发生脑短暂性缺血发作的飞行员脑α波优势频率的不确定性分析
作者:周传岱 韩东旭 刘月红 翟怡娟 李岩松
单位:周传岱. 航天医学工程研究所,北京 100094
关键词:脑电图;不确定性;熵;α节律;短暂性缺血发作
航天医学与医学工程990202Dominant Frequency Uncertainty Analysis of EEG α
Activity in Pilots with Transient Ischemic Attacks
ZHOU Chuan-dai,HAN Dong-xu,LIU Yue-hong,ZHAI Yi-juan,LI Yan-song
(Institute of Space Medico-Engineering,Beijing 100094,China)
, http://www.100md.com
Abstract:Objective To study the characteristics of EEG after tramsient ischemic attack and to offer reference for screening procedure of aircrew and astronaut selection. Method The dominant frequency uncertainty of alpha band EEG in 12 pilots(males; age 30±5) with transient ischemic episodes in middle cerebral artery(MCA) territories and in 20 normal healthy pilots was analyzed with frequency-fluctuation analysis. Result The dominant probability of the main frequency coinciding with sites affected by transient ischaemic attack(TIA) in patient pilots was higher than that in healthy pilots (P<0.01),and the dominant probability ratio logarithmic index I≥0 in all patient pilots with normal EEG, but I<0 in all healthy pilots. It was also found that not only I≥0, but the second component shifted to lower frequency(8 Hz) in patients with slight focal EEG alterations,i.e. slowing of frequency. The relative entropy values (percentage) were decreased significantly in pilots with TIA as compared with healthy pilots (P<0.05). Conclusion The dominant frequency uncertainty analysis of alpha band showed clear superiority of computerized evaluation over routine visual assessment for the diagnosis of minor cerebral ischemia. It offers not only a possibility of studying pathophysiological functional parameter, but also the reference for screening procedure in aircrew and astronaut selection.
, http://www.100md.com
Key words EEG;uncertainty;entropy;alpha rhythm;TIA
摘要:目的 探讨脑短暂性缺血发作(TIA)引起的脑功能紊乱的生物电特征,为飞行员、航天员选拔提供可参考的评价方法。方法 用CFM-8D EEG 监护仪记录了12名飞行员(男性,30±5)发生TIA后的EEG,应用脑波频率涨落分析系统分析了脑α波优势频率的不确定性,并与20名健康飞行员进行了比较。结果 发生TIA但EEG正常的飞行员,其主频出现优势涨落几率与健康飞行员比有明显的差异(P<0.01),且主频几率优势比指数I≥0,而健康飞行员主频几率优势比I<0;与20名健康飞行员比较,相对熵值减少明显(P<0.05)。发生TIA且局部出现EEG改变的飞行员不但I≥0且脑波出现优势频率慢化。结论 应用脑α波优势频率不确定性分析评价脑的缺血反应比EEG判读更优越。该研究结果不仅为TIA脑功能病理生理研究提供了评价参数,而且也为飞行员和航天员选拔提供了评价方法。
, http://www.100md.com 中图分类号:R338.1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1002-0837(1999)02-0084-04
Quantitative EEG in cerebral ischemia was studied by Jonkman et al[1] using the multichannel spectral analysis technique and additional topographic displays of the data provided an overview of distribution of the different EEG parameters within a given frequency range. The event-related desynchronization (ERD) of EEG mapping in patients with TIA was investigated in a follow-up study[2].The dominant frequency analysis of EEG revealed brain response during injury and recovery[3].The bispectrum of EEG signals record from ischemic region in a model of focal cerebral ischemia in rat was analyzed using the third-order recursion method[4]. However, it was found that one of the important features of alpha activity the uncertainty of dominant frequency fluctuation of alpha in EEG could be changed under hypoxic condition[5].The uncertainty of dominant frequency was investigated using relative entropy as parameter in 261 healthy pilots[6],it provided an analytical method for detecting functional changes of the brain.
