肝病患者血浆内皮素水平的临床观察
作者:汤正好 李宜 常立非 章秋霞 马良国
单位:安徽省立医院传染科,合肥 230001
关键词:内皮缩血管肽类;血液;肝炎;血液;肝硬化;血液
安徽医科大学学报000117
摘要 目的 探讨内皮素(ET)在肝病中的血浆水平及其临床意义。方法 用特异性放免法测定30例急性肝炎、30例慢性肝炎、20例重症肝炎、30例肝硬化及20例正常人血浆内皮素浓度。结果 慢性肝炎、重症肝炎及肝硬化有腹水和无腹水者血浆ET水平分别为73.1 ng.L-1±24.7 ng.L-1、89.2 ng.L-1±25.4 ng.L-1、98.5 ng.L-1±27.2 ng.L-1、78.6 ng.L-1±25.1 ng.L-1,均明显高于正常人(48 ng.L-1±22.8 ng.L-1)(P<0.01);慢性肝炎与急性肝炎(58.8 ng.L-1±23.7 ng.L-1)比较差异有显著性(P<0.05);重症肝炎、肝硬化有腹水者与慢性肝炎比较差异亦有显著性(P<0.01);肝硬化有腹水者与无腹水者比较差异有显著性(P<0.01)。结论 肝病时血浆ET水平与肝脏损伤的程度有关,血浆ET水平升高可能促进了肝病的发生与发展,并可能与肝硬化患者腹水形成有一定关系。
, http://www.100md.com
中图分类号 R512.6;R575.2
文献标识码 A 文章编号 1000-1492(2000)01-0048-03
Clinical investigation of plasma levels of endothelin
in patients with liver diseases
Tang Zhenghao, Li Yi, Chang Lifei et al
(Dept of Infectious Diseases,Anhui Provincial Hospital,Hefei 230001)
Abstract Objective To investigate the plasma levels of endothelin and to assess the clinical significance of endothelin in patients with hepatic diseases. Methods Plasma endothelin concentrations were using specific ra-dioimmunoassays in patients with acute hepatitis (n=30), chronic hepatitis (n=30), severe hepatitis (n=20), cirrhosis with ascites (n=15), cirrhosis without ascites (n=15), and normal subjects (n=20). Results The plasma endothelin concentrations were significantly higher in patients with chronic hepatitis (73.1 ng.L-1±24.7 ng.L-1), severe hepatitis (89.2 ng.L-1±25.4 ng.L-1), cirrhosis with ascites (98.5 ng.L-1±27.2 ng.L-1) and cirrhosis without ascites (78.6 ng.L-1±25.1 ng.L-1) than in patients with acute hepatitis (58.8 ng.L-1±23.7 ng.L-1)(P<0.01); patients with severe hepatitis and with cirrhosis had higher plasma levels of endothelin as compared with patients with chronic hepatitis (P<0.01). Furthermore, significant difference was observed between cirrhosis with ascites and without ascites (P<0.01); no significant difference was observed between patients with acute hepatitis and normal subjects(48 ng.L-1±22.8 ng.L-1) as well as between patients with chronic hepatitis and cirrhotics without ascites (P>0.05). Conclusion Elevated plasma endothelin may play a contributory role in development of liver diseases and has a close relation to the formation of ascites in patients with cirrhosis.
