特发性血小板减少性紫癜患儿T细胞免疫功能的变化
作者:周平 吕枫林 姚咏明 王江 于燕
单位:100081 北京,解放军第四六六医院儿科(周平、吕枫林、王江);解放军第三○四医院创伤外科中心(姚咏明,于燕)
关键词:紫癜;血小板减少性;特发性;T淋巴细胞;白细胞介素10;γ-干扰素
中华儿科杂志990104 【摘要】 目的 探讨T淋巴细胞亚群、白细胞介素10(IL-10) 、γ-干扰素(IFN-γ)在特发性血小板减少性紫癜(ITP)中的变化及其用地塞米松(DEX)治疗的影响。方法 采用DEX治疗ITP患
儿,分别于治疗前后采取静脉血标本,应用改良碱性磷酸酶-抗碱性磷酸酶(APAAP)法及酶标记免疫吸附测定(ELISA)法分别检测T细胞亚群及血清IL-10、IFN-γ的含量。结果 ITP患儿DEX治疗前外周血 降低,
降低, 升高,
升高, /
/ 显著降低;DEX治疗后
显著降低;DEX治疗后 、
、 均降低,其中以
均降低,其中以 降低尤为显著,但
降低尤为显著,但 /
/ 明显高于治疗前。ITP患儿DEX治疗前血清IFN-γ显著升高,治疗后则降至正常水平,IFN-γ与外周血小板计数呈显著负相关,但与T淋巴细胞亚群无显著相关性。ITP患儿DEX治疗前血清IL-10显著降低,治疗后升高,ITP患儿血清IL-10与外周血血小板计数呈显著正相关,但与T淋巴细胞亚群无显著相关性。结论 ITP患儿T淋巴细胞亚群表达及比例失调,IFN-γ产生增多,IL-10产生减少,提示辅助T淋巴细胞亚型(Th1/Th2)功能异常。DEX治疗ITP能有效缓解病情。
明显高于治疗前。ITP患儿DEX治疗前血清IFN-γ显著升高,治疗后则降至正常水平,IFN-γ与外周血小板计数呈显著负相关,但与T淋巴细胞亚群无显著相关性。ITP患儿DEX治疗前血清IL-10显著降低,治疗后升高,ITP患儿血清IL-10与外周血血小板计数呈显著正相关,但与T淋巴细胞亚群无显著相关性。结论 ITP患儿T淋巴细胞亚群表达及比例失调,IFN-γ产生增多,IL-10产生减少,提示辅助T淋巴细胞亚型(Th1/Th2)功能异常。DEX治疗ITP能有效缓解病情。
, http://www.100md.com
Changes in T cell-mediated immunity in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura ZHOU Ping*,LU Fenglin, YAO Yongming,et al. * Department of Pediatrics, The 466th Hospital of People's Liberation Army, Beijing 100081
【Abstract】 Objective To investigate the changes in T lymphocyte subsets, interleukin-10 (IL-10) and gamma interferon (IFN-γ) in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) and the effect of dexamethasone (DEX) treatment. Methods The blood samples were collected in ITP patients prior and post DEX treatment. T lymphocyte subsets of peripheral blood were examined by using APAAP method, and serum IL-10, IFN-γ levels were measured by using ELISA assay. Additionally, 12 healthy volunteers served as normal controls.Results Compared to normal controls, these ITP patients showed an elevation in percentage of cells, but decrease in
cells, but decrease in  cells as well as ratio of
cells as well as ratio of  /
/ in peripheral blood. After DEX treatment, the expression of both
in peripheral blood. After DEX treatment, the expression of both cells and
cells and  cells was profoundly inhibited, especially for CD+8 cells, while the ratio of
cells was profoundly inhibited, especially for CD+8 cells, while the ratio of  /
/ was significantly increased. Serum levels of IFN-γ increased obviously in children with ITP and negatively correlated with platelet counts, but they were reduced by DEX. However, serum levels of IL-10, which were diminished in these patients and positively correlated with platelet counts, were increased after DEX treatment. Nevertheless, no marked correlation was found between IFN-γ or IL-10 levels and T lymphocyte subsets. Conclusion In ITP patients, abnormal distribution of T lymphocyte subsets and changes in serum IFN-γ, IL-10 levels may imply the dysfunction of Th1/Th2. Treatment with DEX has beneficial effect on ITP, which appears to be associated with the regulation of T lymphocyte subsets expression and cytokine production.