, http://www.100md.com
The aim of this investigation was to study functional disorders of cortex following transient cerebral ischemic attacks(TIAs),using computerized analysis of changes in uncertainty of alpha dominant frequency,and to compare these data with investigations performed in normal healthy pilots in order to offer reference for the screening procedure in aircrew and astronaut selection.
Methods
Subjects Twelve male pilots(aged 30±5) with transient episodes of ischemia in middle cerebral artery(MCA) territories. The transient focal neurological deficit involved the left MCA territory in eight and the right MCA territory in four patients. The standard EEG evaluated with descriptive visual analysis was normal in seven patients. Five patients showed slight focal alterations, coinciding in four of them with the hemisphere affected by the cerebrovascular episode. Control measurements were carried out in 20 normal healthy male pilots (aged 30±4).
, 百拇医药
EEG recordings According to the 10~20 system, twelve electrodes were placed on F3,F4,C3,C4,P3,P4,O1,O2,F7,F8,T5,T6, using linked ear lobes reference. EEG recordings in patients with their eyes closed were made by means of a CFM-8D EEG monitor within 24 h following the acute event in a quiet, naturally illuminated room, with the subject in a sitting position, and bandpass filtered between 2 Hz and 24 Hz. The EEG data were digitized at a rate of 100 Hz for 240 s and stored on a disk. It was also displayed continuously on a high-resolution color monitor, with a reading sensitivity of 50 μV=10 mm. Registrations with fluctuations of alterness showing a decrease of the EEG power density, appearance of sleep rhythms and EEG registrations not distinctly free of artifacts were excluded from the data for analysis.
, 百拇医药
EEG analysis By means of EEG-ET system, a newer system of frequency-fluctuation analysis was used , the uncertainty of the dominant frequency of alpha band(8~13 Hz) was analyzed according to the following method. Suppose there are six frequency components of alpha, i.e., 8,9, 10,11,12,13(Hz). Let a complete event be made up of the frequency components: A8,A9,A10,A11,A12,A13, and let cumulated probability of maximum power fluctuation in 240 s for each alpha frequency component is P8,P9,P10,P11,P12,P13 respectively, then the six cumulative dominant probability-time curves constructed the competitive synergetic structure of alpha frequency components. Let ΣPi =1 and it's entropy H=-Σpilnpi,(i=8,9,10,11,12,13). If the pis are equal,then H has a maximal value denoted by Hmax.Thus the relative entropy value is Q=(H/Hmax).
, 百拇医药
Results
Dominant probability ratio logarithmic index of α in patient pilots with TIA The cumulated dominant fluctuation probability-time curves for individual frequency of alpha band in both patients and healthy pilots were showed in Fig.1. The uppermost curve in Fig.1 was of the main frequency, i.e., dominant frequency component, and it's probability was the highest in the six frequency components. The second was of the potential dominant frequency component, i.e., second frequency. It was obvious that the main frequency component was 9 Hz, and the second was 10 Hz for both patient pilots with TIA and healthy pilots. But the probability of the main frequency in TIA patient pilots coinciding with sites affected by cerebrovascular episode was more than in healthy pilots. The statistical significance estimated with the unpaired student's t-tests was observed in probability difference of main frequency in patients as compared with healthy (P<0.01). Let the dominant probability ratio logarithmic index I=log[Pmain/(1-Pmain)].The Pmain in the logarithmic formula was the dominant probability value of main frequency. It was found that the dominant probability ratio logarithmic index I<0 in all TIA patient pilots with normal EEG,coinciding in six of them with the hemisphere affected by the cerebrovascular episode, and I<0 in all healthy pilots. Therefore we could conclude from the difference of probability that the smaller the uncertainty of dominant frequency, the larger the dominant probability of main frequency. To be sure, the uncertainty of dominant frequency was decreased in patient pilots with TIA. It was also found that not only I<0 ,but the second component shifted to lower frequency(8 Hz) in patients with slight focal frequency slowing in EEG.
