急性轻、中度缺氧暴露对心理运动及反应时的影响
作者:李学义 吴兴裕 付川 沈小凤 杨长斌 吴燕红
单位:李学义(第四军医大学,航空航天医学系,西安 710032)
关键词:高空缺氧;模拟试验;心理运动;反应时;工效
航天医学与医学工程000401摘要: 目的 研究急性轻、中度缺氧暴露对人的心理运动及视觉反应时的影响。 方法 利用低压舱模拟300 m (对照高度)、2800 m、3600 m、4400 m高度缺氧暴露1 h,考察了18 名健康男性青年被试者指叩测验、简单反应时和选择反应时的变化。 结果 血氧饱和度(SaO2)由地面对照值98%分别降至90%、82%和74%。2800 m 缺氧暴露1 h心理运动绩效的各个参数并无显著改变(P>0.05)。3600 m缺氧暴露时选择反应时的平均反应时明显延长,运动绩效下降(P<0.05),且随着高度的增加以上影响进一步加重(P<0.01)。而简单反应时和指叩测验的绩效暴露于4400 m时仍无显著改变(P>0.05)。 结论 本研究的结果提示,急性缺氧暴露于2800 m高度1 h并未对心理运动产生严重影响,而暴露于3600 m以上高度时会对选择反应时等复杂反应产生负面影响,且随着高度的增加而加重
, http://www.100md.com
中图分类号:R852.11;R853 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1002-0837(2000)04-0235-05
Effects of Acute Exposure to Mild or Moderate Hypoxia on Human Psychomotor Performance and Visual-reaction Time
LI Xue-yi WU Xing-yu YANG Chang-bin WU Yan-hong
(Department of Aerospace Medicine, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an 710032)
FU Chuan SHEN Xiao-feng
, http://www.100md.com (Department of Steward Medicine, China Southwest Airlines,Chendu 610202)
Abstract: Objective The aim of this study was to determine whether psychomotor performance and visual reaction time were affected by acute exposure to mild or moderate hypoxia. Method Eighteen healthy male volunteers performed finger tapping, simple reaction time(SRT) and 4-choice reaction time(CRT) tests at simulated altitude of 300 m (control),2800 m, 3600 m and 4400 m for 1 h in a hypobaric chamber. Result SaO2 decreased from 98%(control) to 90%,82% and 74% respectively at the various altitudes. All the performance parameters showed no significant change after exposure to 2800 m for 1 h relative to ground level(P>0.05). However the mean reaction time of 4-CRT under 3600 m prolonged and performance decreased as compared with baseline value(P<0.05), and the performance decreased further under 4400 m(P<0.01). No significant difference was found in finger tapping and SRT even under exposure to 4400 m for 1 h.Furthermore, no decrease in correct rate were observed at any altitude (P>0.05). Conclusion The results from this study demonstrated that there were no measurable impairment of visual reaction time and psychomotor performance under exposure to an altitude of 2800 m for 1 h. However, adverse effects on psychomotor performance were observed under 3600 m and over.
, http://www.100md.com
Key word:altitude hypoxia;simulated tests;psychomotor;reaction time;performance
It is well known that hypoxia disrupts intracellular process and impairs cellular function.Brain cells with a uniquely high oxygen demand are most susceptible to low oxygen tension.Intellectual impairment is an early sign of hypoxia, and it's particularly dangerous because its signs and symptoms do not usually cause discomfort or pain,making it unlikely that the individual could recognize his own disability: slow thinking,unreliable calculations,faulty memory,poor judgmentand delayed reaction time.As the information and decision-making processes in modern military flight systems have become more and more demanding than those in older systems,any of the above mentioned impairment in pilots could threaten flight safety.There are extensive highland regions in our country,with one sixth of these areas high above 3000 m.If man is to work and live in environments with reduced oxygen levels,the effects of hypoxia on human cognitive performance and the limit of altitude must be further assessed.Although the effects of hypoxia on various complex tasks have been studied extensively but there are conflicting results in the literature regarding the effect of hypobaric hypoxia on cognitive and psychomotor performance[1~11].Therefor,the present study was initiated to observe the effects of hypoxia on psychomotor performance and visual reaction time in order to get more knowledge regarding the prevention of human performance deficits during stay in hypobaric hypoxic environment.
, http://www.100md.com
Method
Subjects The subjects took part in this experiment were 18 healthy young male freshmen from Fourth Military Medical University(FMMU),aged between 17 and 18 years.All the subjects were non-smokers and non-drinkers with normal or corrected to normal visual acuity and normal color vision.They were normally resident at 300 m and none were acclimatized to plateau prior to this experiment.
