通过前房相关免疫偏离阻止实验性自身免疫前葡萄膜炎
作者:李志杰 彭广华 冯 铮 李 辰
单位:
关键词:免疫赦免;免疫偏离;葡萄膜炎;自身免疫;牛黑色素蛋白
眼科新进展990401 摘要 目的 实验性自身免疫性前葡萄膜炎(EAAU)是研究人前葡萄膜炎的有用模型。本研究旨在观察前房相关免疫偏离(ACAID)能否阻止EAAU发生。方法 将溶于磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)的牛黑色素蛋白(BMP)注射于大鼠右眼前房;对照组动物仅注射PBS。7d后,使用添加完全福氏佐剂(CFA)的BMP和百日咳毒素免疫所有动物。通过临床观察和组织病理学检测葡萄膜炎的严重程度和发病率。通过由注射BMP刺激的足垫水肿反应评估迟发型超敏反应(DTH)。结果 与对照组相比,预先眼内注射BMP的大鼠,其EAAU的严重程度和发病率减低,且DTH反应受到显著抑制。结论 这些资料提示ACAID可以用来阻止EAAU的发生。
, 百拇医药
Prevention of experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis
by anterior chamber-associated immune deviation
LI Zhi-Jie,MD, PENG Guang-Hua,MD, FENG Zheng,LI Chen,MD
Key words immune privilege; immune deviation; uveitis; autoimmune; bovine melanin protein
Abstract Objective Experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis (EAAU) is a useful model for human anterior uveitis. The purpose of this study was to observe whether EAAU development could be prevented by anterior chamber-associated immune deviation (ACAID). Methods Bovine melanin protein (BMP) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) was injected into the anterior chamber of the right eye of rats; control animals were injected with PBS alone. Seven days later, all animals were immunized with BMP in complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) and pertussis toxin. The severity and incidence of uveitis was monitored by clinical examination and histopathology. The delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) responses were evaluated by footpad swelling elicited by injection of BMP.Results Rats intraocularly injected with BMP showed a reduced severity and incidence of EAAU, and significantly suppressed DTH response compared to control rats.Conclusion These data suggest that the ACAID procedure can be utilized to prevent the development of EAAU.
, 百拇医药
Certain antigens injected into anterior chamber of the eye elicit uniquely a deviant form of immune response. This spectrum of immunity has been termed anterior chamber-associated immune deviation (ACAID), characterized by impaired delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH), suppression of complement-fixing antibodies production and intact generation of non-complement fixing antibodies and cytotoxic T cells[1,2].It has previously been demonstrated that injection of bovine retinal S antigen or bovine interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein (IRBP) into the AC of Lewis rat and mice eyes reduced the incidences of experimental autoimmune uveitis[3~5] (EAU).In a recent series of elegant studies, Broekhuyse and associates[6~9]described a new experimental autoimmune disease that affects mainly the anterior segment, and named this model experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis (EAAU). In the experiments to be described, EAAU-inducing antigen, bovine melanin protein (BMP) purified from the retinal pigment epithelium, the iris and choroid, has been injected intraocularly into rats to test the hypothesis that induction of ACAID can prevent the development and expression of EAAU.
, http://www.100md.com
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals A total of 60 male Wistar rats, 8 to 10 weeks of age, weighing 150~180g, were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center in Jinan University. All animal procedures were carried out under katamine and chlorpromazine mixtures as anesthetics.
Antigens Sodium dodecyl sulfate-insoluble BMP from the choroid and the remnant retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) was obtained as described by Broekhuyse and Kuhlmann[8]. Briefly, the anterior segment, vitreous, and retina were removed from the fresh pigmented cow eye. The eyecup was rinsed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). The choroid and RPE wererubbed in mortar with water. The suspen-sion was filtrated and centrifuged. The sediment was suspended in 20g*L-1 sodiumdodecyl sulfate, and heated at 75℃. After centrifugation, purified melanin was washed, dried, and stored at -20℃.