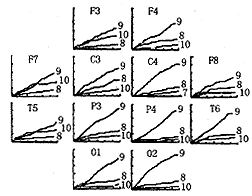
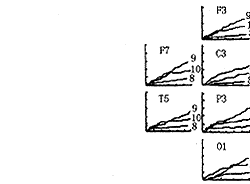
, 百拇医药
Fig.1 The cumulative dominant frequency fluctuation probability-time curve for α band
Ordinate: cumulative probability value(percentage); Abscissa: time(second) .The number at curve's end is the frequency value(in Hz). Upper left: A patient pilot with left cerebrovascular episode. On the left sites coinciding with the hemisphere affected by the episode, the probability of maximum power was converged on 9 Hz, i.e. the dominant fluctuation component, meanwhile the probability of maximum power of other components was lower. Upper right: A patient pilot with right cerebrovascular episode. The structures of frequency on right affected sites is similar to left, but second frequency component was 8 Hz, the frequency slowing, coinciding with patient's EEG showed slight focal alterations. Bottom: a healthy pilot.
, 百拇医药
Entropy change of dominant frequency fluctuation of alpha in patient pilots with TIA The relative entropy values for patients and healthy pilots are showed in Table 1. Decreases in Q were significant at all left electrode sites (P<0.05,or better) coinciding with the left hemisphere af-fected by the cerebrovascular episode in patients as compared with healthy pilots. Significant decreases were also observed at the right parietal-occipital area, corresponding to electrodes P4,O2. There were significant decreases at all right electrode sites(P<0.05, or better) for patients coinciding with the right affected hemisphere, just as above-mentioned,at the opposite parietal-occipital area, corresponding to electrodes P3,O1, the Q values decreased significantly for these patients.
, 百拇医药
Table 1 Relative entropy values (Q) in TIA pilots and healthy pilots Site
healthy pilots
(n=20)
patients
(left MCA n=8)
patients
(right MCA n=4)
F3
0.67±0.16
0.53±0.12*
, http://www.100md.com
0.70±0.15
C3
0.73±0.15
0.53±0.10*
0.72±0.13
P3
0.74±0.17
0.40±0.11**
0.54±0.15*
O1
0.68±0.14
, 百拇医药
0.32±0.07**
0.53±0.14*
F7
0.67±0.15
0.43±0.14*
0.71±0.15
T5
0.75±0.14
0.36±0.10**
0.72±0.12
F4
, http://www.100md.com
0.64±0.15
0.69±0.13
0.46±0.15*
C4
0.74±0.14
0.77±0.15
0.59±0.14*
P4
0.76±0.14
0.65±0.14*
0.40±0.09**
, http://www.100md.com
O2
0.64±0.18
0.55±0.07*
0.34±0.08**
F8
0.68±0.15
0.72±0.14
0.46±0.12*
T6
0.75±0.15
0.73±0.13
, 百拇医药
0.38±0.10**
*P<0.05, **P<0.01,p-values are from unpaired students' as compared with t-tests; Q values are mean ±1 standard deviationDiscussion
The present results strongly support the findings of previous studies concerning dominant frequency fluctuation of alpha in EEG[5,6], in which we found that the maximum power fluctuation in alpha frequency band was converged on the dominant frequency component, and the uncertainty of alpha dominant frequency was reduced, then the dominant component shifted to lower frequency, meanwhile the maximal power fluctuation was almost equally distributed among these frequency components of alpha, so the uncertainty of dominant frequency was going up and the brain was self-organized in a new situation in order to adapt itself to hypoxia.The declined tolerance to acute hypoxic hypoxia could be characterized by the uncertainty of dominant frequency fluctuation of alpha. In this respect our particular interest has been directed towards the uncertainty of alpha dominant frequency in the patients with TIA. The accumulated probability-time curve of dominant frequency fluctuation showed the course of competition of dominant frequency components in alpha band, so the degree of severity of the resulting cerebral dysfunction may be derived from the uncertainty of alpha dominant frequency utilizing the dominant probability ratio logarithmic index I and relative entropy value Q to be able to identify regions affected by cerebral transient ischemic attacks, as well as from the slowing of the dominant frequency component and the dominant probability difference between the main and second frequency components,even though the patient's EEGs did not showed slight focal alterations. In addition, in the group of TIA patient pilots, the opposite sites to parieto-occipital regions were also identified as affected sites by significant decrease of relative entropy value Q and logarithmic index I>0. It maybe implied that these regions were also affected by the opposite hemisphere cerebrovascular episode. By the similar argument to that of hypoxia state, the changes of uncertainty of dominant frequency maybe implied that the brain was self-organized in a new situation in order to adapt itself to ischemia from TIA. And so the dominant frequency uncertainty may be used as a sensitive parameter in detecting even slight functional disturbances of cortical activity in patients with TIA. Therefore the analysis of uncertainty of alpha dominant frequency showed clear superiority of computerized evaluation over routine visual assessment in patients with minor cerebral ischemia. Consequently this method not only offers the possibility of studying pathophysiological functional parameter, but may also provide a reference for screening procedure in aircrew and astronaut selection.
