-inducer cells defined by a new monoclonal antibody, UCHL1 [J]. Immunology, 1986,58(1):63.
[11]Anderson C, Rezuke W N, Kosciol C M,et al. Methods in pathology. Identification of T-cell lymphomas in paraffin-embedded tissues using polyclonal anti-CD3 antibody: comparison with frozen section immunophenotyping and genotypic analysis[J]. Mod Pathol, 1991,4(3):358.
, http://www.100md.com
[12]Lee S P, Tierney R J, Thomas W A, et al. Conserved CTL epitopes within EBV latent membrane protein 2: a potential target for CTL-based tumor therapy[J]. J Immunol, 1997,158(7):3325.
[13]Khanna R, Busson P, Burrows S R, et al. Molecular characterization of antigenprocessing function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC): evidence for efficient presentation of Epstein-Barr virus cytotoxic T-cell epitopes by NPC cells[J]. Cancer Res, 1998,58(2):310.
, 百拇医药
[14]Chen Y, Chew C T, Chan S H. T-cell receptor gene expression in tumourinfiltrating lymphocytes and peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Br J Cancer, 1995,72(1):17.
[15]Khanna R, Burrows S R, Nicholls J, et al. Identification of cytotoxic T cell epitopes within Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) oncogene latent membrane protein 1(LMP1):evidence for HLA A2 supertype-restricted immune recognition of EBV-infected cells by LMP1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes[J]. Eur J Immunol, 1998,28(2):451.
, 百拇医药
[16]Weiss A. Structure and function of the T cell antigen receptor[J]. J Clin Invest, 1990,86(4):1015.
[17]Van der Valk P, Meijer C J L M. Hematopoietic and lymphoid System[A]. In:Sternberg S S, Histology for Pathologists[M]. 2nd ed, Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1997.656.
Received date:1999-05-26, 百拇医药
单位:中山医科大学病理学教研室, 广东 广州 510089
关键词:鼻咽肿瘤;病理学;淋巴细胞;病理学;凋亡
中山医科大学学报000102Correlation Between Infiltrating Lymphoid Cells and
Neoplastic Cell Apoptosis in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
ZONG Yong-sheng
(Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510089, China)
, http://www.100md.com
LI Zhi
(Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510089, China)
LIU Ke-la
(Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510089, China)
MAI Shi-juan
(Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510089, China)
, 百拇医药
LIANG Ying-jie
(Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510089, China)
Abstract:Objective To investigate the correlation between infiltrating lymphoid cells and neoplastic cell apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Methods 38 untreated NPC biopsies were collected from the Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences. TUNEL (TdT-mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling) method was performed for quantitating the apoptosis count (AC, numbers of apoptotic cell from among 5 000 NPC cells). DAKO LSAB kit (K 0681) and respective primary antibodies were used for detecting reactive T-lymphocyte, monocyte/macrophage, pan B-lymphocyte, and accessory dendritic cell immunohistochemically. The amount of infiltrating lymphoid cells was indicated in terms of TCI (T-cell index), MMI (monocyte/macrophage index), BCI (B-cell index), and DCI (dendritic cell index) by their cell numbers per one average high power field, respectively. Results ①The AC varied greatly from case to case in untreated NPCs, the mean value being (12.9±13.9)/5 000; ②The AC was both positively correlated with TCI (P<0.05) and MMI (P<0.05), but not with BCI (P>0.05) and DCI (P>0.05). Conclusions ①The infiltrating T-lymphocytes representing cell-mediated immunity are able to induce NPC cell apoptosis; ②The infiltrating monocytes/macrophages might principally be an apoptosis-inducer or as a consequence of degraded apoptotic debris; ③The infiltrating B-lymphocytes representing humoural immunity and antigen presenting dendritic cells as well are not directly correlated with NPC cell apoptosis.