Altitude Simulation The tests were carried out in a hypobaric chamber afforded by Department of Aerospace Medicine (DAM),FMMU.The subjects were randomly exposed to four altitudes (300 m,2800 m,3600 m and 4400 m),meanwhile they were asked to perform the psychomotor tests twice in 1 h period at each altitude(5 and 60 min after ascenting to the prescribed altitude).9~11 min were needed to complete the tests.The order of exposure to the various altitudes was randomly chosen by the chamber operator and the subjects and experimenters inside the chamber were without knowledge of it.The project and experimental protocol were approved by the department of technology and engineering of the DAM.The altitude in hypobaric chamber ascended to the test's at a speed of 15 m/s and maintained it for 1 h.After having finished all the tests,the hypobaric chamber was recompressed to the ground level (300 m high above sea level in Xi'an) at a speed of 5 m/s.During the descent,subjects were told to swallow and do Valsalva maneuver to prevent otitic Barotrauma.The chamber was continuously ventilated with fresh air.Other environmental factor's score: noise 75 dB(A); temperature 20.4~25.1℃;relative humidity 25%~43% and light breeze.All subjects wore flight headgear and earplugs inside the chamber to reduce the distraction of noise.Tests were performed at 18:30~21:30 to eliminate influence of circadian rhythm.The time between every two ascents was longer than 48 h.
, 百拇医药
Experimental Design and Procedure
To get familiar with the environment and tests,prior to the experiment the subjects were briefly told about the purpose and process of the experiment and they practiced the doings in the tests for 1 wk in order to get the manipulation stable.Analysis of variance for repeated measurements was carried out to compare with the baseline value at 300 m to minimize the effects of other factors such as noise,fatigue,learning effects etc.To reduce errors,all the test operations were carried out in standard orders and with fixed apparatuses by a same instructor.The subjects SaO2(Arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation) was monitored with a finger oximeter then the blood pressure and heart rate were measured after exposure to each altitude.
, http://www.100md.com
Psychomotor tests The software of Computer-administered tests used in this trial for finger tapping,simple visual reaction time and 4-CRT tests as provided by the Department of Occupational Health,Shanghai Medical University[12,13].The tests were controlled by,and all data were recorded on a PC 486.Subjects were seated at a table on which a visual display unit was placed,45 cm away from the subjects.
Finger tapping test: The subject tapped a key (“enter”) as rapidly as possible with the preferred index finger.The number of taps was counted for 20 s automatically by the computer,each 20 s trial was followed by a rest of approximately 30 s ; then the test was repeated with the non-preferred hand.
, http://www.100md.com
Visual simple reaction time test: a red square(2cm×2cm) was presented on the screen of the computer.Once it appeared,the subject must respond by depressing the corresponding button of the joystick as quickly as possible.The time interval between trials was varied randomly between 3 and 6 s,a total of 20 responses were made in each run.The computer recorded the time interval between onset of the display of the square and the depression of the corresponding button.
, 百拇医药 Visual 4-CRT test: there were four lights displayed on the computer screen (corresponding to index and middle finger of the two hands),one of them was red and the others were blue,the task was changed either when the subject responded or after a limit of 2 s.The subject's task was to push the red light corresponding button on the joystick as quickly as possible without error.The time interval between trials was varied randomly between 2 and 7 s,a total of 40 responses were made in each run.The reaction time was measured as the time interval from onset of the light until the joystick button was depressed.Mean of all correct reaction times and errors(including lost response in 2 s) were recorded by the computer.
, 百拇医药
Statistical analysis The Statistical Package for Social Science(SPSS) software package was used for the statistical analysis.Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and two-tailed paired T-test were used to analyze the effects of hypoxia on motor performance,and auto-control was used to compare the difference between control and each altitude group basing on the subject's own baseline points.Results were considered significant at P<0.05 level.
Result
, 百拇医药
Changes of physiologic parameters after exposure to hypoxia for 1 h
Fig 1 illustrated the effects of hypoxia on SaO2(Arterial oxyhemoglobin satura-tion),as expected,SaO2 level decreased gradually with the increase of altitude (decreased from the baseline value of 98% to 90%,82% and 74% respectively after exposure to 2800 m,3600 m and 4400 m for 1 h).Blood pressure did not show any appreciable difference as compared with baseline and heart rate also showed no significant change,except that it became significantly higher than the control value after exposure to 4400 m(P<0.05)as shown in Fig 2 and Fig 3.
