新生儿窒息后血浆胆红素水平的动态变化及其临床意义(1)
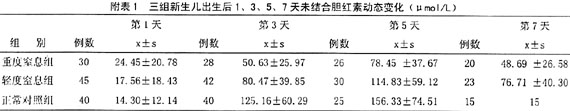 |
[摘要]目的了解窒息后新生儿血浆胆红素水平的动态变化,掌握临床干预的最佳时机。方法对75例窒息后新生儿(重度组30例,轻度组45例)及正常新生儿40例(对照组)在生后1、3、5、7天进行血浆胆红素水平测定。结果与正常新生儿相比,缺氧新生儿黄疸出现早,上升较快,峰值较低,持续时间亦短,并与缺氧程度相关,差异有显著性意义。结论重视窒息新生儿黄疸的早期监测与干预,是避免神经系统伤残的关键。
关键词:窒息 新生儿 胆红素 缺氧症
The changes in plasma level of bilirubin in the newborns with asphyxia and their clinical significance.Zhuang LiangPeng,Li XueZhen, et al. Department of pediatrics, The People's hospital of XuWen County, XuWen, Guangdong 524100.
[Abstract] ObjectiveTo detect the changes of plasma level of bilirubin in the newborns with asphyxia and determine the optimal opportunity of clinical intervention.MethodsPlasma bilirubin level was measured in 75 cases with asphyxial neonates ( 30 serious cases, 45 moderate cases ) and 40 normal newborns on day 1、3、5 and 7 oflife respectively.ResultHypoxic jaundice in neonates occured at an earlier stage and developed faster than normal neonatal jaundice. The peak values of bilirubin in neonates with hypoxic jaundice was lower, and the duration of jaundice was also shorter as compared to the normal neonates with physiological jaundice; the level of bilirubin and duration of jaundice correlated sighificantly with the severities of hypoxia. Condusion Paying great attention to the early observation and intervention of jaundie in asphyxial neonates is important to prevent the central nervous system from poisoning caused by bilirubin. ......
您现在查看是摘要页,全文长 4355 字符。