, 百拇医药
Key words: nasopharyngeal neoplasms/pathology; lymphocytes/pathology; apoptosis
CLC number: R 739.6 Document code: A
Article ID:1000-257 X(2000)01-0006-05
摘 要:目的 研究鼻咽癌中浸润的淋巴类细胞与癌细胞凋亡间的相关性。方法 收集中山医科大学病理学教研室38例未经治疗的鼻咽癌活检标本。应用TUNEL (TdT-mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling)方法定量检测凋亡癌细胞计数(每5 000个鼻咽癌细胞中的凋亡细胞数)。以免疫组化法分别检测T细胞,单核/巨噬细胞,B细胞和树突状细胞。结果 ① 在未经治疗的鼻咽癌活检标本各例间癌细胞凋亡计数差异很大,平均为(12.9±13.9)/5 000; ② 凋亡癌细胞计数与T细胞指数(I,即平均每个高倍视野浸润的T淋巴细胞数)和单核/巨噬细胞指数(moncyte macro phage index,MMI,即平均每个高倍视野浸润的单核/巨噬细胞数)均呈正相关,P<0.05,但凋亡癌细胞计数与B细胞指数(平均每个高倍视野浸润的B淋巴细胞数)和树突状细胞指数(平均每个高倍视野浸润的树突状细胞数)无相关性,P>0.05。结论 ① 代表细胞介导免疫的浸润性T淋巴细胞可以诱导鼻咽癌细胞凋亡; ② 浸润的单核/巨噬细胞可能主要是癌细胞凋亡的诱导者也可能部分是凋亡的后果; ③ 代表体液免疫的浸润性B淋巴细胞和递呈抗原的树突状细胞与鼻咽癌细胞的凋亡无直接相关性。
, 百拇医药
分类号: R 739.6 文献标识码:A
文章编号: 1000-257X(2000)01-0006-05▲
Lymphoinfiltration is a pathognomonic feature of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC)[1], and the amount of infiltrating lymphoid cells including T lymphocyte, monocyte/macrophage, B lymphocyte, and dendritic cell could influence the patients' prognosis[2]. On the other hand, neoplastic cell apoptosis could always be found in human untreated NPC biopsies[3,4]as well as NPC cell line nude mice transplants[5,6]. Does correlation between infiltrating lymphoid cells and neoplastic cell apoptosis exist in untreated NPC? What kinds of infiltrating lymphoid cells are correlated with NPC cell apoptosis? What role do the infiltrating lymphoid cells play on NPC cell apoptosis? This research was aiming at the issues just mentioned above.
, http://www.100md.com
1 MATERIAL & METHODS
1.1 Material
Thirty-eight untreated NPC biopsies were collected from the Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University of Medical Sciences in the year 1997. All the biopsy specimens were fixed in 10% formalin and embedded with paraffin. The paraffin blocks were consecutively sectioned.
1.2 H&E stain
Routine haematoxylin and eosin staining (H&E) was performed on every NPC biopsy slide.
, http://www.100md.com
1.3 In-situ cell death detection
TUNEL [TdT (Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase)-mediated fluorescein-dUTP Nick End Labeling]method was performed for detection and quantification of apoptosis count by use of Boehringer Mannheim “in-situ cell death detection kit, AP (Cat. No. 1684809)". The working procedure was carried out following the enclosed instruction in the kit. The positive signals showed dark purple color.
1.4 Immunohistochemistry
, 百拇医药
LSAB immunohistochemistry and respective primary antibodies were performed for detection of reactive T-lymphocyte, monocyte/macrophage, B-lymphocyte and accessory dendritic cell using DAKO LSAB kit (K 0681) and primary antibodies. The primary antibodies used were UCHL1, Lysozyme EC 3.2.1.17 (Muramidase), L26 and S-100 for reactive T cell, monocyte/macrophage, pan B cell and accessory dendritic cell, respectively. The working dilutions of these antibodies were 1/100, 1/300, 1/100 and 1/150 for UCHL 1, Lysozyme EC 3.2.1.17, L26, and S-100, respectively. Microwave pretreatment using pH6.0 citrate buffer was done before adding the UCHL1 or L26 diluted antibody solution. Trypsin pretreatment was adopted for immunohistochemical detection of S-100 and Lysozyme EC 3.2.1.17.
, 百拇医药
1.5 Apoptosis count of NPC cells
Apoptosis count (AC) of NPC cells was indicated as the numbers of apoptotic cell from among 5 000 NPC cells demonstrated on TUNEL slide by the use of “in-situ cell death detection kit". TCI(T cell index), MMI (monocyte/macrophage index), BCI (B cell index), and DCI (dendritic cell index) were shown as the numbers of positive cell per one average high power field (10×40) by counting at least 5 appropriate fields on their respective immunohistochemically stained slides.
, 百拇医药
1.6 Statistical analysis
Spearman rank correlation was used for statistical analysis.