, http://www.100md.com
Effects of exposure to different levels of altitudes on finger tapping test and visual simple reaction time test
The data concerning effect of acute hypoxia on finger tapping test and visual simple reaction time test were shown in Tab 1.The data revealed that no significant difference in tapping numbers were found during exposure to the various altitudes as compared with the baseline value (P>0.05).Moreover,neither mean simple reaction time nor error numbers showed any significant change as compared with the baseline values even after exposure to 4400 m for 1 h(P>0.05).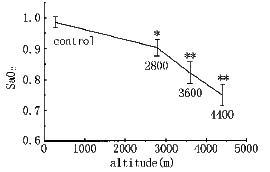
, http://www.100md.com
Fig.1 Changes of SaO2 after 1 h exposure to different levels of altitude
*P<0.05,**P<0.01,as compared with control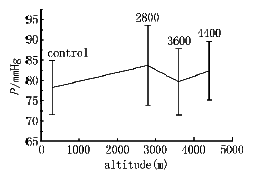
Fig.2 Changes of Blood Pressure after 1 h exposure to different levels of altitude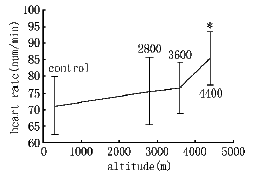
Fig.3 Changes of heart rate after 1 h exposure to different levels of altitude
, 百拇医药
*P<0.05,**P<0.01,as compared with control
Effects of exposure to different altitudes on visual 4-CRT test
The changes of visual 4-CRT during exposure to acute hypoxia were shown in Tab 2.The mean reaction time did not show significant prolongation compared with baseline after exposure to 2800 m for 1 h(P>0.05).However the significantly slower response times were obtained at 3600 m relative to ground level and increased further at 4400 m(P<0.01).The error rate was not
, 百拇医药
Table 1 Effects of exposure to different altitude for 1 h on finger tapping test and simple visual reaction time test ( ±s,n=18) altitude
±s,n=18) altitude
(m)
finger tapping test(number of tapping)
simple visual reaction time test
preferred hand
non-preferred hand
, http://www.100md.com mean react time(ms)
error rate(%)
control
160.4±8.1
158.6±9.0
247.0±10.1
1.07±0.10
2800
155.8±12.1
158.2±10.7
239.4±9.3
, 百拇医药 0.89±0.11
3600
163.7±9.3
167.8±12.6
250.7±7.9
0.78±0.14
4400
162.7±9.0
171.4±12.5
243.7±13.4
0.71±0.12
Note:*P<0.05,**P<0.01,as compared with controlTable 2 Effects of exposure to different altitude for 1 h on visual 4-choice reaction time test(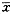 ±s,n=18) altitude(m)
±s,n=18) altitude(m)
, 百拇医药
mean response time(ms)
correct number
error rate(%)
performance(%)
control
276.2±38.0
37.2±2.3
7.0±0.4
98.1±3.1
2800
299.3±41.2
, 百拇医药
36.4±2.5
9.0±0.6
93.2±10.2
3600
316.1±30.6**
37.0±2.2
7.5±0.5
92.2±7.3*
4400
338.1±27.6**
36.7±2.0
, http://www.100md.com
8.2±0.5
86.1±6.7**
Note:*P<0.05,**P<0.01,as compared with control
affected during exposure to hypoxia despite the fact that pressure was equivalent to altitude of 4400 m(P>0.05).
Discussion
As was known,Bangda's aerodrome (about 4330 m high)in Tibet is one of the highest aerodromes in the world,Gongga's aerodrome in Lhasa is 3541 m above sea level and the extent of hypoxia after landing is close to or above the limit of mental performance[1].The problem regarding the effects of mild or moderate hypoxia on cognitive and psychomotor performance needs to be resolved,since it may affect flight operation and safety.
, http://www.100md.com
The most important work showing the effects of hypoxia on psychomotor performance is by Denison DM et al[2] who reported that longer reaction times were found at 5000 ft(1524 m) and 8000 ft(2438 m) altitudes,they concluded that the longer reaction time were caused by mild hypoxia.Schlichting and Knight et al[6] also suggested that motor functions such as finger dexterity and arm-hand steadiness might be more sensitive to hypoxia than cognitive functions.However these findings were not confirmed in a number of other studies designed to assess the effects of hypoxia on reaction time (Paul and Fraser[4]) who found that the ability to learn new tasks in serial choice reaction time test was not impaired by hypoxia at an altitude approximately 3658 m,and that performance for the psychomotor tests improved with number of performance test assessions despite the fact that the total ambient pressures were equivalent to altitudes of 1524 m,3048 and 3658 m respectively.Mackintosh et al[5] presented similar results from measurements of reaction time at altitudes of 4790 m and 5008 m,thus inconsistence exist in literatures regarding effects of hypoxia on psychomotor performance.The purpose of the present study is to seek for further elaboration about the effects of mild and moderate hypoxia on psychomotor performance to provide reference for highland airlines.