, 百拇医药
Anterior chamber inoculation Anterior chamber (AC) injection of BMP was carried out as described previously[10].Briefly, anesthetized rats received AC injections with Hamilton syringe. For each injection, 3μL of air followed by 10μL of antigen were drawn into the tubing. For AC inoculations, an oblique transcorneal paracentesis tunnel was formed with a sharp needle. The blunt needle was inserted through this track, followed by inoculation of 10 μL of antigen and 3μL of air, sealing the injection tract. The AC of the right eye of each mouse received 10μg.L-1of antigen.
, 百拇医药
Induction and assessment of DTH Induction and assessment of DTH was accomplished as previously described[11]. Briefly, animals were immunized subcutaneously with 100 μg BMP and complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA, Sigma) 7 days after AC inoculation of BMP. Seven days after immunization, 100μg of BMP in 10μL PBS was injected into the left footpad of the rat. The right footpad, served as unchallenged control, was injected with PBS alone. Footpad swelling was measured 24 hours later with an engineer's micrometer. Units of swelling were determined by the difference in thickness between the challenged left footpad and the unchallenged control right footpad of experimental animals. The unpaired Student's t test was performed for statistics analysis.
, http://www.100md.com
Induction and assessment of EAAU Seven daye after AC inoculation of BMP or PBS, a 1∶1 mixture of 100 μg BMP in 0.05 mL PBS and CFA (0.05mL) was injected subcutaneously into the base of the tail of rats. At the same time, 50 μg BMP (0.1mL) and Bordetella pertussis 3 ×109 organisms in 0.1mL PBS were injected intraperitoneally. Experimental animals were examined every other day using the slitlamp microscope and the dissecting microscope by three masked investigators. The clinical observations were graded on a scale of 0 to 4, based on the following criteria[12]: 0 = no inflammation; 0.5+ = mild dilatation of iris vessels and/or flare in the anterior chamber; 1+ = cells in the anterior chamber and/or fibrin at the pupillary margin; 2+ = fibrin in the anterior chamber and/or synechiae; 3+ = fibrin clots in the anterior chamber and/or corneal edema; and 4+ = hypopyon, hyphema, and/or loss of re reflex.
, http://www.100md.com
Histopathologic studies The eyes of rats were fixed in 40g*L-1 glutaraldehyde for 30 minutes and then transferred into 100g.L-1buffered formalin. After appropriate fixation, the tissues were embedded in methacrylate and sectioned for routine histopathology.
RESULTS
Induction of ACAID with BMP BMP and PBS (positive control) were inoculated into the AC of the right eye of rats seven days prior to immunization of all rats with BMP in CFA subcutaneously. Assay for DTH response was performed by injection of BMP in the right footpad of rats seven days after immunization. Footpad swelling was measured 48 hours later. The results are shown in Figure 1. An impaired BMP-specific DTH response was found in the AC-BMP pretreated group of rats, whereas the PBS pretreated group made vigorous DTH responses.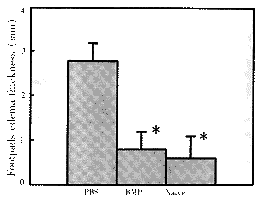
, http://www.100md.com
Figure 1 Induction of ACAID with BMP. Rats were immunized SC with 50μg BMP in CFA and pertussis toxin 7 days after an AC injection of BMP (50μg), or PBS. Their footpads were challenged with injections of BMP (100μg) seven days thereafter. Mean footpad swelling responses (±standard error) 24h after challenge are presented.*indicate values significantly greater than negative controls (P<0.05)
Effects of ACAID induction on BMP-induced experimental autoimmune uveitis We clinically tested the possibility that the above suppression of DTH would impair the development of EAAU in rats. On day 0 rats received intracameral injections of BMP into one eye. Seven days later all rats including positive control rats received injections of BMP in CFA and pertussis toxin in footpads, then followed by clinical observation. The results, depicted in Table 1, reveal that no animals developed EAAU in negative control (Group 1) and seven out of ten developed EAAU in positive control (Group 2). Interestingly, in the rats pretreated with intracameral injection of BMP, only 2 animals developed EAAU (Group 3).