was significantly increased. Serum levels of IFN-γ increased obviously in children with ITP and negatively correlated with platelet counts, but they were reduced by DEX. However, serum levels of IL-10, which were diminished in these patients and positively correlated with platelet counts, were increased after DEX treatment. Nevertheless, no marked correlation was found between IFN-γ or IL-10 levels and T lymphocyte subsets. Conclusion In ITP patients, abnormal distribution of T lymphocyte subsets and changes in serum IFN-γ, IL-10 levels may imply the dysfunction of Th1/Th2. Treatment with DEX has beneficial effect on ITP, which appears to be associated with the regulation of T lymphocyte subsets expression and cytokine production.
, 百拇医药
【Key words】 Purpura, thrombocytopenic, idiopathic T-lymphocyte subsets Interleukin-10 Gamma interferon
特发性血小板减少性紫癜(ITP)的发病机制尚未完全明确,目前认为其发生不仅与B细胞功能异常有关,与T淋巴细胞、自然杀伤细胞(NK)的表达及功能的改变均密切相关[1,2]。我们采用地塞米松(DEX)治疗ITP,检测治疗前后患儿外周血T淋巴细胞亚群、血清白细胞介素10(IL-10)、γ-干扰素(IFN-γ)含量的变化,并分析IL-10、IFN-γ与T淋巴细胞亚群及外周血血小板计数的相关性,旨在进一步探讨ITP自身免疫的病理机制,并为其治疗提供理论依据。
对象和方法
一、对象
1996年12月~1998年4月,住我院的ITP患儿共13例[3],男7例,女6例;年龄为1.0~12.0岁,平均为4.2岁。其中血小板低于2.5×109/L者10例,血小板为(2.5~5.0)×109/L者3例。对照组小儿12例,为同期健康体检小儿,其中男8例,女4例,年龄为3.0~8.0岁,平均3.4岁。
, http://www.100md.com
二、方法
1.所有ITP患儿均以DEX 1 mg/(kg.d)静脉滴注,7天后逐渐减量,2周后改为泼尼松口服,DEX治疗前及治疗后14天各抽血1次。
2.T淋巴细胞亚群的测定:采用改良碱性磷酸酶-抗碱性磷酸酶(APAAP)法测定, 、
、 单抗由军事医学科学院基础医学研究所提供。
单抗由军事医学科学院基础医学研究所提供。
3.IFN-γ、IL-10的测定:采用酶标记免疫吸附测定(ELISA)法,试剂系美国Genzyme公司产品,按试剂盒说明进行检测。
三、统计学处理
采用t检验和直线回归相关分析,结果以均数±标准差(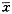 ±s)表示。
±s)表示。
, 百拇医药
结果
一、ITP患儿外周血T淋巴细胞亚群的变化
ITP患儿外周血 为(35±6)%,为对照组小儿的86.3%[4];
为(35±6)%,为对照组小儿的86.3%[4]; 为(32±10)%,是对照组小儿的116.6%;
为(32±10)%,是对照组小儿的116.6%; /
/ 为(1.1±0.3)%,较对照组小儿显著降低[4]。DEX治疗后,
为(1.1±0.3)%,较对照组小儿显著降低[4]。DEX治疗后, 为(29±5)%,CD+8为(20±6)%,均显著低于治疗前(P<0.05~0.01),
为(29±5)%,CD+8为(20±6)%,均显著低于治疗前(P<0.05~0.01), /
/ 为(1.5±0.3)%,较治疗前显著升高(P<0.01)(表1)。
为(1.5±0.3)%,较治疗前显著升高(P<0.01)(表1)。
, http://www.100md.com
二、ITP患儿血清IFN-γ、IL-10的变化
ITP患儿DEX治疗前血清IFN-γ显著高于对照组,DEX治疗后则降至正常水平。而其血清IL-10水平,DEX治疗前显著低于对照组,治疗后则明显升高(表1) 。
表1 ITP患儿治疗前后血清IFN-γ、IL-10及外周血T淋巴细胞亚群的变化(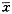 ±s) 组别