2 RESULTS
2.1 Morphology of neoplastic cell apoptosis and infiltrating lymphoid cells
According to the criteria of WHO's histological classification, all of the 38 NPC biopsies were of the non-keratinizing carcinoma in type. Among them, 30 belong to undifferentiated subtype (undifferentiated carcinoma of nasopharyngeal type), and 8 belong to differentiated subtype (differentiated non-keratinizing carcinoma). The neoplastic cell AC varied greatly from case to case, the mean value was (12.9±13.2)/5 000. On H&E stained slides, the typically morphological changes of apoptotic cells, such as condensed nucleus and eosinophilic cytoplasm (Fig.1), apoptotic bodies (Fig.2) and apoptotic bodies phagocytosed by neighboring neoplastic cell or macrophage (Fig.3) could be found. These apoptotic cells and bodies showed end-labeling signals on TUNEL slide (Fig.4). The reactive T-lymphocytes (Fig.5), monocytes/macrophages (Fig.6), pan B-lymphocytes (Fig.7) and accessory dendritic cells (Fig.8) infiltrating within the NPC tissues could be clearly distinguished on their specifically stained slides.
 图1 鼻咽未分化癌 示核固缩的调亡细胞;Fig.1 Undifferentiated carcinoma of the nasopharynxShowing an apoptotic cell with condensed nucleus ( H&E 5×100)
图1 鼻咽未分化癌 示核固缩的调亡细胞;Fig.1 Undifferentiated carcinoma of the nasopharynxShowing an apoptotic cell with condensed nucleus ( H&E 5×100)  图2 鼻咽未分化癌 示调亡小体;Fig.2 Undifferenb`ated carcinoma of the nasopharyiixShowing apoptoiic bodies (H&E 5×100)
图2 鼻咽未分化癌 示调亡小体;Fig.2 Undifferenb`ated carcinoma of the nasopharyiixShowing apoptoiic bodies (H&E 5×100)  图3鼻咽未分化癌 示被邻近的瘤细胞所吞噬的调亡小体;Fig.3 Undifferentiated carcinoma of thf nasopharynxShowing an apoptotic body phagocytosed by a neighboring neoplastic cell(H&E 5×100)
图3鼻咽未分化癌 示被邻近的瘤细胞所吞噬的调亡小体;Fig.3 Undifferentiated carcinoma of thf nasopharynxShowing an apoptotic body phagocytosed by a neighboring neoplastic cell(H&E 5×100)  图4调亡中的TUNEL阳性尽咽癌细胞和调亡小体;Fig. 4 TUNEL-positive NPC cells undergoing apoptosis and apoptotic bodies(TUNEL 5×100)
图4调亡中的TUNEL阳性尽咽癌细胞和调亡小体;Fig. 4 TUNEL-positive NPC cells undergoing apoptosis and apoptotic bodies(TUNEL 5×100)  图5鼻咽癌组织中浸润的T淋巴细胞:Fig. 5 T-lymphi)cytes infiltrati`ng in NPC tissue(UCHLI IHC 5×20)
图5鼻咽癌组织中浸润的T淋巴细胞:Fig. 5 T-lymphi)cytes infiltrati`ng in NPC tissue(UCHLI IHC 5×20)  图6鼻咽癌组织中浸润的单核/巨噬细胞;Fig. 6 Monocytes/macrophages infiltrating in NPC tissiie(Lysozyme IHC 5×20)
图6鼻咽癌组织中浸润的单核/巨噬细胞;Fig. 6 Monocytes/macrophages infiltrating in NPC tissiie(Lysozyme IHC 5×20)  图7鼻咽癌组织中浸润的L淋巴细胞;Fig. 7 B-ly'nphocytes infiltrating in NPC tissue(M6 IHC 5×20)
图7鼻咽癌组织中浸润的L淋巴细胞;Fig. 7 B-ly'nphocytes infiltrating in NPC tissue(M6 IHC 5×20)  图8鼻咽癌组织中浸涧的树状突细胞Fig. 8 Dendritic cells iiifiltrating in NPC tissue(5100 IHC 5×20) 2.2 Correlation between neoplastic cell apoptosis count and the indexes of infiltrating lymphoid cells
图8鼻咽癌组织中浸涧的树状突细胞Fig. 8 Dendritic cells iiifiltrating in NPC tissue(5100 IHC 5×20) 2.2 Correlation between neoplastic cell apoptosis count and the indexes of infiltrating lymphoid cells, 百拇医药
The mean values of AC, TCI, MMI, BCI and DCI were 12.9±13.2, 43.7±29.3, 41.4±29.7, 15.1±17.0 and 23.6±23.8, respectively. Rank correlation test was statistically calculated between these indexes by Spearman's formula. The data obtained showed that ①there was significant difference between AC and TCI (r=0.347, P<0.05) as well as AC and MMI (r=0.476, P<0.05); and ② no correlation existed between AC and BCI (r=-0.024,P>0.05) as well as AC and DCI (r=0.189, P>0.05).