, http://www.100md.com
Table 1 Clinical evaluation for induction of EAAU Group
Inoculation routes
Clinical findings
Number of positive EAAU
Day0
Day7
1
CFA+Pertussis
0/10
2
, 百拇医药 PBS AC
BMP in CFA+Pertussis
7/10
3
BMP AC
BMP in CFA+Pertussis
3/10
Histopathological examination After the termination of EAAU on day 20 post-inoculation, all the rats were killed and their eyes were examined histologically. The results confirmed the clinical assessment of uveitis.
, 百拇医药
DISCUSSION
Antigens injected into the AC of the eye exert a profound and unique influence upon the system apparatus. Our experiments have demonstrated that ACAID can be induced in rats by BMP, hereby expanding the list of antigens capable of inducing this phenomenon. In addition, we have explored the possibility that antigen-ssion of an autoimmune disease. Our experimental results indicate the prior inoculation of BMP antigen into the anterior chamber of one eye inhibits the eventual development of EAAU in rats receiving a uveitogenic regimen. Other studies[1,2,4]have suggested previously that the phenomenon of ACAID may be a physiological adaptation by which the eye is protected against vision-destroying inflammation directed at unique ocular antigens. The current results are consistent with this suggestion.
, 百拇医药
The protection by AC-injected BMP antigen may be related to suppression of antigen-specific DTH. It is generally believed that T cells that mediated DTH are the primary immune effectors of EAU, and there appears to be a good correlation between experimental maneuvers to prevent EAU and the impairment of DTH. Like EAU, EAAU is mediated by T cells, as evidenced by the findings that the disease can be adoptively transferred by sensitized CD4 lymphocytes[7], but not by hyperimmune serum[7], and is inhibited by cyclosporine[6].
, 百拇医药
Other antigen-specific strategies have been employed by other investigators to prevent clinical and experimental autoimmune uveitis, including intravenous injection[13]and oral feeding of antigen[14]. In general, repeated administrations were necessary in order to achieve amelioration of uveitis. The advantage of a treatment regimen based of ACAID is that only a single injection of antigen is required, and the protection of the uveal tract is virtually complete.
, 百拇医药
The success with which EAAU can be abrogated by AC injection of BMP suggests a potential avenue of therapy for ocular autoimmune disorders. Our results lead us to suggest that introcular injections of autoantigens might be considered as a means of preventing ocular disease, especially if the molecular nature of the antigens is known.
注释:Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No:39500158),Huo Yingdong Education Foundation in Ministry of Education,and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
, http://www.100md.com
About LI Zhi-Jie He received his Doctoral degree in medicine from the Jinan University,China,and pursued postdoctoral training in transgene animal and molecular biology at the National Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Biology in the Chinese Academy of Medicine.He is presently an associate Professor in the Department of Ophthalmology and Senior Scientist at the Institute of Tissue Transplantation and Immunology,Jinan University.His major research interests include immunoregulatory mechanisms of the eye and ocular immunologic diseases.Tel:+86-20-85220298(O),Fax:+86-20-85221941,E-mail:tlaj@jun.edu.cn
, 百拇医药
From the Department of Ophthalmology,Institute of Tissue Transplantation & Immunology,Jinan University ,Guangzhou 510632,Guangdong Province,P.R.China.
REFERENCES
1 Streilein JW. Immunoregulatory mechanism of the eye.Prog Ret Eye Res 1999; 18∶357-370.
2 Peng GH,Li ZJ.Cellular and molecular basis for ocula immune privilege[Review].Chin Ophthal Res 1999;17:153-156.
, 百拇医药
3 Mizuno K, Streilein JW. Anterior chamber injection of S antigen prevents the development of experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU). In Usui M, Ohno S and Aoki K Ed: Ocular immunology today. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers 1990∶143-146.
4 Hara Y, Capsi RR, Wiggert B, et al. Suppression of experimental autoimmune uveitis in mice by induction of anterior chamber-associated immune deviation with interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein. J Immunol 1992; 148∶1685-1692.