±s) 组别
例数
IFN-γ(ng/L)
IL-10(ng/L)
例数 (%)
(%) (%)
(%) /
/
, http://www.100md.com
对照组
12
593±264
27±4
31
41±7
27± 4
1.6±0.3
ITP组
治疗前
13
1 819±569
17±5
, http://www.100md.com
13
35±6
32±10
1.1±0.3
治疗后
13
582±225
23±6
13
29±5
20± 6
1.5±0.3
治疗前与正常比t值
, http://www.100md.com
6.808*
5.065*
2.606**
2.172**
5.175*
治疗前后配对比t值
7.332*
2.746**
2.782**
3.154*
, 百拇医药
4.015*
* P<0.01 ** P<0.05
三、ITP患儿血清IFN-γ、IL-10与外周血血小板、T淋巴细胞亚群的相关性
ITP患儿血清IFN-γ与外周血血小板计数呈显著负相关(r =-0.517,P<0.01),与T淋巴细胞亚群无显著相关关系。IL-10与外周血血小板计数呈显著正相关(r =0.418,P<0.05),与T淋巴细胞亚群无明显相关关系。
讨论
ITP系自身免疫性疾病,由于体内抗原如人类白细胞抗原-DR(HLA-DR)的表达异常,激活了自身反应性T淋巴细胞,并诱导抗血小板自身抗体产生增多[5]。本研究结果显示,ITP患儿外周血 为正常儿童的86.3%,
为正常儿童的86.3%, 较正常儿童明显增多,
较正常儿童明显增多, /
/ 显著降低,提示ITP患儿外周血T淋巴细胞表面标志表达异常,T淋巴细胞亚群比例失调,与文献报道一致[1]。DEX治疗后,
显著降低,提示ITP患儿外周血T淋巴细胞表面标志表达异常,T淋巴细胞亚群比例失调,与文献报道一致[1]。DEX治疗后, 、
、 均明显下降,但
均明显下降,但 /
/ 显著升高,提示DEX抑制了ITP患儿T淋巴细胞抗原的表达,其中对CD+8抑制尤甚。由于异常激活的
显著升高,提示DEX抑制了ITP患儿T淋巴细胞抗原的表达,其中对CD+8抑制尤甚。由于异常激活的 具有抑制造血的作用,这样DEX抑制CD+8细胞的表达,可能有助于血小板的生成。
具有抑制造血的作用,这样DEX抑制CD+8细胞的表达,可能有助于血小板的生成。
, http://www.100md.com
辅助型T淋巴细胞(Th)可分为Th1和Th2,其中Th1主要分泌白细胞介素2(IL-2)、IFN-γ等,调节细胞免疫;Th2主要分泌白细胞介素4(IL-4),IL-10等,参与体液免疫。IFN-γ能抑制Th2类细胞因子的产生,促进Th1类细胞因子的产生。相反,IL-10可抑制Th1类细胞因子的产生,促Th2类细胞因子的产生。本组资料显示,ITP患儿血清IFN-γ显著升高,而IL-10显著降低,提示ITP患儿Th1/Th2功能异常,Th1活力增强。
IFN-γ具有强大的免疫调节作用,可影响B细胞增殖分化成为浆细胞,使免疫球蛋白分泌增加,并通过上调巨噬细胞Fc受体的表达而增强单核巨噬细胞功能[6]。因此,ITP患儿血清
IFN-γ升高可能导致机体血小板相关抗体分泌增多,巨噬细胞对血小板破坏增强。进一步分析发现,ITP患儿血小板破坏越严重,IFN-γ增高越显著。但IFN-γ与外周血T淋巴细胞亚群间未显示出明显的相关性,可能与我们观察例数较少有关。
, http://www.100md.com
IL-10为体内重要的免疫抑制因子,它能抑制巨噬细胞、Th1细胞因子的合成,下调巨噬细胞抗原提呈功能,抑制IFN-γ的mRNA转录[7]。ITP患儿血清IL-10降低,对IFN-γ的抑制减弱。相关分析表明,ITP患儿血清IL-10与其外周血血小板计数呈显著正相关关系,初步提示体内IL-10的异常改变可能参与了ITP的病理过程。
DEX作为一种强有力的免疫抑制剂,在临床上治疗ITP取得了良好疗效。研究表明,DEX在转录水平能抑制多种细胞因子如肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)、IL-2、IFN-γ的产生。我们的研究结果表明,DEX显著抑制了ITP患儿血清IFN-γ的产生,但对IL-10的产生无抑制作用。相反,DEX治疗后,ITP患儿血清IL-10显著升高,与Ramierz等[8]的报道基本相符。
上述结果表明,ITP患儿存在T淋巴细胞免疫功能紊乱, IFN-γ产生增多,IL-10产生减少。其详细作用机制目前尚未明了,有待进一步探讨。
, 百拇医药
参考文献
[1] Garcia-Suarez J, Prieto A, Reyes E, et al. The clinical outcome of autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura patients is related to their T cell immunodeficiency. Br J Haematol, 1993, 84:464-470.