, 百拇医药
The expected decrease in SaO2 with increasing altitude is evident.The results of this experiment suggested that impaired psychomotor performance as expected was not seen in any of its parameter under exposure to 2800 m for 1 h,the serial reaction time also showed no significant increase as compared with ground level value.It indicated that there is no measurable decrease in motor performance and visual reaction time at this altitude level.This is similar to Fowler 's reports who measured performance on serial choice response time task under two levels of altitudes and concluded that the threshold altitude for perceptual motor deficits was in fact 9750 ft(approximately 2971 m)[1].However,the mean reaction time of 4-CRT were significantly longer at both 3600 m and 4400 m as compared with control level value in our experiment but no general change was found in finger tapping and simple reaction time despite the fact that pressure was equivalent to altitude of 4400 m.It implicated that the judgement response time was affected while locomotion speed was unaffected at these altitude.It suggests that the judgment response time might be more sensitive to hypoxia than simple locomotion time.This partially agreed with Fowler's report who suggested that the effects of hypoxia on complex tasks can be explained by deficits in a few mechanisms common to all tasks rather than deficits to a wide range of mechanisms[13].
, 百拇医药
Our opinion is that the effects of hypoxia on cognitive performance might be associated with psychologic elements which involved in and changed work efficiency to some different extents.The same degree of hypoxia may have different effects on different basic psychologic elements,in other words different element has different sensitivities to hypoxia and the altitude dependent mode could't explain the multidimensional characteristic of mental workload.This reasoning is well supported by the results of our laboratory trials,which indicated that psychomotor performance was unaffected at 2800 m yet the attention,thinking,memory and mood states were proved to be impaired at this altitude[7~9].Furthermore,the overall data of this trial showed no general impairment of finger tapping test and simple reaction time during exposure to 3600 m and 4400 m for 1 h,however the more difficult task of 4-CRT was significantly prolonged at these altitude,it suggests that the difficult task was more sensitive to hypoxia than easier tasks.Berry et al also proved that performance of figure symbol denotation test and that of tap test were different at a same hypoxia level[10].Other complementary tests and a greater sample of subjects are inquired in further studies in order to get more information about the mechanisms concerning the effects of hypoxia on cognitive performance.
, http://www.100md.com
[References]
[1] Fowler B,Kelso B,Elcombe DD,et al.The threshold for hypoxia effects on perceptual-motor performance[J].Human Factor,1987,29:61~66
[2] Denison DM,Ledwrth F,Poulton EC.Complex reaction times at simulated cabin altitude of 5000 ft and 8000 ft[J].Aerospace Medicine,1966,37,1010~1013
[3] Kobric JL,Dusek ER.Effects of hypoxia on voluntary response time to peripherally located stimuli[J].Journal Appl Psychology,1970,29:444~448
, 百拇医药
[4] Paul MA,Fraser WD.Performance during mild acute hypoxia[J].Aviate Space Environ Med,1994,65:891~899
[5] Mackintosh JH,Thomas DJ,Olive JE.The effect of altitude on tests of reaction time and alertness[J].Aviate Space Environ Med,1988,59:246~248
[6] Schlichting CL,Knight DR,Cymerman A.Cognitive and motor performance under reduced oxygen[R].The 30th Annual Conference of the Military Testing Association,Arlington,VA,1988 NTIS,AD-A215 179/3/x48
, http://www.100md.com
[7] LI Xueyi,WU Xingyu,ZHUANG Yong et al.Effects of acute mild and moderate hypoxia on dual task performance[J].Chinese Journal of Behavioral Medical Science,1999,(8):34~35
李学义,吴兴裕,庄勇等.急性轻、中度缺氧暴露对双任务作业绩效的影响[J].中国行为医学科学,1999,(8):34~35
[8] LI Xueyi,WU Xingyu,HAN Liping et al.Effects of acute hypoxia on humanperformance of attention span and attention shift[J].Journal Fourth Mil Med Univ,1999,20(1):71~73
, 百拇医药
李学义,吴兴裕,韩厉萍等.急性中度缺氧对注意广度及注意转移能力的影响[J].第四军医大学学报,1999,20(1):71~73
[9] LI Xue-yi,WU Xing-yu,FU Chuan et al.Effects of acute mild and moderate hypoxia on human mood state[J].Space Medicine & Medical Engineering,2000,13(1):1~5
李学义,吴兴裕,付 川等.急性轻、中度缺氧暴露对人情绪的影响[J].航天医学与医学工程,2000,13(1):1~5
[10] Berry DT,McConnell JW,Phillips BA,et al.Isocapnic hypoxemia and neuropsychological functioning[J].J Clin Experi Neuropsychology,1989,11(2):241~251
, http://www.100md.com
[11] Fowler B,Banner J,Pogue J.The slowing of visual processing by hypoxia[J].Ergonomics,1993,36(6):727~735