, 百拇医药
5 Mizuno K, Clark AF, Streilein JW: Ocular injection of retinal S antigen: suppression of autoimmune uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1989; 30∶772-774.
6 Broekhhuyse RM, Kuhlmann ED, Winkens HJ, et al. Experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis (EAAU), a new form of experimental uveitis. I. Induction by a detergent-insoluble, intrinsic protein fraction of the retina pigment epithelium. Exp Eye Res 1991; 52∶465-74.
7 Broekhhuyse RM, Kuhlmann ED, Winkens HJ. Experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis (EAAU). II. Dose-dependent induction and adoptive transfer using a melanin-bound antigen of the retinal pigment epithelium. Exp Eye Res 1992; 55∶401-411.
, 百拇医药
8 Broekhuyse RM, Kuhjmann ED. Experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis. The preparation of uveiogenic ocular melanin. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1993; 34∶698-700.
9 Broekhhuyse RM, Kuhlmann ED, Winkens HJ. Experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis (EAAU). III. Induction by immunization with purified uveal and skin melanins. Exp Eye Res 1993; 56∶575-583.
10 Li Z, Peng G, Li C. Anterior chamber-associated immune deviation during normal pregnancy in rabbits. Chin Ophthal Res 1999; 17∶161-164.
, 百拇医药
11 Li Z, Peng G, Li C. Vitreous cavity-associated immune deviation induced by retinal S antigen. Eye Sci 1999; 15: (in press).
12 Chan CC, Hikita N, Dastgheib K, et al. Experimental melanin-protein-induced uveitis in the Lewis rat: Immunopathologic processes. Ophthalmology 1994; 101∶1275-1280.
13 Saaamoto Y. Immunomodulation of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis by intravenous injection of uveitogenic peptides. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1992; 33∶2641-2649.
14 Nussenblatt RB, Gery I, Weiner HL, et al. Treatment of uveitis by oral administration of retinal antigens: Results of a phase I/II randomized masked trial. Am J Ophthalmol 1997; 123∶583-592.
收稿日期:1999-07-20, 百拇医药
单位:
关键词:免疫赦免;免疫偏离;葡萄膜炎;自身免疫;牛黑色素蛋白
眼科新进展990401 摘要 目的 实验性自身免疫性前葡萄膜炎(EAAU)是研究人前葡萄膜炎的有用模型。本研究旨在观察前房相关免疫偏离(ACAID)能否阻止EAAU发生。方法 将溶于磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)的牛黑色素蛋白(BMP)注射于大鼠右眼前房;对照组动物仅注射PBS。7d后,使用添加完全福氏佐剂(CFA)的BMP和百日咳毒素免疫所有动物。通过临床观察和组织病理学检测葡萄膜炎的严重程度和发病率。通过由注射BMP刺激的足垫水肿反应评估迟发型超敏反应(DTH)。结果 与对照组相比,预先眼内注射BMP的大鼠,其EAAU的严重程度和发病率减低,且DTH反应受到显著抑制。结论 这些资料提示ACAID可以用来阻止EAAU的发生。
, 百拇医药
Prevention of experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis
by anterior chamber-associated immune deviation
LI Zhi-Jie,MD, PENG Guang-Hua,MD, FENG Zheng,LI Chen,MD
Key words immune privilege; immune deviation; uveitis; autoimmune; bovine melanin protein
Abstract Objective Experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis (EAAU) is a useful model for human anterior uveitis. The purpose of this study was to observe whether EAAU development could be prevented by anterior chamber-associated immune deviation (ACAID). Methods Bovine melanin protein (BMP) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) was injected into the anterior chamber of the right eye of rats; control animals were injected with PBS alone. Seven days later, all animals were immunized with BMP in complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) and pertussis toxin. The severity and incidence of uveitis was monitored by clinical examination and histopathology. The delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) responses were evaluated by footpad swelling elicited by injection of BMP.Results Rats intraocularly injected with BMP showed a reduced severity and incidence of EAAU, and significantly suppressed DTH response compared to control rats.Conclusion These data suggest that the ACAID procedure can be utilized to prevent the development of EAAU.