[2] Semple JW, Bruce S, Freedman J. Suppressed natural killer cell activity in patients with chronic autoimmune thrombocytopemic purpura. Am J Hematol, 1991, 37:258-262.
[3] 特发性血小板减少性紫癜诊疗常规.中华儿科杂志,1987, 25:104-105.
, 百拇医药
[4] 曾柏锦,钱幼琼, 郑德元,等.营养不良及低血锌患儿IgG亚类缺陷及T细胞亚群改变.中华儿科杂志,1991,29:11-13.
[5] Semple JW, Miler Y, Cosgrave D, et al. Differences in serum cytokine levels in acute and chronic autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura: relationship to platelet phenotype and antiplatelet T-cell reactivity. Blood, 1996, 87:4245-4254.
[6] Garcia-Suarez J, Prieto A, Reyes E, et al. Abnormal gamma-IFN and alpha-TNF secretion in purified CD2+ cells from autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura (ATP) patients: their implication in the clinical caurse of the disease. Am J Hematol, 1995, 49:271-276.
, 百拇医药
[7] Krakauer T. Differential inhibitory effects of interleukin-10, interleukin-4, and dexamethasone on staphylococcal enterotoxin-induced cytokine production and T cell activation. J Leuka Biol,1995, 57:450-454.
[8] Ramierz F, Fowell DJ, Pukivec M, et al. Glucocorticoids promote a Th2 cytokine production by CD4+ T cells in vitro. J Immunol, 1996,156:2406-2412.
(收稿:1998-08-17 修回:1998-09-25), 百拇医药
单位:100081 北京,解放军第四六六医院儿科(周平、吕枫林、王江);解放军第三○四医院创伤外科中心(姚咏明,于燕)
关键词:紫癜;血小板减少性;特发性;T淋巴细胞;白细胞介素10;γ-干扰素
中华儿科杂志990104 【摘要】 目的 探讨T淋巴细胞亚群、白细胞介素10(IL-10) 、γ-干扰素(IFN-γ)在特发性血小板减少性紫癜(ITP)中的变化及其用地塞米松(DEX)治疗的影响。方法 采用DEX治疗ITP患
儿,分别于治疗前后采取静脉血标本,应用改良碱性磷酸酶-抗碱性磷酸酶(APAAP)法及酶标记免疫吸附测定(ELISA)法分别检测T细胞亚群及血清IL-10、IFN-γ的含量。结果 ITP患儿DEX治疗前外周血
 降低,
降低, 升高,
升高, /
/ 显著降低;DEX治疗后
显著降低;DEX治疗后 、
、 均降低,其中以
均降低,其中以 降低尤为显著,但
降低尤为显著,但 /
/ 明显高于治疗前。ITP患儿DEX治疗前血清IFN-γ显著升高,治疗后则降至正常水平,IFN-γ与外周血小板计数呈显著负相关,但与T淋巴细胞亚群无显著相关性。ITP患儿DEX治疗前血清IL-10显著降低,治疗后升高,ITP患儿血清IL-10与外周血血小板计数呈显著正相关,但与T淋巴细胞亚群无显著相关性。结论 ITP患儿T淋巴细胞亚群表达及比例失调,IFN-γ产生增多,IL-10产生减少,提示辅助T淋巴细胞亚型(Th1/Th2)功能异常。DEX治疗ITP能有效缓解病情。
明显高于治疗前。ITP患儿DEX治疗前血清IFN-γ显著升高,治疗后则降至正常水平,IFN-γ与外周血小板计数呈显著负相关,但与T淋巴细胞亚群无显著相关性。ITP患儿DEX治疗前血清IL-10显著降低,治疗后升高,ITP患儿血清IL-10与外周血血小板计数呈显著正相关,但与T淋巴细胞亚群无显著相关性。结论 ITP患儿T淋巴细胞亚群表达及比例失调,IFN-γ产生增多,IL-10产生减少,提示辅助T淋巴细胞亚型(Th1/Th2)功能异常。DEX治疗ITP能有效缓解病情。, http://www.100md.com
Changes in T cell-mediated immunity in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura ZHOU Ping*,LU Fenglin, YAO Yongming,et al. * Department of Pediatrics, The 466th Hospital of People's Liberation Army, Beijing 100081