, 百拇医药
MeSH endothelins/blood; hepatitis/blood; liver cirrhosis/blood
内皮素(Endothelin, ET)是一种由血管内皮细胞合成和释放的含有21个氨基酸残基的血管活性肽,具有强烈而持久的血管收缩作用〔1〕,根据编码的基因不同分为ET-1、ET-2、ET-3三种〔2〕。研究表明,ET除在血管紧张性的调节上起着重要作用外,还在肝脏中发挥着重要的生物效应。我们应用特异性放射免疫分析法对急、慢性肝炎、重症肝炎以及肝硬化患者血浆ET水平进行了检测,以探讨ET在肝病中的病理生理意义。
1 材料与方法
1.1 研究对象 110例患者为我院1996年1月~1998年12月的住院患者,参照1995年全国传染病与寄生虫病学术会议修订的诊断标准诊断和分型〔3〕。急性肝炎30例,男26例、女4例,平均年龄为26岁(18~54岁);慢性肝炎30例;男25例、女5例,平均年龄34岁(12~61岁);重症型肝炎20例,男16例、女性4例,平均年龄45岁(26~65岁);肝硬化有腹水者15例,男11例,女4例,平均年龄58岁(46~68岁);肝硬化无腹水者15例,男12例、女3例,平均年龄52岁(28~66岁)。正常人:我院健康献血员共20例,男10例、女10例,平均年龄39岁(20~62岁)。
, http://www.100md.com
1.2 标本采集 急、慢性肝炎,重症肝炎患者于肝功能异常高峰期在早晨安静状态下空腹卧位,采集肘静脉血2 ml,肝硬变患者低盐饮食并停用利尿剂3天后于早晨安静状态下,空腹卧位采集肘静脉血2 ml。所有标本置于含EDTA二钠30 μl和400 IU的抑肽酶试管中混合,并立即离心,血浆置-20℃冰箱中保存待测。
1.3 测定方法 血浆ET采用特异性放射免疫法测定,试剂盒由解放军总医院东亚免疫技术研究所提供,标准曲线测定范围5~5120 ng.L-1 ,灵敏度为2 ng.L-1 ,批间变异<15%,批内变异<10%。与心纳素,血管紧张Ⅰ、Ⅱ及舒血管肠肽,降钙素基因相关肽无交叉反应。
2 结果
肝病患者与正常人血浆ET水平检测结果见表1。结果显示,所有肝病患者血浆ET水平均有不同程度的升高,尤其重症肝炎与肝硬化有腹水者升高最为明显,经统计学分析:急性肝炎与正常人比较差异无显著性(P>0.05),而慢性肝炎、重症肝炎、肝硬化有腹水者及无腹水者与正常人比较ET水平明显升高(P<0.01);重症肝炎及肝硬化有腹水组明显高于慢性肝炎组(P<0.01),而肝硬化无腹水组与慢性肝炎比较差异无显著性(P>0.05);肝硬化有腹水组与无腹水组比较差异有显著性(P<0.01)。
, 百拇医药
表1 各组肝病患者血浆ET检测结果(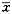 ±s) 组别
±s) 组别
n
ET/ng.L-1
急性肝炎
30
58.8±23.7
慢性肝炎
30
73.1±24.7
重症肝炎
20
, 百拇医药
89.2±25.4
肝硬化有腹水
15
98.5±27.2
肝硬化无腹水
15
78.6±25.1
正常人
20
48.4±22.8
3 讨论
ET是迄今发现的作用最强、持续时间最长的缩血管活性肽〔1〕,目前已证实ET除分布在全身血管内皮细胞外,还广泛分布于心、肝、脑、肺、肾等多种非血管组织,通过与ET受体结合发挥多种生物学效应。肝脏中除血管内皮细胞表达ET外,星状细胞及Kupffers细胞也有ET的表达。动物实验证实,在肝脏缺血再灌注损伤时,肝组织内血液中ET水平明显增加〔4〕。另有学者通过PCR技术发现肝硬化患者肝窦内皮细胞及星状细胞上ET-1 mRNA表达明显增加〔5〕,说明肝脏损伤时肝组织内ET合成增加。
, http://www.100md.com
但迄今为止,对肝病患者血浆ET水平的研究结果却不一致。Uchihara等〔6〕研究发现肝硬化有腹水者血浆ET水平是正常人的两倍多。Asbert等〔7〕亦发现肝硬化有腹水者血浆ET水平明显高于正常对照和代偿期肝硬化者。而Lerman等〔8〕和Veglio等〔9〕则发现肝硬化有腹水者血浆ET水平并不升高而是正常或降低。此可能与所研究的患者病情轻重程度或研究的方法、条件不同有关。
本组资料结果显示:慢性肝炎、重症肝炎、肝硬化患者血浆ET水平均高于正常对照及急性肝炎组,尤其是重症肝炎与肝硬化有腹水者升高最为明显,提示血浆ET水平与肝脏损伤的程度可能存在一定的关系。肝脏损伤越重,肝及其他组织、血管内皮ET合成则越多,血浆ET水平升高;而ET的增多又可引起肝窦的收缩,肝细胞缺血、缺氧进一步加重肝脏损伤的程度〔10〕。由于循环中的ET主要经肺、肾清除,而经肝脏清除的ET量极少,故因肝清除功能下降而引起血浆ET水平升高的可能性不大。
, 百拇医药
本组资料还显示,肝硬化有腹水者血浆ET水平明显高于无腹水者,与Asbert等〔7〕报道的结果基本一致。其原因可能是由于肝硬化失代偿时体内内毒素水平升高,而内毒素则是刺激ET产生和释放的主要因素之一,可刺激肝组织及其他组织细胞和血管内皮细胞合成和分泌ET,从而导致血浆ET水平升高〔11〕。
肝病患者血浆ET水平升高表明ET在肝病的发生发展中可能起到了一定的促进作用,但由于ET与其他多种血管活性介质如前列腺素、血管紧张素Ⅱ、内皮衍生的血管舒张因子(EDRF)等共同参与体内血管舒缩的调节,因此,ET在肝病中与其他血管活性调节因子之间的相互关系值得进一步研究。
作者简介:汤正好,男,33岁,硕士,主治医师;
马良国,男,60岁,主任医师
参考文献
, http://www.100md.com
1,Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S et al. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature, 1988;332:411~415
2,Inoue A, Yanagisawa M, Kimura S et al. The human endothelin family, three structurally and pharmacologically distinct isopeptides predicted by three separate genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1989;86:2863~2867
3,中华医学会. 病毒性肝炎防治方案(试行).中华传染病杂志,1995;13(4):241~247
, 百拇医药
4,Kawanura E, Yamanaka N, Okamoto E et al. Response of Plasma and tissue endothelin-1 to liver ischemia and its implication in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Hepatology, 1995;21(4):1138~1143
5,Pinzani M, Milani S, Franco R et al. Endothelin is overexpressed in human cirrhotic liver and exerts multiple effects on actived hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology, 1996;110(2):534~548