, http://www.100md.com 3 DISCUSSION
NPC was formerly called lymphoepithelioma[7]because of a mixed appearance of epithelial and lymphoid cells presenting in tumour growth histopathologically. Since the report of Svoboda et al[8], it is popularly recognized that the lymphoinfiltration is representing an immunological response against epithelial neoplastic cells[9]. In 1993, Zong et al[2]. reported the effect of infiltrating lymphoid cells on NPC patients' prognosis; and recently Li and Zong described the apoptotic features of NPC cells in untreated NPC biopsies[3]and NPC cell line nude mice transplants[5,6]. These findings logically lead the authors to study the correlation between infiltrating lymphoid cells and neoplastic cell apoptosis in NPC. The authors think that to illustrate the basic molecular events involved in untreated NPC cell apoptosis will be of benefit for designing therapeutic research work because either radiotherapy or chemotherapy would play some therapeutic effects on NPC mainly through the pathway of apoptosis.
, 百拇医药
Though the AC and TCI were both varied greatly from case to case, there was a definite positive rank correlation between them as shown in the above result. Worthy to be noted is that a monoclonal antibody, clone UCHL1, was used for detecting infiltrating T-lymphocytes in this study. This antibody can recognize a 180 185ku determinant of reactive T-lymphocytes[10]and is not able to demonstrate pan T cells; and therefore it is an excellent marker for detecting reactive T cell or memory/effector cell[11]. Therefore, the reactive infiltrating T-lymphocytes might have the ability to induce neoplastic cell apoptosis in untreated NPC. According to the logical postulation, the authors further assume that the cell-mediated immunity represented by reactive T cells might exert its effect on NPC cell apoptosis. This finding is an additional evidence and theoretical basis for investigating therapeutic agents to enhance human cell-mediated immunity against NPC[12]. But however, though the authors had demonstrated a definite linkage of reactive T cells and neoplastic cell apoptosis, the interactions between tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and NPC cells would be very complex. On the one hand, NPC cells harbouring Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) could process and present EBV-encoded antigens onto cytotoxic T cells[13]; and on the other hand, the TILs could express T cell receptor gene[14]in NPC tissues. So, the issue concerning correlation of reactive T lymphocytes and NPC cell apoptosis is worthy to be further investigated.
, 百拇医药
How to interpret the positive correlation between AC and MMI? The macrophages can produce a whole array of cytokines including TNF-α(tumour necrosis factor-α) that will combine with TNFR (tumour necrosis factor receptor) expressed on NPC cell surface and trigger the TNF-α-mediated apoptosis[15]. The macrophages can process and present antigens, such as EBV-encoded LMP-1 onto the infiltrating CTLs (cytotoxic T-lymphocytes) in cooperation with HLA A2 antigen[15]. And then, the stimulated CTLs would undergo TCR (T cell receptor) gene rearrangements and become tumour-specific[15,16]. By clonal proliferation the tumour-specific CTLs will in their turn induce apoptosis. However, a few infiltrating monocytes/macrophages might be a consequence of phagocytosis initiated by degraded apoptotic cells (or secondary necrosis following apoptosis). Accordingly, besides reactive T cells, the infiltrating monocytes/macrophages might also play a role in inducing NPC cell apoptosis. It should be noted herein that besides apoptosis-inducing action, the macrophages might lyse the tumour cells by producing some toxic metabolites and proteolytic enzyme[15], therefore resulting in necrosis.
, 百拇医药
No correlation existed between AC and BCI. This revealed that the amount of infiltrating B-lymphocytes, which represent humoural immunity, could not directly influence neoplastic cell apoptosis. It should be pointed out that the humoural immunity might be indirectly even though very little related to apoptosis because, as it is popularly known, there are interactions between cell-mediated and humoural immunity.