【Abstract】 Objective To investigate the changes in T lymphocyte subsets, interleukin-10 (IL-10) and gamma interferon (IFN-γ) in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) and the effect of dexamethasone (DEX) treatment. Methods The blood samples were collected in ITP patients prior and post DEX treatment. T lymphocyte subsets of peripheral blood were examined by using APAAP method, and serum IL-10, IFN-γ levels were measured by using ELISA assay. Additionally, 12 healthy volunteers served as normal controls.Results Compared to normal controls, these ITP patients showed an elevation in percentage of
 cells, but decrease in
cells, but decrease in  cells as well as ratio of
cells as well as ratio of  /
/ in peripheral blood. After DEX treatment, the expression of both
in peripheral blood. After DEX treatment, the expression of both cells and
cells and  cells was profoundly inhibited, especially for CD+8 cells, while the ratio of
cells was profoundly inhibited, especially for CD+8 cells, while the ratio of  /
/ was significantly increased. Serum levels of IFN-γ increased obviously in children with ITP and negatively correlated with platelet counts, but they were reduced by DEX. However, serum levels of IL-10, which were diminished in these patients and positively correlated with platelet counts, were increased after DEX treatment. Nevertheless, no marked correlation was found between IFN-γ or IL-10 levels and T lymphocyte subsets. Conclusion In ITP patients, abnormal distribution of T lymphocyte subsets and changes in serum IFN-γ, IL-10 levels may imply the dysfunction of Th1/Th2. Treatment with DEX has beneficial effect on ITP, which appears to be associated with the regulation of T lymphocyte subsets expression and cytokine production.
was significantly increased. Serum levels of IFN-γ increased obviously in children with ITP and negatively correlated with platelet counts, but they were reduced by DEX. However, serum levels of IL-10, which were diminished in these patients and positively correlated with platelet counts, were increased after DEX treatment. Nevertheless, no marked correlation was found between IFN-γ or IL-10 levels and T lymphocyte subsets. Conclusion In ITP patients, abnormal distribution of T lymphocyte subsets and changes in serum IFN-γ, IL-10 levels may imply the dysfunction of Th1/Th2. Treatment with DEX has beneficial effect on ITP, which appears to be associated with the regulation of T lymphocyte subsets expression and cytokine production., 百拇医药