6,Uchihara M, Izumi N, Sato C et al. Clinical significance of evevated plasma endothelin concentration in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology, 1992;16(1):95~99
, 百拇医药
7,Asbert M, Gines A, Gines P et al. Circulating levels of endothelin in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology, 1993;104(5):1485~1491
8,Lerman A, Click RL, Narr BJ et al. Evaluation of plasma endothelin associated with systemic hypertension in humans following orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation, 1991;51(3):646~650
9,Veglio F, Pinna G, Melchio R et al. Plasma endothelin levels in cirrhotic subjects. J Hepatol, 1992;15(1):85~87
, 百拇医药
10,Okumura S, Takei Y, Kawano S et al. Vasoactive effect of endothelin-1 on rat liver in vivo. Hepatology, 1994;19(1):155~161
11,Sugiura M, Inagami T, Kon V. Endotoxinstimulates endothelin-release in vivo and in vitro as determined by radioimmunoassay. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1989;161(5):1220~1227
1999-09-16收稿,1999-12-14修回, http://www.100md.com
单位:安徽省立医院传染科,合肥 230001
关键词:内皮缩血管肽类;血液;肝炎;血液;肝硬化;血液
安徽医科大学学报000117
摘要 目的 探讨内皮素(ET)在肝病中的血浆水平及其临床意义。方法 用特异性放免法测定30例急性肝炎、30例慢性肝炎、20例重症肝炎、30例肝硬化及20例正常人血浆内皮素浓度。结果 慢性肝炎、重症肝炎及肝硬化有腹水和无腹水者血浆ET水平分别为73.1 ng.L-1±24.7 ng.L-1、89.2 ng.L-1±25.4 ng.L-1、98.5 ng.L-1±27.2 ng.L-1、78.6 ng.L-1±25.1 ng.L-1,均明显高于正常人(48 ng.L-1±22.8 ng.L-1)(P<0.01);慢性肝炎与急性肝炎(58.8 ng.L-1±23.7 ng.L-1)比较差异有显著性(P<0.05);重症肝炎、肝硬化有腹水者与慢性肝炎比较差异亦有显著性(P<0.01);肝硬化有腹水者与无腹水者比较差异有显著性(P<0.01)。结论 肝病时血浆ET水平与肝脏损伤的程度有关,血浆ET水平升高可能促进了肝病的发生与发展,并可能与肝硬化患者腹水形成有一定关系。
, http://www.100md.com
中图分类号 R512.6;R575.2
文献标识码 A 文章编号 1000-1492(2000)01-0048-03
Clinical investigation of plasma levels of endothelin
in patients with liver diseases
Tang Zhenghao, Li Yi, Chang Lifei et al
(Dept of Infectious Diseases,Anhui Provincial Hospital,Hefei 230001)
Abstract Objective To investigate the plasma levels of endothelin and to assess the clinical significance of endothelin in patients with hepatic diseases. Methods Plasma endothelin concentrations were using specific ra-dioimmunoassays in patients with acute hepatitis (n=30), chronic hepatitis (n=30), severe hepatitis (n=20), cirrhosis with ascites (n=15), cirrhosis without ascites (n=15), and normal subjects (n=20). Results The plasma endothelin concentrations were significantly higher in patients with chronic hepatitis (73.1 ng.L-1±24.7 ng.L-1), severe hepatitis (89.2 ng.L-1±25.4 ng.L-1), cirrhosis with ascites (98.5 ng.L-1±27.2 ng.L-1) and cirrhosis without ascites (78.6 ng.L-1±25.1 ng.L-1) than in patients with acute hepatitis (58.8 ng.L-1±23.7 ng.L-1)(P<0.01); patients with severe hepatitis and with cirrhosis had higher plasma levels of endothelin as compared with patients with chronic hepatitis (P<0.01). Furthermore, significant difference was observed between cirrhosis with ascites and without ascites (P<0.01); no significant difference was observed between patients with acute hepatitis and normal subjects(48 ng.L-1±22.8 ng.L-1) as well as between patients with chronic hepatitis and cirrhotics without ascites (P>0.05). Conclusion Elevated plasma endothelin may play a contributory role in development of liver diseases and has a close relation to the formation of ascites in patients with cirrhosis.