The infiltrating dendritic cells might be originated from perivascular tissue as opposed to a derivation from the mononuclear phagocyte system[17]. Unlike monocytes/macrophages, the dendritic cells are poorly phagocytic and have large amount of class Ⅱ molecules on their cell surface[15]. So, the dendritic cells are much more associated with humoural immunity and thus reasonably showed no close correlation between DCI and AC in untreated NPC.
, http://www.100md.com
(本文图见插页1)■
Foundation item:This work was supported by the grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China(39730200-Ⅱ)
Biography: ZONG Yong-sheng (1927-), corresponding author, Jiangsu Province of China, Professor of Pathology.
References:
[1]Zong Y S, Lin H, Choy D T, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma and lymphoinfiltration [J]. Oncology, 1991, 48(4):290.
, http://www.100md.com
[2]Zong Y S, Zhang C Q, Zhang F, et al. Infiltrating lymphocytes and accessory cells in nasopharyngeal carcinoma [J]. Jpn J Cancer Res, 1993, 84(8):900.
[3]李 智,宗永生. 鼻咽癌组织中瘤细胞表达bc1-2、bax和p53及其与凋亡的关系[J].临床与实验病理学杂志, 1999, 15(2):127.
[4]Mutirangura A,Pornthanakasem W, Theamboonlers A, et al. Epstein-Barr viral DNA in serum of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma [J]. Clin Cancer Res, 1998,4(3):665.
, 百拇医药
[5]李 智,宗永生.鼻咽癌细胞株裸鼠移植瘤中癌细胞增生凋亡及其相关基因的表达[J]. 中山医科大学学报,1999,20(1):12.
[6]李 智,傅茂福,宗永生. 鼻咽癌细胞株裸鼠移植瘤中癌细胞的凋亡[J]. 癌症,1999,18(2):172.
[7]Chin K Y, Szutu C. Lymphoepithelioma, a pathological study of 97 cases [J]. Chinese Medical Journal, 1940, Supplement:94.
[8]Svoboda D J, Kirchiner F R, Shanmugaratnam K. The fine structure of nasopharyngeal carcinoma [A]. In:Muri C S, Shanmugaratnam K. Cancer of the Nasopharynx[H]. Copenhagen: UICC Monograph Series Publishing House, 1967,163~171.
, 百拇医药
[9]Kumar V, Cotran R S, Robbins S L. Basic Pathology [M]. 6th ed. Philadelphia:W B Saunders Company, 1997.82~83.
[10]Smith S H, Brown M H, Rowe D, et al.Functional subsets of human helper-inducer cells defined by a new monoclonal antibody, UCHL1 [J]. Immunology, 1986,58(1):63.
[11]Anderson C, Rezuke W N, Kosciol C M,et al. Methods in pathology. Identification of T-cell lymphomas in paraffin-embedded tissues using polyclonal anti-CD3 antibody: comparison with frozen section immunophenotyping and genotypic analysis[J]. Mod Pathol, 1991,4(3):358.
, http://www.100md.com
[12]Lee S P, Tierney R J, Thomas W A, et al. Conserved CTL epitopes within EBV latent membrane protein 2: a potential target for CTL-based tumor therapy[J]. J Immunol, 1997,158(7):3325.
[13]Khanna R, Busson P, Burrows S R, et al. Molecular characterization of antigenprocessing function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC): evidence for efficient presentation of Epstein-Barr virus cytotoxic T-cell epitopes by NPC cells[J]. Cancer Res, 1998,58(2):310.
, 百拇医药
[14]Chen Y, Chew C T, Chan S H. T-cell receptor gene expression in tumourinfiltrating lymphocytes and peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Br J Cancer, 1995,72(1):17.
[15]Khanna R, Burrows S R, Nicholls J, et al. Identification of cytotoxic T cell epitopes within Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) oncogene latent membrane protein 1(LMP1):evidence for HLA A2 supertype-restricted immune recognition of EBV-infected cells by LMP1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes[J]. Eur J Immunol, 1998,28(2):451.
, 百拇医药
[16]Weiss A. Structure and function of the T cell antigen receptor[J]. J Clin Invest, 1990,86(4):1015.
[17]Van der Valk P, Meijer C J L M. Hematopoietic and lymphoid System[A]. In:Sternberg S S, Histology for Pathologists[M]. 2nd ed, Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1997.656.
Received date:1999-05-26, 百拇医药