[12] LIANG Youxin.Introduction to the WHO neurobehavioral core test battery[J].Journal of Industrial Hygiene and Occupational Disease,1987,13(6):331~339
梁有信.介绍WHO推荐的神经行为核心测验组合[J].工业卫生与职业病杂志,1987,13(6):331~339
[13] SUN Rongkun,LIANG Youxin.Study and advance of computer-administered neurobehavioral evaluation system[J].Occupational Med,1990,17(2):109~113
孙荣昆,梁有信.计算机化神经行为评价系统的研究与进展[J].职业医学,1990,17(2):109~113
Recieved date:1999-11-01, 百拇医药
单位:李学义(第四军医大学,航空航天医学系,西安 710032)
关键词:高空缺氧;模拟试验;心理运动;反应时;工效
航天医学与医学工程000401摘要: 目的 研究急性轻、中度缺氧暴露对人的心理运动及视觉反应时的影响。 方法 利用低压舱模拟300 m (对照高度)、2800 m、3600 m、4400 m高度缺氧暴露1 h,考察了18 名健康男性青年被试者指叩测验、简单反应时和选择反应时的变化。 结果 血氧饱和度(SaO2)由地面对照值98%分别降至90%、82%和74%。2800 m 缺氧暴露1 h心理运动绩效的各个参数并无显著改变(P>0.05)。3600 m缺氧暴露时选择反应时的平均反应时明显延长,运动绩效下降(P<0.05),且随着高度的增加以上影响进一步加重(P<0.01)。而简单反应时和指叩测验的绩效暴露于4400 m时仍无显著改变(P>0.05)。 结论 本研究的结果提示,急性缺氧暴露于2800 m高度1 h并未对心理运动产生严重影响,而暴露于3600 m以上高度时会对选择反应时等复杂反应产生负面影响,且随着高度的增加而加重
, http://www.100md.com
中图分类号:R852.11;R853 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1002-0837(2000)04-0235-05
Effects of Acute Exposure to Mild or Moderate Hypoxia on Human Psychomotor Performance and Visual-reaction Time
LI Xue-yi WU Xing-yu YANG Chang-bin WU Yan-hong
(Department of Aerospace Medicine, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an 710032)
FU Chuan SHEN Xiao-feng
, http://www.100md.com (Department of Steward Medicine, China Southwest Airlines,Chendu 610202)
Abstract: Objective The aim of this study was to determine whether psychomotor performance and visual reaction time were affected by acute exposure to mild or moderate hypoxia. Method Eighteen healthy male volunteers performed finger tapping, simple reaction time(SRT) and 4-choice reaction time(CRT) tests at simulated altitude of 300 m (control),2800 m, 3600 m and 4400 m for 1 h in a hypobaric chamber. Result SaO2 decreased from 98%(control) to 90%,82% and 74% respectively at the various altitudes. All the performance parameters showed no significant change after exposure to 2800 m for 1 h relative to ground level(P>0.05). However the mean reaction time of 4-CRT under 3600 m prolonged and performance decreased as compared with baseline value(P<0.05), and the performance decreased further under 4400 m(P<0.01). No significant difference was found in finger tapping and SRT even under exposure to 4400 m for 1 h.Furthermore, no decrease in correct rate were observed at any altitude (P>0.05). Conclusion The results from this study demonstrated that there were no measurable impairment of visual reaction time and psychomotor performance under exposure to an altitude of 2800 m for 1 h. However, adverse effects on psychomotor performance were observed under 3600 m and over.
, http://www.100md.com
Key word:altitude hypoxia;simulated tests;psychomotor;reaction time;performance
It is well known that hypoxia disrupts intracellular process and impairs cellular function.Brain cells with a uniquely high oxygen demand are most susceptible to low oxygen tension.Intellectual impairment is an early sign of hypoxia, and it's particularly dangerous because its signs and symptoms do not usually cause discomfort or pain,making it unlikely that the individual could recognize his own disability: slow thinking,unreliable calculations,faulty memory,poor judgmentand delayed reaction time.As the information and decision-making processes in modern military flight systems have become more and more demanding than those in older systems,any of the above mentioned impairment in pilots could threaten flight safety.There are extensive highland regions in our country,with one sixth of these areas high above 3000 m.If man is to work and live in environments with reduced oxygen levels,the effects of hypoxia on human cognitive performance and the limit of altitude must be further assessed.Although the effects of hypoxia on various complex tasks have been studied extensively but there are conflicting results in the literature regarding the effect of hypobaric hypoxia on cognitive and psychomotor performance[1~11].Therefor,the present study was initiated to observe the effects of hypoxia on psychomotor performance and visual reaction time in order to get more knowledge regarding the prevention of human performance deficits during stay in hypobaric hypoxic environment.
, http://www.100md.com
Method
Subjects The subjects took part in this experiment were 18 healthy young male freshmen from Fourth Military Medical University(FMMU),aged between 17 and 18 years.All the subjects were non-smokers and non-drinkers with normal or corrected to normal visual acuity and normal color vision.They were normally resident at 300 m and none were acclimatized to plateau prior to this experiment.