【Key words】 Purpura, thrombocytopenic, idiopathic T-lymphocyte subsets Interleukin-10 Gamma interferon
特发性血小板减少性紫癜(ITP)的发病机制尚未完全明确,目前认为其发生不仅与B细胞功能异常有关,与T淋巴细胞、自然杀伤细胞(NK)的表达及功能的改变均密切相关[1,2]。我们采用地塞米松(DEX)治疗ITP,检测治疗前后患儿外周血T淋巴细胞亚群、血清白细胞介素10(IL-10)、γ-干扰素(IFN-γ)含量的变化,并分析IL-10、IFN-γ与T淋巴细胞亚群及外周血血小板计数的相关性,旨在进一步探讨ITP自身免疫的病理机制,并为其治疗提供理论依据。
对象和方法
一、对象
1996年12月~1998年4月,住我院的ITP患儿共13例[3],男7例,女6例;年龄为1.0~12.0岁,平均为4.2岁。其中血小板低于2.5×109/L者10例,血小板为(2.5~5.0)×109/L者3例。对照组小儿12例,为同期健康体检小儿,其中男8例,女4例,年龄为3.0~8.0岁,平均3.4岁。
, http://www.100md.com
二、方法
1.所有ITP患儿均以DEX 1 mg/(kg.d)静脉滴注,7天后逐渐减量,2周后改为泼尼松口服,DEX治疗前及治疗后14天各抽血1次。
2.T淋巴细胞亚群的测定:采用改良碱性磷酸酶-抗碱性磷酸酶(APAAP)法测定,
 、
、 单抗由军事医学科学院基础医学研究所提供。
单抗由军事医学科学院基础医学研究所提供。3.IFN-γ、IL-10的测定:采用酶标记免疫吸附测定(ELISA)法,试剂系美国Genzyme公司产品,按试剂盒说明进行检测。
三、统计学处理
采用t检验和直线回归相关分析,结果以均数±标准差(
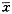 ±s)表示。
±s)表示。, 百拇医药
结果
一、ITP患儿外周血T淋巴细胞亚群的变化
ITP患儿外周血
 为(35±6)%,为对照组小儿的86.3%[4];
为(35±6)%,为对照组小儿的86.3%[4]; 为(32±10)%,是对照组小儿的116.6%;
为(32±10)%,是对照组小儿的116.6%; /
/ 为(1.1±0.3)%,较对照组小儿显著降低[4]。DEX治疗后,
为(1.1±0.3)%,较对照组小儿显著降低[4]。DEX治疗后, 为(29±5)%,CD+8为(20±6)%,均显著低于治疗前(P<0.05~0.01),
为(29±5)%,CD+8为(20±6)%,均显著低于治疗前(P<0.05~0.01), /
/ 为(1.5±0.3)%,较治疗前显著升高(P<0.01)(表1)。
为(1.5±0.3)%,较治疗前显著升高(P<0.01)(表1)。, http://www.100md.com
二、ITP患儿血清IFN-γ、IL-10的变化
ITP患儿DEX治疗前血清IFN-γ显著高于对照组,DEX治疗后则降至正常水平。而其血清IL-10水平,DEX治疗前显著低于对照组,治疗后则明显升高(表1) 。
表1 ITP患儿治疗前后血清IFN-γ、IL-10及外周血T淋巴细胞亚群的变化(
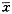 ±s) 组别
±s) 组别例数
IFN-γ(ng/L)
IL-10(ng/L)
例数
 (%)
(%) (%)
(%) /
/
, http://www.100md.com
对照组
12
593±264
27±4
31
41±7
27± 4
1.6±0.3
ITP组
治疗前
13
1 819±569
17±5
, http://www.100md.com
13
35±6
32±10
1.1±0.3
治疗后
13
582±225
23±6
13
29±5
20± 6
1.5±0.3
治疗前与正常比t值
, http://www.100md.com
6.808*
5.065*
2.606**
2.172**
5.175*
治疗前后配对比t值
7.332*
2.746**
2.782**
3.154*
, 百拇医药
4.015*
* P<0.01 ** P<0.05
三、ITP患儿血清IFN-γ、IL-10与外周血血小板、T淋巴细胞亚群的相关性
ITP患儿血清IFN-γ与外周血血小板计数呈显著负相关(r =-0.517,P<0.01),与T淋巴细胞亚群无显著相关关系。IL-10与外周血血小板计数呈显著正相关(r =0.418,P<0.05),与T淋巴细胞亚群无明显相关关系。
讨论
ITP系自身免疫性疾病,由于体内抗原如人类白细胞抗原-DR(HLA-DR)的表达异常,激活了自身反应性T淋巴细胞,并诱导抗血小板自身抗体产生增多[5]。本研究结果显示,ITP患儿外周血
 为正常儿童的86.3%,
为正常儿童的86.3%, 较正常儿童明显增多,
较正常儿童明显增多, /
/ 显著降低,提示ITP患儿外周血T淋巴细胞表面标志表达异常,T淋巴细胞亚群比例失调,与文献报道一致[1]。DEX治疗后,
显著降低,提示ITP患儿外周血T淋巴细胞表面标志表达异常,T淋巴细胞亚群比例失调,与文献报道一致[1]。DEX治疗后, 、
、 均明显下降,但
均明显下降,但 /
/ 显著升高,提示DEX抑制了ITP患儿T淋巴细胞抗原的表达,其中对CD+8抑制尤甚。由于异常激活的
显著升高,提示DEX抑制了ITP患儿T淋巴细胞抗原的表达,其中对CD+8抑制尤甚。由于异常激活的 具有抑制造血的作用,这样DEX抑制CD+8细胞的表达,可能有助于血小板的生成。