, 百拇医药
References
[1]Jonkman EJ, van Huffenlen AG,Pfurtscheller G.Quantitative EEG in cerebral ischemia[C].In:Lopes da Silva FH,Strom van Leeumen W,Remond A(eds).Clinical applications of computer analysis of EEG and other neurophysiological signals.Amsterdam Elsevier,1986:205~237
[2]Koener E,Ott E,Kaiserfeld Pet al.EEG mapping in patients with transient ischemic attacks:a follow-up study[C].In:Maurer K(ed). Topographic brain mapping of EEG and evoked potentials.Heidelberg Springer-Verlag berlin,1989:209~218
, http://www.100md.com
[3]Vaibhava Goeal,Thkor NV.Dominant frequency analysis of EEG reveals brain's response during injury and recovery[J].IEEE Trans Biomid Eng,1996,43(11):1083~1092
[4]张继武,郑崇勋.局灶性脑缺血脑电信号的双谱分析[J].航天医学与医学工程,1998,11(2):97~101
[5]周传岱,徐国林,朱治平等. 急性缺氧态脑α波自组织特征分析[J].航天医学与医学工程,1992,5(4):245~249
[6]周传岱,翟怡娟,刘月红等. 261名歼击机飞行员脑波α频段涨落图特征的研究[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 1998,11(1):11~15
Received date:May 11,1998, 百拇医药
单位:周传岱. 航天医学工程研究所,北京 100094
关键词:脑电图;不确定性;熵;α节律;短暂性缺血发作
航天医学与医学工程990202Dominant Frequency Uncertainty Analysis of EEG α
Activity in Pilots with Transient Ischemic Attacks
ZHOU Chuan-dai,HAN Dong-xu,LIU Yue-hong,ZHAI Yi-juan,LI Yan-song
(Institute of Space Medico-Engineering,Beijing 100094,China)
, http://www.100md.com
Abstract:Objective To study the characteristics of EEG after tramsient ischemic attack and to offer reference for screening procedure of aircrew and astronaut selection. Method The dominant frequency uncertainty of alpha band EEG in 12 pilots(males; age 30±5) with transient ischemic episodes in middle cerebral artery(MCA) territories and in 20 normal healthy pilots was analyzed with frequency-fluctuation analysis. Result The dominant probability of the main frequency coinciding with sites affected by transient ischaemic attack(TIA) in patient pilots was higher than that in healthy pilots (P<0.01),and the dominant probability ratio logarithmic index I≥0 in all patient pilots with normal EEG, but I<0 in all healthy pilots. It was also found that not only I≥0, but the second component shifted to lower frequency(8 Hz) in patients with slight focal EEG alterations,i.e. slowing of frequency. The relative entropy values (percentage) were decreased significantly in pilots with TIA as compared with healthy pilots (P<0.05). Conclusion The dominant frequency uncertainty analysis of alpha band showed clear superiority of computerized evaluation over routine visual assessment for the diagnosis of minor cerebral ischemia. It offers not only a possibility of studying pathophysiological functional parameter, but also the reference for screening procedure in aircrew and astronaut selection.