, 百拇医药
MeSH endothelins/blood; hepatitis/blood; liver cirrhosis/blood
内皮素(Endothelin, ET)是一种由血管内皮细胞合成和释放的含有21个氨基酸残基的血管活性肽,具有强烈而持久的血管收缩作用〔1〕,根据编码的基因不同分为ET-1、ET-2、ET-3三种〔2〕。研究表明,ET除在血管紧张性的调节上起着重要作用外,还在肝脏中发挥着重要的生物效应。我们应用特异性放射免疫分析法对急、慢性肝炎、重症肝炎以及肝硬化患者血浆ET水平进行了检测,以探讨ET在肝病中的病理生理意义。
1 材料与方法
1.1 研究对象 110例患者为我院1996年1月~1998年12月的住院患者,参照1995年全国传染病与寄生虫病学术会议修订的诊断标准诊断和分型〔3〕。急性肝炎30例,男26例、女4例,平均年龄为26岁(18~54岁);慢性肝炎30例;男25例、女5例,平均年龄34岁(12~61岁);重症型肝炎20例,男16例、女性4例,平均年龄45岁(26~65岁);肝硬化有腹水者15例,男11例,女4例,平均年龄58岁(46~68岁);肝硬化无腹水者15例,男12例、女3例,平均年龄52岁(28~66岁)。正常人:我院健康献血员共20例,男10例、女10例,平均年龄39岁(20~62岁)。
, http://www.100md.com
1.2 标本采集 急、慢性肝炎,重症肝炎患者于肝功能异常高峰期在早晨安静状态下空腹卧位,采集肘静脉血2 ml,肝硬变患者低盐饮食并停用利尿剂3天后于早晨安静状态下,空腹卧位采集肘静脉血2 ml。所有标本置于含EDTA二钠30 μl和400 IU的抑肽酶试管中混合,并立即离心,血浆置-20℃冰箱中保存待测。
1.3 测定方法 血浆ET采用特异性放射免疫法测定,试剂盒由解放军总医院东亚免疫技术研究所提供,标准曲线测定范围5~5120 ng.L-1 ,灵敏度为2 ng.L-1 ,批间变异<15%,批内变异<10%。与心纳素,血管紧张Ⅰ、Ⅱ及舒血管肠肽,降钙素基因相关肽无交叉反应。
2 结果
肝病患者与正常人血浆ET水平检测结果见表1。结果显示,所有肝病患者血浆ET水平均有不同程度的升高,尤其重症肝炎与肝硬化有腹水者升高最为明显,经统计学分析:急性肝炎与正常人比较差异无显著性(P>0.05),而慢性肝炎、重症肝炎、肝硬化有腹水者及无腹水者与正常人比较ET水平明显升高(P<0.01);重症肝炎及肝硬化有腹水组明显高于慢性肝炎组(P<0.01),而肝硬化无腹水组与慢性肝炎比较差异无显著性(P>0.05);肝硬化有腹水组与无腹水组比较差异有显著性(P<0.01)。
, 百拇医药
表1 各组肝病患者血浆ET检测结果(
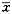 ±s) 组别
±s) 组别n
ET/ng.L-1
急性肝炎
30
58.8±23.7
慢性肝炎
30
73.1±24.7
重症肝炎
20
, 百拇医药
89.2±25.4
肝硬化有腹水
15
98.5±27.2
肝硬化无腹水
15
78.6±25.1
正常人
20
48.4±22.8
3 讨论
ET是迄今发现的作用最强、持续时间最长的缩血管活性肽〔1〕,目前已证实ET除分布在全身血管内皮细胞外,还广泛分布于心、肝、脑、肺、肾等多种非血管组织,通过与ET受体结合发挥多种生物学效应。肝脏中除血管内皮细胞表达ET外,星状细胞及Kupffers细胞也有ET的表达。动物实验证实,在肝脏缺血再灌注损伤时,肝组织内血液中ET水平明显增加〔4〕。另有学者通过PCR技术发现肝硬化患者肝窦内皮细胞及星状细胞上ET-1 mRNA表达明显增加〔5〕,说明肝脏损伤时肝组织内ET合成增加。
, http://www.100md.com
但迄今为止,对肝病患者血浆ET水平的研究结果却不一致。Uchihara等〔6〕研究发现肝硬化有腹水者血浆ET水平是正常人的两倍多。Asbert等〔7〕亦发现肝硬化有腹水者血浆ET水平明显高于正常对照和代偿期肝硬化者。而Lerman等〔8〕和Veglio等〔9〕则发现肝硬化有腹水者血浆ET水平并不升高而是正常或降低。此可能与所研究的患者病情轻重程度或研究的方法、条件不同有关。
本组资料结果显示:慢性肝炎、重症肝炎、肝硬化患者血浆ET水平均高于正常对照及急性肝炎组,尤其是重症肝炎与肝硬化有腹水者升高最为明显,提示血浆ET水平与肝脏损伤的程度可能存在一定的关系。肝脏损伤越重,肝及其他组织、血管内皮ET合成则越多,血浆ET水平升高;而ET的增多又可引起肝窦的收缩,肝细胞缺血、缺氧进一步加重肝脏损伤的程度〔10〕。由于循环中的ET主要经肺、肾清除,而经肝脏清除的ET量极少,故因肝清除功能下降而引起血浆ET水平升高的可能性不大。
, 百拇医药
本组资料还显示,肝硬化有腹水者血浆ET水平明显高于无腹水者,与Asbert等〔7〕报道的结果基本一致。其原因可能是由于肝硬化失代偿时体内内毒素水平升高,而内毒素则是刺激ET产生和释放的主要因素之一,可刺激肝组织及其他组织细胞和血管内皮细胞合成和分泌ET,从而导致血浆ET水平升高〔11〕。