, 百拇医药
Certain antigens injected into anterior chamber of the eye elicit uniquely a deviant form of immune response. This spectrum of immunity has been termed anterior chamber-associated immune deviation (ACAID), characterized by impaired delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH), suppression of complement-fixing antibodies production and intact generation of non-complement fixing antibodies and cytotoxic T cells[1,2].It has previously been demonstrated that injection of bovine retinal S antigen or bovine interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein (IRBP) into the AC of Lewis rat and mice eyes reduced the incidences of experimental autoimmune uveitis[3~5] (EAU).In a recent series of elegant studies, Broekhuyse and associates[6~9]described a new experimental autoimmune disease that affects mainly the anterior segment, and named this model experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis (EAAU). In the experiments to be described, EAAU-inducing antigen, bovine melanin protein (BMP) purified from the retinal pigment epithelium, the iris and choroid, has been injected intraocularly into rats to test the hypothesis that induction of ACAID can prevent the development and expression of EAAU.
, http://www.100md.com
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals A total of 60 male Wistar rats, 8 to 10 weeks of age, weighing 150~180g, were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center in Jinan University. All animal procedures were carried out under katamine and chlorpromazine mixtures as anesthetics.
Antigens Sodium dodecyl sulfate-insoluble BMP from the choroid and the remnant retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) was obtained as described by Broekhuyse and Kuhlmann[8]. Briefly, the anterior segment, vitreous, and retina were removed from the fresh pigmented cow eye. The eyecup was rinsed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). The choroid and RPE wererubbed in mortar with water. The suspen-sion was filtrated and centrifuged. The sediment was suspended in 20g*L-1 sodiumdodecyl sulfate, and heated at 75℃. After centrifugation, purified melanin was washed, dried, and stored at -20℃.
, 百拇医药
Anterior chamber inoculation Anterior chamber (AC) injection of BMP was carried out as described previously[10].Briefly, anesthetized rats received AC injections with Hamilton syringe. For each injection, 3μL of air followed by 10μL of antigen were drawn into the tubing. For AC inoculations, an oblique transcorneal paracentesis tunnel was formed with a sharp needle. The blunt needle was inserted through this track, followed by inoculation of 10 μL of antigen and 3μL of air, sealing the injection tract. The AC of the right eye of each mouse received 10μg.L-1of antigen.
, 百拇医药
Induction and assessment of DTH Induction and assessment of DTH was accomplished as previously described[11]. Briefly, animals were immunized subcutaneously with 100 μg BMP and complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA, Sigma) 7 days after AC inoculation of BMP. Seven days after immunization, 100μg of BMP in 10μL PBS was injected into the left footpad of the rat. The right footpad, served as unchallenged control, was injected with PBS alone. Footpad swelling was measured 24 hours later with an engineer's micrometer. Units of swelling were determined by the difference in thickness between the challenged left footpad and the unchallenged control right footpad of experimental animals. The unpaired Student's t test was performed for statistics analysis.
, http://www.100md.com
Induction and assessment of EAAU Seven daye after AC inoculation of BMP or PBS, a 1∶1 mixture of 100 μg BMP in 0.05 mL PBS and CFA (0.05mL) was injected subcutaneously into the base of the tail of rats. At the same time, 50 μg BMP (0.1mL) and Bordetella pertussis 3 ×109 organisms in 0.1mL PBS were injected intraperitoneally. Experimental animals were examined every other day using the slitlamp microscope and the dissecting microscope by three masked investigators. The clinical observations were graded on a scale of 0 to 4, based on the following criteria[12]: 0 = no inflammation; 0.5+ = mild dilatation of iris vessels and/or flare in the anterior chamber; 1+ = cells in the anterior chamber and/or fibrin at the pupillary margin; 2+ = fibrin in the anterior chamber and/or synechiae; 3+ = fibrin clots in the anterior chamber and/or corneal edema; and 4+ = hypopyon, hyphema, and/or loss of re reflex.