, http://www.100md.com
Key words EEG;uncertainty;entropy;alpha rhythm;TIA
摘要:目的 探讨脑短暂性缺血发作(TIA)引起的脑功能紊乱的生物电特征,为飞行员、航天员选拔提供可参考的评价方法。方法 用CFM-8D EEG 监护仪记录了12名飞行员(男性,30±5)发生TIA后的EEG,应用脑波频率涨落分析系统分析了脑α波优势频率的不确定性,并与20名健康飞行员进行了比较。结果 发生TIA但EEG正常的飞行员,其主频出现优势涨落几率与健康飞行员比有明显的差异(P<0.01),且主频几率优势比指数I≥0,而健康飞行员主频几率优势比I<0;与20名健康飞行员比较,相对熵值减少明显(P<0.05)。发生TIA且局部出现EEG改变的飞行员不但I≥0且脑波出现优势频率慢化。结论 应用脑α波优势频率不确定性分析评价脑的缺血反应比EEG判读更优越。该研究结果不仅为TIA脑功能病理生理研究提供了评价参数,而且也为飞行员和航天员选拔提供了评价方法。
, http://www.100md.com 中图分类号:R338.1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1002-0837(1999)02-0084-04
Quantitative EEG in cerebral ischemia was studied by Jonkman et al[1] using the multichannel spectral analysis technique and additional topographic displays of the data provided an overview of distribution of the different EEG parameters within a given frequency range. The event-related desynchronization (ERD) of EEG mapping in patients with TIA was investigated in a follow-up study[2].The dominant frequency analysis of EEG revealed brain response during injury and recovery[3].The bispectrum of EEG signals record from ischemic region in a model of focal cerebral ischemia in rat was analyzed using the third-order recursion method[4]. However, it was found that one of the important features of alpha activity the uncertainty of dominant frequency fluctuation of alpha in EEG could be changed under hypoxic condition[5].The uncertainty of dominant frequency was investigated using relative entropy as parameter in 261 healthy pilots[6],it provided an analytical method for detecting functional changes of the brain.
, http://www.100md.com
The aim of this investigation was to study functional disorders of cortex following transient cerebral ischemic attacks(TIAs),using computerized analysis of changes in uncertainty of alpha dominant frequency,and to compare these data with investigations performed in normal healthy pilots in order to offer reference for the screening procedure in aircrew and astronaut selection.
Methods
Subjects Twelve male pilots(aged 30±5) with transient episodes of ischemia in middle cerebral artery(MCA) territories. The transient focal neurological deficit involved the left MCA territory in eight and the right MCA territory in four patients. The standard EEG evaluated with descriptive visual analysis was normal in seven patients. Five patients showed slight focal alterations, coinciding in four of them with the hemisphere affected by the cerebrovascular episode. Control measurements were carried out in 20 normal healthy male pilots (aged 30±4).
, 百拇医药
EEG recordings According to the 10~20 system, twelve electrodes were placed on F3,F4,C3,C4,P3,P4,O1,O2,F7,F8,T5,T6, using linked ear lobes reference. EEG recordings in patients with their eyes closed were made by means of a CFM-8D EEG monitor within 24 h following the acute event in a quiet, naturally illuminated room, with the subject in a sitting position, and bandpass filtered between 2 Hz and 24 Hz. The EEG data were digitized at a rate of 100 Hz for 240 s and stored on a disk. It was also displayed continuously on a high-resolution color monitor, with a reading sensitivity of 50 μV=10 mm. Registrations with fluctuations of alterness showing a decrease of the EEG power density, appearance of sleep rhythms and EEG registrations not distinctly free of artifacts were excluded from the data for analysis.
, 百拇医药
EEG analysis By means of EEG-ET system, a newer system of frequency-fluctuation analysis was used , the uncertainty of the dominant frequency of alpha band(8~13 Hz) was analyzed according to the following method. Suppose there are six frequency components of alpha, i.e., 8,9, 10,11,12,13(Hz). Let a complete event be made up of the frequency components: A8,A9,A10,A11,A12,A13, and let cumulated probability of maximum power fluctuation in 240 s for each alpha frequency component is P8,P9,P10,P11,P12,P13 respectively, then the six cumulative dominant probability-time curves constructed the competitive synergetic structure of alpha frequency components. Let ΣPi =1 and it's entropy H=-Σpilnpi,(i=8,9,10,11,12,13). If the pis are equal,then H has a maximal value denoted by Hmax.Thus the relative entropy value is Q=(H/Hmax).