Altitude Simulation The tests were carried out in a hypobaric chamber afforded by Department of Aerospace Medicine (DAM),FMMU.The subjects were randomly exposed to four altitudes (300 m,2800 m,3600 m and 4400 m),meanwhile they were asked to perform the psychomotor tests twice in 1 h period at each altitude(5 and 60 min after ascenting to the prescribed altitude).9~11 min were needed to complete the tests.The order of exposure to the various altitudes was randomly chosen by the chamber operator and the subjects and experimenters inside the chamber were without knowledge of it.The project and experimental protocol were approved by the department of technology and engineering of the DAM.The altitude in hypobaric chamber ascended to the test's at a speed of 15 m/s and maintained it for 1 h.After having finished all the tests,the hypobaric chamber was recompressed to the ground level (300 m high above sea level in Xi'an) at a speed of 5 m/s.During the descent,subjects were told to swallow and do Valsalva maneuver to prevent otitic Barotrauma.The chamber was continuously ventilated with fresh air.Other environmental factor's score: noise 75 dB(A); temperature 20.4~25.1℃;relative humidity 25%~43% and light breeze.All subjects wore flight headgear and earplugs inside the chamber to reduce the distraction of noise.Tests were performed at 18:30~21:30 to eliminate influence of circadian rhythm.The time between every two ascents was longer than 48 h.
, 百拇医药
Experimental Design and Procedure
To get familiar with the environment and tests,prior to the experiment the subjects were briefly told about the purpose and process of the experiment and they practiced the doings in the tests for 1 wk in order to get the manipulation stable.Analysis of variance for repeated measurements was carried out to compare with the baseline value at 300 m to minimize the effects of other factors such as noise,fatigue,learning effects etc.To reduce errors,all the test operations were carried out in standard orders and with fixed apparatuses by a same instructor.The subjects SaO2(Arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation) was monitored with a finger oximeter then the blood pressure and heart rate were measured after exposure to each altitude.
, http://www.100md.com
Psychomotor tests The software of Computer-administered tests used in this trial for finger tapping,simple visual reaction time and 4-CRT tests as provided by the Department of Occupational Health,Shanghai Medical University[12,13].The tests were controlled by,and all data were recorded on a PC 486.Subjects were seated at a table on which a visual display unit was placed,45 cm away from the subjects.
Finger tapping test: The subject tapped a key (“enter”) as rapidly as possible with the preferred index finger.The number of taps was counted for 20 s automatically by the computer,each 20 s trial was followed by a rest of approximately 30 s ; then the test was repeated with the non-preferred hand.
, http://www.100md.com
Visual simple reaction time test: a red square(2cm×2cm) was presented on the screen of the computer.Once it appeared,the subject must respond by depressing the corresponding button of the joystick as quickly as possible.The time interval between trials was varied randomly between 3 and 6 s,a total of 20 responses were made in each run.The computer recorded the time interval between onset of the display of the square and the depression of the corresponding button.
, 百拇医药 Visual 4-CRT test: there were four lights displayed on the computer screen (corresponding to index and middle finger of the two hands),one of them was red and the others were blue,the task was changed either when the subject responded or after a limit of 2 s.The subject's task was to push the red light corresponding button on the joystick as quickly as possible without error.The time interval between trials was varied randomly between 2 and 7 s,a total of 40 responses were made in each run.The reaction time was measured as the time interval from onset of the light until the joystick button was depressed.Mean of all correct reaction times and errors(including lost response in 2 s) were recorded by the computer.
, 百拇医药
Statistical analysis The Statistical Package for Social Science(SPSS) software package was used for the statistical analysis.Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and two-tailed paired T-test were used to analyze the effects of hypoxia on motor performance,and auto-control was used to compare the difference between control and each altitude group basing on the subject's own baseline points.Results were considered significant at P<0.05 level.
Result
, 百拇医药
Changes of physiologic parameters after exposure to hypoxia for 1 h
Fig 1 illustrated the effects of hypoxia on SaO2(Arterial oxyhemoglobin satura-tion),as expected,SaO2 level decreased gradually with the increase of altitude (decreased from the baseline value of 98% to 90%,82% and 74% respectively after exposure to 2800 m,3600 m and 4400 m for 1 h).Blood pressure did not show any appreciable difference as compared with baseline and heart rate also showed no significant change,except that it became significantly higher than the control value after exposure to 4400 m(P<0.05)as shown in Fig 2 and Fig 3.
, http://www.100md.com
Effects of exposure to different levels of altitudes on finger tapping test and visual simple reaction time test
The data concerning effect of acute hypoxia on finger tapping test and visual simple reaction time test were shown in Tab 1.The data revealed that no significant difference in tapping numbers were found during exposure to the various altitudes as compared with the baseline value (P>0.05).Moreover,neither mean simple reaction time nor error numbers showed any significant change as compared with the baseline values even after exposure to 4400 m for 1 h(P>0.05).