, http://www.100md.com
Histopathologic studies The eyes of rats were fixed in 40g*L-1 glutaraldehyde for 30 minutes and then transferred into 100g.L-1buffered formalin. After appropriate fixation, the tissues were embedded in methacrylate and sectioned for routine histopathology.
RESULTS
Induction of ACAID with BMP BMP and PBS (positive control) were inoculated into the AC of the right eye of rats seven days prior to immunization of all rats with BMP in CFA subcutaneously. Assay for DTH response was performed by injection of BMP in the right footpad of rats seven days after immunization. Footpad swelling was measured 48 hours later. The results are shown in Figure 1. An impaired BMP-specific DTH response was found in the AC-BMP pretreated group of rats, whereas the PBS pretreated group made vigorous DTH responses.

, http://www.100md.com
Figure 1 Induction of ACAID with BMP. Rats were immunized SC with 50μg BMP in CFA and pertussis toxin 7 days after an AC injection of BMP (50μg), or PBS. Their footpads were challenged with injections of BMP (100μg) seven days thereafter. Mean footpad swelling responses (±standard error) 24h after challenge are presented.*indicate values significantly greater than negative controls (P<0.05)
Effects of ACAID induction on BMP-induced experimental autoimmune uveitis We clinically tested the possibility that the above suppression of DTH would impair the development of EAAU in rats. On day 0 rats received intracameral injections of BMP into one eye. Seven days later all rats including positive control rats received injections of BMP in CFA and pertussis toxin in footpads, then followed by clinical observation. The results, depicted in Table 1, reveal that no animals developed EAAU in negative control (Group 1) and seven out of ten developed EAAU in positive control (Group 2). Interestingly, in the rats pretreated with intracameral injection of BMP, only 2 animals developed EAAU (Group 3).
, http://www.100md.com
Table 1 Clinical evaluation for induction of EAAU Group
Inoculation routes
Clinical findings
Number of positive EAAU
Day0
Day7
1
CFA+Pertussis
0/10
2
, 百拇医药 PBS AC
BMP in CFA+Pertussis
7/10
3
BMP AC
BMP in CFA+Pertussis
3/10
Histopathological examination After the termination of EAAU on day 20 post-inoculation, all the rats were killed and their eyes were examined histologically. The results confirmed the clinical assessment of uveitis.
, 百拇医药
DISCUSSION
Antigens injected into the AC of the eye exert a profound and unique influence upon the system apparatus. Our experiments have demonstrated that ACAID can be induced in rats by BMP, hereby expanding the list of antigens capable of inducing this phenomenon. In addition, we have explored the possibility that antigen-ssion of an autoimmune disease. Our experimental results indicate the prior inoculation of BMP antigen into the anterior chamber of one eye inhibits the eventual development of EAAU in rats receiving a uveitogenic regimen. Other studies[1,2,4]have suggested previously that the phenomenon of ACAID may be a physiological adaptation by which the eye is protected against vision-destroying inflammation directed at unique ocular antigens. The current results are consistent with this suggestion.
, 百拇医药
The protection by AC-injected BMP antigen may be related to suppression of antigen-specific DTH. It is generally believed that T cells that mediated DTH are the primary immune effectors of EAU, and there appears to be a good correlation between experimental maneuvers to prevent EAU and the impairment of DTH. Like EAU, EAAU is mediated by T cells, as evidenced by the findings that the disease can be adoptively transferred by sensitized CD4 lymphocytes[7], but not by hyperimmune serum[7], and is inhibited by cyclosporine[6].
, 百拇医药
Other antigen-specific strategies have been employed by other investigators to prevent clinical and experimental autoimmune uveitis, including intravenous injection[13]and oral feeding of antigen[14]. In general, repeated administrations were necessary in order to achieve amelioration of uveitis. The advantage of a treatment regimen based of ACAID is that only a single injection of antigen is required, and the protection of the uveal tract is virtually complete.