, 百拇医药
Results
Dominant probability ratio logarithmic index of α in patient pilots with TIA The cumulated dominant fluctuation probability-time curves for individual frequency of alpha band in both patients and healthy pilots were showed in Fig.1. The uppermost curve in Fig.1 was of the main frequency, i.e., dominant frequency component, and it's probability was the highest in the six frequency components. The second was of the potential dominant frequency component, i.e., second frequency. It was obvious that the main frequency component was 9 Hz, and the second was 10 Hz for both patient pilots with TIA and healthy pilots. But the probability of the main frequency in TIA patient pilots coinciding with sites affected by cerebrovascular episode was more than in healthy pilots. The statistical significance estimated with the unpaired student's t-tests was observed in probability difference of main frequency in patients as compared with healthy (P<0.01). Let the dominant probability ratio logarithmic index I=log[Pmain/(1-Pmain)].The Pmain in the logarithmic formula was the dominant probability value of main frequency. It was found that the dominant probability ratio logarithmic index I<0 in all TIA patient pilots with normal EEG,coinciding in six of them with the hemisphere affected by the cerebrovascular episode, and I<0 in all healthy pilots. Therefore we could conclude from the difference of probability that the smaller the uncertainty of dominant frequency, the larger the dominant probability of main frequency. To be sure, the uncertainty of dominant frequency was decreased in patient pilots with TIA. It was also found that not only I<0 ,but the second component shifted to lower frequency(8 Hz) in patients with slight focal frequency slowing in EEG.



, 百拇医药
Fig.1 The cumulative dominant frequency fluctuation probability-time curve for α band
Ordinate: cumulative probability value(percentage); Abscissa: time(second) .The number at curve's end is the frequency value(in Hz). Upper left: A patient pilot with left cerebrovascular episode. On the left sites coinciding with the hemisphere affected by the episode, the probability of maximum power was converged on 9 Hz, i.e. the dominant fluctuation component, meanwhile the probability of maximum power of other components was lower. Upper right: A patient pilot with right cerebrovascular episode. The structures of frequency on right affected sites is similar to left, but second frequency component was 8 Hz, the frequency slowing, coinciding with patient's EEG showed slight focal alterations. Bottom: a healthy pilot.
, 百拇医药
Entropy change of dominant frequency fluctuation of alpha in patient pilots with TIA The relative entropy values for patients and healthy pilots are showed in Table 1. Decreases in Q were significant at all left electrode sites (P<0.05,or better) coinciding with the left hemisphere af-fected by the cerebrovascular episode in patients as compared with healthy pilots. Significant decreases were also observed at the right parietal-occipital area, corresponding to electrodes P4,O2. There were significant decreases at all right electrode sites(P<0.05, or better) for patients coinciding with the right affected hemisphere, just as above-mentioned,at the opposite parietal-occipital area, corresponding to electrodes P3,O1, the Q values decreased significantly for these patients.