, http://www.100md.com
Fig.1 Changes of SaO2 after 1 h exposure to different levels of altitude
*P<0.05,**P<0.01,as compared with control

Fig.2 Changes of Blood Pressure after 1 h exposure to different levels of altitude

Fig.3 Changes of heart rate after 1 h exposure to different levels of altitude
, 百拇医药
*P<0.05,**P<0.01,as compared with control
Effects of exposure to different altitudes on visual 4-CRT test
The changes of visual 4-CRT during exposure to acute hypoxia were shown in Tab 2.The mean reaction time did not show significant prolongation compared with baseline after exposure to 2800 m for 1 h(P>0.05).However the significantly slower response times were obtained at 3600 m relative to ground level and increased further at 4400 m(P<0.01).The error rate was not
, 百拇医药
Table 1 Effects of exposure to different altitude for 1 h on finger tapping test and simple visual reaction time test (
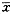 ±s,n=18) altitude
±s,n=18) altitude(m)
finger tapping test(number of tapping)
simple visual reaction time test
preferred hand
non-preferred hand
, http://www.100md.com mean react time(ms)
error rate(%)
control
160.4±8.1
158.6±9.0
247.0±10.1
1.07±0.10
2800
155.8±12.1
158.2±10.7
239.4±9.3
, 百拇医药 0.89±0.11
3600
163.7±9.3
167.8±12.6
250.7±7.9
0.78±0.14
4400
162.7±9.0
171.4±12.5
243.7±13.4
0.71±0.12
Note:*P<0.05,**P<0.01,as compared with controlTable 2 Effects of exposure to different altitude for 1 h on visual 4-choice reaction time test(
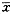 ±s,n=18) altitude(m)
±s,n=18) altitude(m), 百拇医药
mean response time(ms)
correct number
error rate(%)
performance(%)
control
276.2±38.0
37.2±2.3
7.0±0.4
98.1±3.1
2800
299.3±41.2
, 百拇医药
36.4±2.5
9.0±0.6
93.2±10.2
3600
316.1±30.6**
37.0±2.2
7.5±0.5
92.2±7.3*
4400
338.1±27.6**
36.7±2.0
, http://www.100md.com
8.2±0.5
86.1±6.7**
Note:*P<0.05,**P<0.01,as compared with control
affected during exposure to hypoxia despite the fact that pressure was equivalent to altitude of 4400 m(P>0.05).
Discussion
As was known,Bangda's aerodrome (about 4330 m high)in Tibet is one of the highest aerodromes in the world,Gongga's aerodrome in Lhasa is 3541 m above sea level and the extent of hypoxia after landing is close to or above the limit of mental performance[1].The problem regarding the effects of mild or moderate hypoxia on cognitive and psychomotor performance needs to be resolved,since it may affect flight operation and safety.
, http://www.100md.com
The most important work showing the effects of hypoxia on psychomotor performance is by Denison DM et al[2] who reported that longer reaction times were found at 5000 ft(1524 m) and 8000 ft(2438 m) altitudes,they concluded that the longer reaction time were caused by mild hypoxia.Schlichting and Knight et al[6] also suggested that motor functions such as finger dexterity and arm-hand steadiness might be more sensitive to hypoxia than cognitive functions.However these findings were not confirmed in a number of other studies designed to assess the effects of hypoxia on reaction time (Paul and Fraser[4]) who found that the ability to learn new tasks in serial choice reaction time test was not impaired by hypoxia at an altitude approximately 3658 m,and that performance for the psychomotor tests improved with number of performance test assessions despite the fact that the total ambient pressures were equivalent to altitudes of 1524 m,3048 and 3658 m respectively.Mackintosh et al[5] presented similar results from measurements of reaction time at altitudes of 4790 m and 5008 m,thus inconsistence exist in literatures regarding effects of hypoxia on psychomotor performance.The purpose of the present study is to seek for further elaboration about the effects of mild and moderate hypoxia on psychomotor performance to provide reference for highland airlines.
, 百拇医药
The expected decrease in SaO2 with increasing altitude is evident.The results of this experiment suggested that impaired psychomotor performance as expected was not seen in any of its parameter under exposure to 2800 m for 1 h,the serial reaction time also showed no significant increase as compared with ground level value.It indicated that there is no measurable decrease in motor performance and visual reaction time at this altitude level.This is similar to Fowler 's reports who measured performance on serial choice response time task under two levels of altitudes and concluded that the threshold altitude for perceptual motor deficits was in fact 9750 ft(approximately 2971 m)[1].However,the mean reaction time of 4-CRT were significantly longer at both 3600 m and 4400 m as compared with control level value in our experiment but no general change was found in finger tapping and simple reaction time despite the fact that pressure was equivalent to altitude of 4400 m.It implicated that the judgement response time was affected while locomotion speed was unaffected at these altitude.It suggests that the judgment response time might be more sensitive to hypoxia than simple locomotion time.This partially agreed with Fowler's report who suggested that the effects of hypoxia on complex tasks can be explained by deficits in a few mechanisms common to all tasks rather than deficits to a wide range of mechanisms[13].