肝病患者血浆ET水平升高表明ET在肝病的发生发展中可能起到了一定的促进作用,但由于ET与其他多种血管活性介质如前列腺素、血管紧张素Ⅱ、内皮衍生的血管舒张因子(EDRF)等共同参与体内血管舒缩的调节,因此,ET在肝病中与其他血管活性调节因子之间的相互关系值得进一步研究。
作者简介:汤正好,男,33岁,硕士,主治医师;
马良国,男,60岁,主任医师
参考文献
, http://www.100md.com
1,Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S et al. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature, 1988;332:411~415
2,Inoue A, Yanagisawa M, Kimura S et al. The human endothelin family, three structurally and pharmacologically distinct isopeptides predicted by three separate genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1989;86:2863~2867
3,中华医学会. 病毒性肝炎防治方案(试行).中华传染病杂志,1995;13(4):241~247
, 百拇医药
4,Kawanura E, Yamanaka N, Okamoto E et al. Response of Plasma and tissue endothelin-1 to liver ischemia and its implication in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Hepatology, 1995;21(4):1138~1143
5,Pinzani M, Milani S, Franco R et al. Endothelin is overexpressed in human cirrhotic liver and exerts multiple effects on actived hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology, 1996;110(2):534~548
6,Uchihara M, Izumi N, Sato C et al. Clinical significance of evevated plasma endothelin concentration in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology, 1992;16(1):95~99
, 百拇医药
7,Asbert M, Gines A, Gines P et al. Circulating levels of endothelin in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology, 1993;104(5):1485~1491
8,Lerman A, Click RL, Narr BJ et al. Evaluation of plasma endothelin associated with systemic hypertension in humans following orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation, 1991;51(3):646~650
9,Veglio F, Pinna G, Melchio R et al. Plasma endothelin levels in cirrhotic subjects. J Hepatol, 1992;15(1):85~87
, 百拇医药
10,Okumura S, Takei Y, Kawano S et al. Vasoactive effect of endothelin-1 on rat liver in vivo. Hepatology, 1994;19(1):155~161
11,Sugiura M, Inagami T, Kon V. Endotoxinstimulates endothelin-release in vivo and in vitro as determined by radioimmunoassay. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1989;161(5):1220~1227
1999-09-16收稿,1999-12-14修回, http://www.100md.com