, 百拇医药
Table 1 Relative entropy values (Q) in TIA pilots and healthy pilots Site
healthy pilots
(n=20)
patients
(left MCA n=8)
patients
(right MCA n=4)
F3
0.67±0.16
0.53±0.12*
, http://www.100md.com
0.70±0.15
C3
0.73±0.15
0.53±0.10*
0.72±0.13
P3
0.74±0.17
0.40±0.11**
0.54±0.15*
O1
0.68±0.14
, 百拇医药
0.32±0.07**
0.53±0.14*
F7
0.67±0.15
0.43±0.14*
0.71±0.15
T5
0.75±0.14
0.36±0.10**
0.72±0.12
F4
, http://www.100md.com
0.64±0.15
0.69±0.13
0.46±0.15*
C4
0.74±0.14
0.77±0.15
0.59±0.14*
P4
0.76±0.14
0.65±0.14*
0.40±0.09**
, http://www.100md.com
O2
0.64±0.18
0.55±0.07*
0.34±0.08**
F8
0.68±0.15
0.72±0.14
0.46±0.12*
T6
0.75±0.15
0.73±0.13
, 百拇医药
0.38±0.10**
*P<0.05, **P<0.01,p-values are from unpaired students' as compared with t-tests; Q values are mean ±1 standard deviationDiscussion
The present results strongly support the findings of previous studies concerning dominant frequency fluctuation of alpha in EEG[5,6], in which we found that the maximum power fluctuation in alpha frequency band was converged on the dominant frequency component, and the uncertainty of alpha dominant frequency was reduced, then the dominant component shifted to lower frequency, meanwhile the maximal power fluctuation was almost equally distributed among these frequency components of alpha, so the uncertainty of dominant frequency was going up and the brain was self-organized in a new situation in order to adapt itself to hypoxia.The declined tolerance to acute hypoxic hypoxia could be characterized by the uncertainty of dominant frequency fluctuation of alpha. In this respect our particular interest has been directed towards the uncertainty of alpha dominant frequency in the patients with TIA. The accumulated probability-time curve of dominant frequency fluctuation showed the course of competition of dominant frequency components in alpha band, so the degree of severity of the resulting cerebral dysfunction may be derived from the uncertainty of alpha dominant frequency utilizing the dominant probability ratio logarithmic index I and relative entropy value Q to be able to identify regions affected by cerebral transient ischemic attacks, as well as from the slowing of the dominant frequency component and the dominant probability difference between the main and second frequency components,even though the patient's EEGs did not showed slight focal alterations. In addition, in the group of TIA patient pilots, the opposite sites to parieto-occipital regions were also identified as affected sites by significant decrease of relative entropy value Q and logarithmic index I>0. It maybe implied that these regions were also affected by the opposite hemisphere cerebrovascular episode. By the similar argument to that of hypoxia state, the changes of uncertainty of dominant frequency maybe implied that the brain was self-organized in a new situation in order to adapt itself to ischemia from TIA. And so the dominant frequency uncertainty may be used as a sensitive parameter in detecting even slight functional disturbances of cortical activity in patients with TIA. Therefore the analysis of uncertainty of alpha dominant frequency showed clear superiority of computerized evaluation over routine visual assessment in patients with minor cerebral ischemia. Consequently this method not only offers the possibility of studying pathophysiological functional parameter, but may also provide a reference for screening procedure in aircrew and astronaut selection.
, 百拇医药
References
[1]Jonkman EJ, van Huffenlen AG,Pfurtscheller G.Quantitative EEG in cerebral ischemia[C].In:Lopes da Silva FH,Strom van Leeumen W,Remond A(eds).Clinical applications of computer analysis of EEG and other neurophysiological signals.Amsterdam Elsevier,1986:205~237
[2]Koener E,Ott E,Kaiserfeld Pet al.EEG mapping in patients with transient ischemic attacks:a follow-up study[C].In:Maurer K(ed). Topographic brain mapping of EEG and evoked potentials.Heidelberg Springer-Verlag berlin,1989:209~218
, http://www.100md.com
[3]Vaibhava Goeal,Thkor NV.Dominant frequency analysis of EEG reveals brain's response during injury and recovery[J].IEEE Trans Biomid Eng,1996,43(11):1083~1092
[4]张继武,郑崇勋.局灶性脑缺血脑电信号的双谱分析[J].航天医学与医学工程,1998,11(2):97~101
[5]周传岱,徐国林,朱治平等. 急性缺氧态脑α波自组织特征分析[J].航天医学与医学工程,1992,5(4):245~249
[6]周传岱,翟怡娟,刘月红等. 261名歼击机飞行员脑波α频段涨落图特征的研究[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 1998,11(1):11~15
Received date:May 11,1998, 百拇医药