, 百拇医药
Our opinion is that the effects of hypoxia on cognitive performance might be associated with psychologic elements which involved in and changed work efficiency to some different extents.The same degree of hypoxia may have different effects on different basic psychologic elements,in other words different element has different sensitivities to hypoxia and the altitude dependent mode could't explain the multidimensional characteristic of mental workload.This reasoning is well supported by the results of our laboratory trials,which indicated that psychomotor performance was unaffected at 2800 m yet the attention,thinking,memory and mood states were proved to be impaired at this altitude[7~9].Furthermore,the overall data of this trial showed no general impairment of finger tapping test and simple reaction time during exposure to 3600 m and 4400 m for 1 h,however the more difficult task of 4-CRT was significantly prolonged at these altitude,it suggests that the difficult task was more sensitive to hypoxia than easier tasks.Berry et al also proved that performance of figure symbol denotation test and that of tap test were different at a same hypoxia level[10].Other complementary tests and a greater sample of subjects are inquired in further studies in order to get more information about the mechanisms concerning the effects of hypoxia on cognitive performance.
, http://www.100md.com
[References]
[1] Fowler B,Kelso B,Elcombe DD,et al.The threshold for hypoxia effects on perceptual-motor performance[J].Human Factor,1987,29:61~66
[2] Denison DM,Ledwrth F,Poulton EC.Complex reaction times at simulated cabin altitude of 5000 ft and 8000 ft[J].Aerospace Medicine,1966,37,1010~1013
[3] Kobric JL,Dusek ER.Effects of hypoxia on voluntary response time to peripherally located stimuli[J].Journal Appl Psychology,1970,29:444~448
, 百拇医药
[4] Paul MA,Fraser WD.Performance during mild acute hypoxia[J].Aviate Space Environ Med,1994,65:891~899
[5] Mackintosh JH,Thomas DJ,Olive JE.The effect of altitude on tests of reaction time and alertness[J].Aviate Space Environ Med,1988,59:246~248
[6] Schlichting CL,Knight DR,Cymerman A.Cognitive and motor performance under reduced oxygen[R].The 30th Annual Conference of the Military Testing Association,Arlington,VA,1988 NTIS,AD-A215 179/3/x48
, http://www.100md.com
[7] LI Xueyi,WU Xingyu,ZHUANG Yong et al.Effects of acute mild and moderate hypoxia on dual task performance[J].Chinese Journal of Behavioral Medical Science,1999,(8):34~35
李学义,吴兴裕,庄勇等.急性轻、中度缺氧暴露对双任务作业绩效的影响[J].中国行为医学科学,1999,(8):34~35
[8] LI Xueyi,WU Xingyu,HAN Liping et al.Effects of acute hypoxia on humanperformance of attention span and attention shift[J].Journal Fourth Mil Med Univ,1999,20(1):71~73
, 百拇医药
李学义,吴兴裕,韩厉萍等.急性中度缺氧对注意广度及注意转移能力的影响[J].第四军医大学学报,1999,20(1):71~73
[9] LI Xue-yi,WU Xing-yu,FU Chuan et al.Effects of acute mild and moderate hypoxia on human mood state[J].Space Medicine & Medical Engineering,2000,13(1):1~5
李学义,吴兴裕,付 川等.急性轻、中度缺氧暴露对人情绪的影响[J].航天医学与医学工程,2000,13(1):1~5
[10] Berry DT,McConnell JW,Phillips BA,et al.Isocapnic hypoxemia and neuropsychological functioning[J].J Clin Experi Neuropsychology,1989,11(2):241~251
, http://www.100md.com
[11] Fowler B,Banner J,Pogue J.The slowing of visual processing by hypoxia[J].Ergonomics,1993,36(6):727~735
[12] LIANG Youxin.Introduction to the WHO neurobehavioral core test battery[J].Journal of Industrial Hygiene and Occupational Disease,1987,13(6):331~339
梁有信.介绍WHO推荐的神经行为核心测验组合[J].工业卫生与职业病杂志,1987,13(6):331~339
[13] SUN Rongkun,LIANG Youxin.Study and advance of computer-administered neurobehavioral evaluation system[J].Occupational Med,1990,17(2):109~113
孙荣昆,梁有信.计算机化神经行为评价系统的研究与进展[J].职业医学,1990,17(2):109~113
Recieved date:1999-11-01, 百拇医药