具有抑制造血的作用,这样DEX抑制CD+8细胞的表达,可能有助于血小板的生成。, http://www.100md.com
辅助型T淋巴细胞(Th)可分为Th1和Th2,其中Th1主要分泌白细胞介素2(IL-2)、IFN-γ等,调节细胞免疫;Th2主要分泌白细胞介素4(IL-4),IL-10等,参与体液免疫。IFN-γ能抑制Th2类细胞因子的产生,促进Th1类细胞因子的产生。相反,IL-10可抑制Th1类细胞因子的产生,促Th2类细胞因子的产生。本组资料显示,ITP患儿血清IFN-γ显著升高,而IL-10显著降低,提示ITP患儿Th1/Th2功能异常,Th1活力增强。
IFN-γ具有强大的免疫调节作用,可影响B细胞增殖分化成为浆细胞,使免疫球蛋白分泌增加,并通过上调巨噬细胞Fc受体的表达而增强单核巨噬细胞功能[6]。因此,ITP患儿血清
IFN-γ升高可能导致机体血小板相关抗体分泌增多,巨噬细胞对血小板破坏增强。进一步分析发现,ITP患儿血小板破坏越严重,IFN-γ增高越显著。但IFN-γ与外周血T淋巴细胞亚群间未显示出明显的相关性,可能与我们观察例数较少有关。
, http://www.100md.com
IL-10为体内重要的免疫抑制因子,它能抑制巨噬细胞、Th1细胞因子的合成,下调巨噬细胞抗原提呈功能,抑制IFN-γ的mRNA转录[7]。ITP患儿血清IL-10降低,对IFN-γ的抑制减弱。相关分析表明,ITP患儿血清IL-10与其外周血血小板计数呈显著正相关关系,初步提示体内IL-10的异常改变可能参与了ITP的病理过程。
DEX作为一种强有力的免疫抑制剂,在临床上治疗ITP取得了良好疗效。研究表明,DEX在转录水平能抑制多种细胞因子如肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)、IL-2、IFN-γ的产生。我们的研究结果表明,DEX显著抑制了ITP患儿血清IFN-γ的产生,但对IL-10的产生无抑制作用。相反,DEX治疗后,ITP患儿血清IL-10显著升高,与Ramierz等[8]的报道基本相符。
上述结果表明,ITP患儿存在T淋巴细胞免疫功能紊乱, IFN-γ产生增多,IL-10产生减少。其详细作用机制目前尚未明了,有待进一步探讨。
, 百拇医药
参考文献
[1] Garcia-Suarez J, Prieto A, Reyes E, et al. The clinical outcome of autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura patients is related to their T cell immunodeficiency. Br J Haematol, 1993, 84:464-470.
[2] Semple JW, Bruce S, Freedman J. Suppressed natural killer cell activity in patients with chronic autoimmune thrombocytopemic purpura. Am J Hematol, 1991, 37:258-262.
[3] 特发性血小板减少性紫癜诊疗常规.中华儿科杂志,1987, 25:104-105.
, 百拇医药
[4] 曾柏锦,钱幼琼, 郑德元,等.营养不良及低血锌患儿IgG亚类缺陷及T细胞亚群改变.中华儿科杂志,1991,29:11-13.
[5] Semple JW, Miler Y, Cosgrave D, et al. Differences in serum cytokine levels in acute and chronic autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura: relationship to platelet phenotype and antiplatelet T-cell reactivity. Blood, 1996, 87:4245-4254.
[6] Garcia-Suarez J, Prieto A, Reyes E, et al. Abnormal gamma-IFN and alpha-TNF secretion in purified CD2+ cells from autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura (ATP) patients: their implication in the clinical caurse of the disease. Am J Hematol, 1995, 49:271-276.
, 百拇医药
[7] Krakauer T. Differential inhibitory effects of interleukin-10, interleukin-4, and dexamethasone on staphylococcal enterotoxin-induced cytokine production and T cell activation. J Leuka Biol,1995, 57:450-454.
[8] Ramierz F, Fowell DJ, Pukivec M, et al. Glucocorticoids promote a Th2 cytokine production by CD4+ T cells in vitro. J Immunol, 1996,156:2406-2412.
(收稿:1998-08-17 修回:1998-09-25), 百拇医药