, 百拇医药
The success with which EAAU can be abrogated by AC injection of BMP suggests a potential avenue of therapy for ocular autoimmune disorders. Our results lead us to suggest that introcular injections of autoantigens might be considered as a means of preventing ocular disease, especially if the molecular nature of the antigens is known.
注释:Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No:39500158),Huo Yingdong Education Foundation in Ministry of Education,and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
, http://www.100md.com
About LI Zhi-Jie He received his Doctoral degree in medicine from the Jinan University,China,and pursued postdoctoral training in transgene animal and molecular biology at the National Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Biology in the Chinese Academy of Medicine.He is presently an associate Professor in the Department of Ophthalmology and Senior Scientist at the Institute of Tissue Transplantation and Immunology,Jinan University.His major research interests include immunoregulatory mechanisms of the eye and ocular immunologic diseases.Tel:+86-20-85220298(O),Fax:+86-20-85221941,E-mail:tlaj@jun.edu.cn
, 百拇医药
From the Department of Ophthalmology,Institute of Tissue Transplantation & Immunology,Jinan University ,Guangzhou 510632,Guangdong Province,P.R.China.
REFERENCES
1 Streilein JW. Immunoregulatory mechanism of the eye.Prog Ret Eye Res 1999; 18∶357-370.
2 Peng GH,Li ZJ.Cellular and molecular basis for ocula immune privilege[Review].Chin Ophthal Res 1999;17:153-156.
, 百拇医药
3 Mizuno K, Streilein JW. Anterior chamber injection of S antigen prevents the development of experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU). In Usui M, Ohno S and Aoki K Ed: Ocular immunology today. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers 1990∶143-146.
4 Hara Y, Capsi RR, Wiggert B, et al. Suppression of experimental autoimmune uveitis in mice by induction of anterior chamber-associated immune deviation with interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein. J Immunol 1992; 148∶1685-1692.
, 百拇医药
5 Mizuno K, Clark AF, Streilein JW: Ocular injection of retinal S antigen: suppression of autoimmune uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1989; 30∶772-774.
6 Broekhhuyse RM, Kuhlmann ED, Winkens HJ, et al. Experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis (EAAU), a new form of experimental uveitis. I. Induction by a detergent-insoluble, intrinsic protein fraction of the retina pigment epithelium. Exp Eye Res 1991; 52∶465-74.
7 Broekhhuyse RM, Kuhlmann ED, Winkens HJ. Experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis (EAAU). II. Dose-dependent induction and adoptive transfer using a melanin-bound antigen of the retinal pigment epithelium. Exp Eye Res 1992; 55∶401-411.
, 百拇医药
8 Broekhuyse RM, Kuhjmann ED. Experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis. The preparation of uveiogenic ocular melanin. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1993; 34∶698-700.
9 Broekhhuyse RM, Kuhlmann ED, Winkens HJ. Experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis (EAAU). III. Induction by immunization with purified uveal and skin melanins. Exp Eye Res 1993; 56∶575-583.
10 Li Z, Peng G, Li C. Anterior chamber-associated immune deviation during normal pregnancy in rabbits. Chin Ophthal Res 1999; 17∶161-164.
, 百拇医药
11 Li Z, Peng G, Li C. Vitreous cavity-associated immune deviation induced by retinal S antigen. Eye Sci 1999; 15: (in press).
12 Chan CC, Hikita N, Dastgheib K, et al. Experimental melanin-protein-induced uveitis in the Lewis rat: Immunopathologic processes. Ophthalmology 1994; 101∶1275-1280.
13 Saaamoto Y. Immunomodulation of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis by intravenous injection of uveitogenic peptides. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1992; 33∶2641-2649.
14 Nussenblatt RB, Gery I, Weiner HL, et al. Treatment of uveitis by oral administration of retinal antigens: Results of a phase I/II randomized masked trial. Am J Ophthalmol 1997; 123∶583-592.
收稿日期:1999-07-20, 百拇医药